Xi Yuan
Mapping the maturation of TCM as an adjuvant to radiotherapy
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:The integration of complementary medicine into oncology represents a paradigm shift that has seen to increasing adoption of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) as an adjuvant to radiotherapy. About twenty-five years since the formal institutionalization of integrated oncology, it is opportune to synthesize the trajectory of evidence for TCM as an adjuvant to radiotherapy. Here we conduct a large-scale analysis of 69,745 publications (2000 - 2025), emerging a cyclical evolution defined by coordinated expansion and contraction in publication output, international collaboration, and funding commitments that mirrors a define-ideate-test pattern. Using a theme modeling workflow designed to determine a stable thematic structure of the field, we identify five dominant thematic axes - cancer types, supportive care, clinical endpoints, mechanisms, and methodology - that signal a focus on patient well-being, scientific rigor and mechanistic exploration. Cross-theme integration of TCM is patient-centered and systems-oriented. Together with the emergent cycles of evolution, the thematic structure demonstrates progressive specialization and potential defragmentation of the field or saturation of existing research agenda. The analysis points to a field that has matured its current research agenda and is likely at the cusp of something new. Additionally, the field exhibits positive reporting of findings that is homogeneous across publication types, thematic areas, and the cycles of evolution suggesting a system-wide positive reporting bias agnostic to structural drivers.
GCR: Geometry-Consistent Routing for Task-Agnostic Continual Anomaly Detection
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Feature-based anomaly detection is widely adopted in industrial inspection due to the strong representational power of large pre-trained vision encoders. While most existing methods focus on improving within-category anomaly scoring, practical deployments increasingly require task-agnostic operation under continual category expansion, where the category identity is unknown at test time. In this setting, overall performance is often dominated by expert selection, namely routing an input to an appropriate normality model before any head-specific scoring is applied. However, routing rules that compare head-specific anomaly scores across independently constructed heads are unreliable in practice, as score distributions can differ substantially across categories in scale and tail behavior. We propose GCR, a lightweight mixture-of-experts framework for stabilizing task-agnostic continual anomaly detection through geometry-consistent routing. GCR routes each test image directly in a shared frozen patch-embedding space by minimizing an accumulated nearest-prototype distance to category-specific prototype banks, and then computes anomaly maps only within the routed expert using a standard prototype-based scoring rule. By separating cross-head decision making from within-head anomaly scoring, GCR avoids cross-head score comparability issues without requiring end-to-end representation learning. Experiments on MVTec AD and VisA show that geometry-consistent routing substantially improves routing stability and mitigates continual performance collapse, achieving near-zero forgetting while maintaining competitive detection and localization performance. These results indicate that many failures previously attributed to representation forgetting can instead be explained by decision-rule instability in cross-head routing. Code is available at https://github.com/jw-chae/GCR
HCMA-UNet: A Hybrid CNN-Mamba UNet with Inter-Slice Self-Attention for Efficient Breast Cancer Segmentation
Jan 01, 2025



Abstract:Breast cancer lesion segmentation in DCE-MRI remains challenging due to heterogeneous tumor morphology and indistinct boundaries. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel hybrid segmentation network, HCMA-UNet, for lesion segmentation of breast cancer. Our network consists of a lightweight CNN backbone and a Multi-view Inter-Slice Self-Attention Mamba (MISM) module. The MISM module integrates Visual State Space Block (VSSB) and Inter-Slice Self-Attention (ISSA) mechanism, effectively reducing parameters through Asymmetric Split Channel (ASC) strategy to achieve efficient tri-directional feature extraction. Our lightweight model achieves superior performance with 2.87M parameters and 126.44 GFLOPs. A Feature-guided Region-aware loss function (FRLoss) is proposed to enhance segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments on one private and two public DCE-MRI breast cancer datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining computational efficiency. FRLoss also exhibits good cross-architecture generalization capabilities. The source code and dataset is available on this link.
Harnessing Intra-group Variations Via a Population-Level Context for Pathology Detection
Mar 04, 2024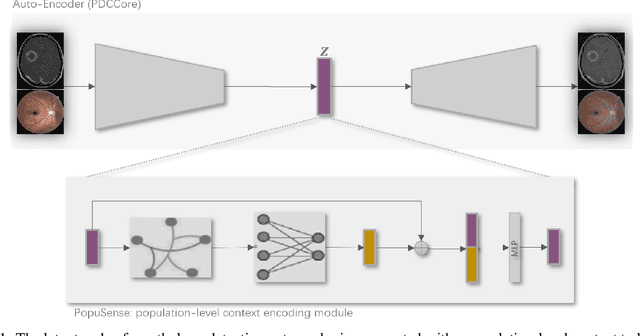
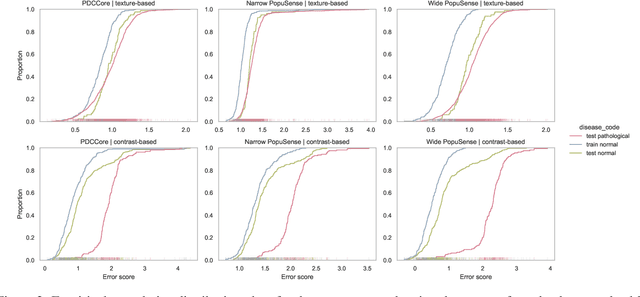
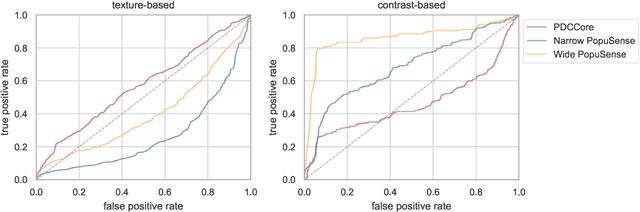
Abstract:Realizing sufficient separability between the distributions of healthy and pathological samples is a critical obstacle for pathology detection convolutional models. Moreover, these models exhibit a bias for contrast-based images, with diminished performance on texture-based medical images. This study introduces the notion of a population-level context for pathology detection and employs a graph theoretic approach to model and incorporate it into the latent code of an autoencoder via a refinement module we term PopuSense. PopuSense seeks to capture additional intra-group variations inherent in biomedical data that a local or global context of the convolutional model might miss or smooth out. Experiments on contrast-based and texture-based images, with minimal adaptation, encounter the existing preference for intensity-based input. Nevertheless, PopuSense demonstrates improved separability in contrast-based images, presenting an additional avenue for refining representations learned by a model.
GAME: Generalized deep learning model towards multimodal data integration for early screening of adolescent mental disorders
Sep 18, 2023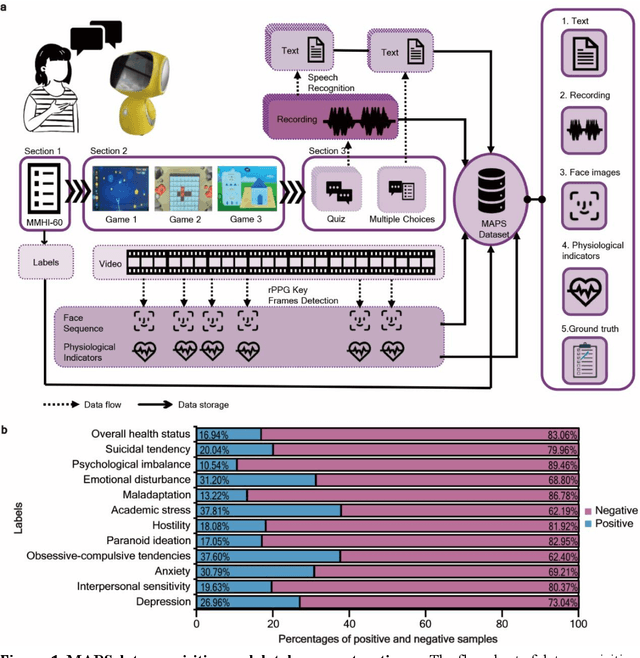


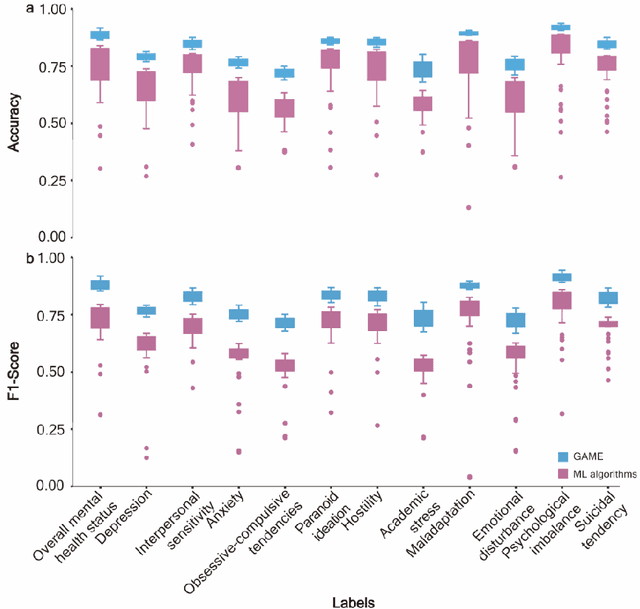
Abstract:The timely identification of mental disorders in adolescents is a global public health challenge.Single factor is difficult to detect the abnormality due to its complex and subtle nature. Additionally, the generalized multimodal Computer-Aided Screening (CAS) systems with interactive robots for adolescent mental disorders are not available. Here, we design an android application with mini-games and chat recording deployed in a portable robot to screen 3,783 middle school students and construct the multimodal screening dataset, including facial images, physiological signs, voice recordings, and textual transcripts.We develop a model called GAME (Generalized Model with Attention and Multimodal EmbraceNet) with novel attention mechanism that integrates cross-modal features into the model. GAME evaluates adolescent mental conditions with high accuracy (73.34%-92.77%) and F1-Score (71.32%-91.06%).We find each modality contributes dynamically to the mental disorders screening and comorbidities among various mental disorders, indicating the feasibility of explainable model. This study provides a system capable of acquiring multimodal information and constructs a generalized multimodal integration algorithm with novel attention mechanisms for the early screening of adolescent mental disorders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge