Wubo Li
Speech SIMCLR: Combining Contrastive and Reconstruction Objective for Self-supervised Speech Representation Learning
Oct 27, 2020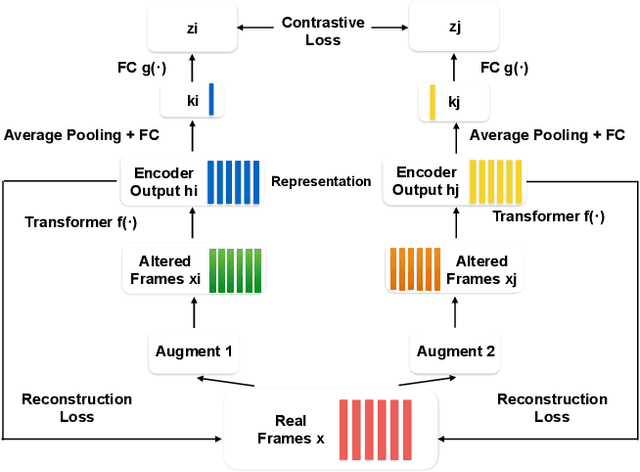

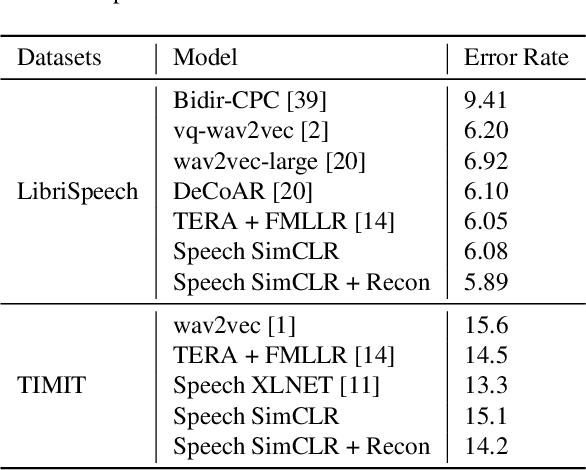
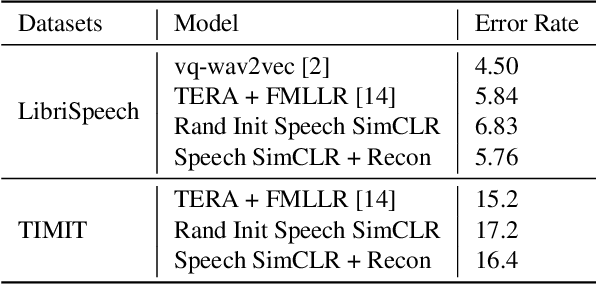
Abstract:Self-supervised visual pretraining has shown significant progress recently. Among those methods, SimCLR greatly advanced the state of the art in self-supervised and semi-supervised learning on ImageNet. The input feature representations for speech and visual tasks are both continuous, so it is natural to consider applying similar objective on speech representation learning. In this paper, we propose Speech SimCLR, a new self-supervised objective for speech representation learning. During training, Speech SimCLR applies augmentation on raw speech and its spectrogram. Its objective is the combination of contrastive loss that maximizes agreement between differently augmented samples in the latent space and reconstruction loss of input representation. The proposed method achieved competitive results on speech emotion recognition and speech recognition. When used as feature extractor, our best model achieved 5.89% word error rate on LibriSpeech test-clean set using LibriSpeech 960 hours as pretraining data and LibriSpeech train-clean-100 set as fine-tuning data, which is the lowest error rate obtained in this setup to the best of our knowledge.
TMT: A Transformer-based Modal Translator for Improving Multimodal Sequence Representations in Audio Visual Scene-aware Dialog
Oct 21, 2020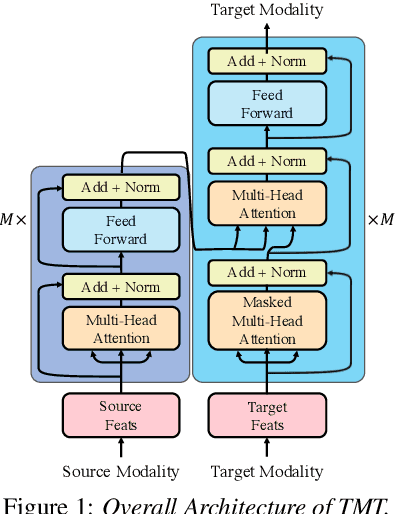
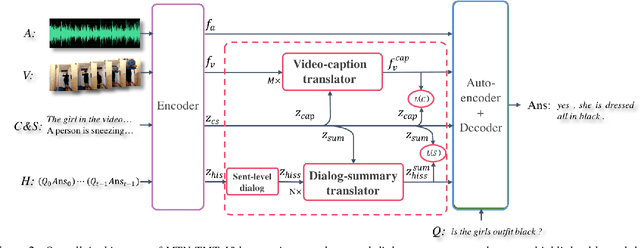
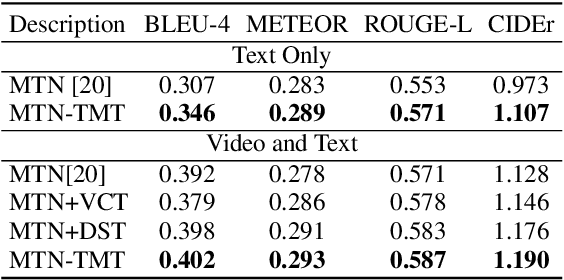
Abstract:Audio Visual Scene-aware Dialog (AVSD) is a task to generate responses when discussing about a given video. The previous state-of-the-art model shows superior performance for this task using Transformer-based architecture. However, there remain some limitations in learning better representation of modalities. Inspired by Neural Machine Translation (NMT), we propose the Transformer-based Modal Translator (TMT) to learn the representations of the source modal sequence by translating the source modal sequence to the related target modal sequence in a supervised manner. Based on Multimodal Transformer Networks (MTN), we apply TMT to video and dialog, proposing MTN-TMT for the video-grounded dialog system. On the AVSD track of the Dialog System Technology Challenge 7, MTN-TMT outperforms the MTN and other submission models in both Video and Text task and Text Only task. Compared with MTN, MTN-TMT improves all metrics, especially, achieving relative improvement up to 14.1% on CIDEr. Index Terms: multimodal learning, audio-visual scene-aware dialog, neural machine translation, multi-task learning
A Further Study of Unsupervised Pre-training for Transformer Based Speech Recognition
Jun 23, 2020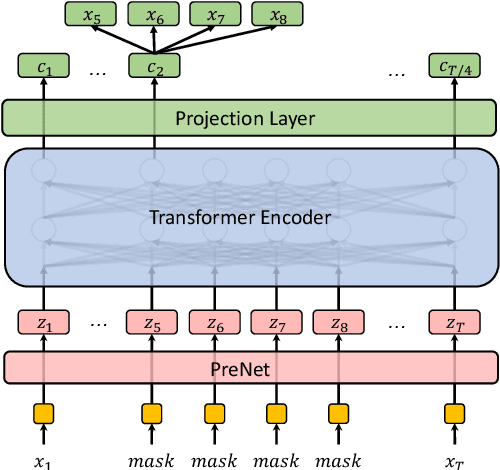
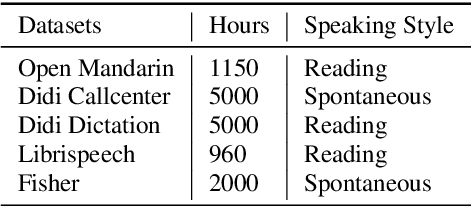
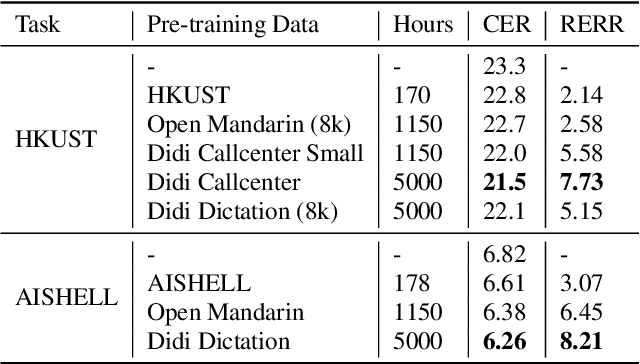
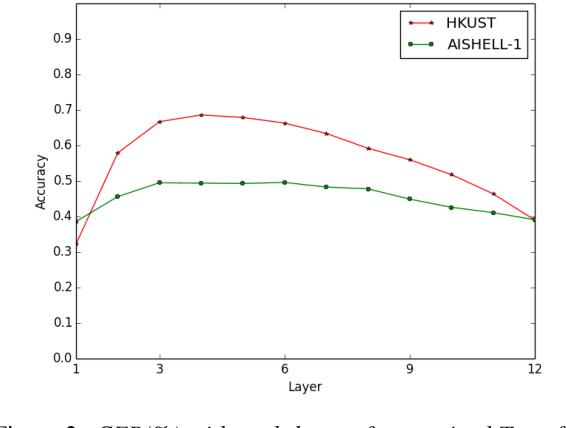
Abstract:Building a good speech recognition system usually requires large amounts of transcribed data, which is expensive to collect. To tackle this problem, many unsupervised pre-training methods have been proposed. Among these methods, Masked Predictive Coding achieved significant improvements on various speech recognition datasets with BERT-like Masked Reconstruction loss and Transformer backbone. However, many aspects of MPC have not been fully investigated. In this paper, we conduct a further study on MPC and focus on three important aspects: the effect of pre-training data speaking style, its extension on streaming model, and how to better transfer learned knowledge from pre-training stage to downstream tasks. Experiments reveled that pre-training data with matching speaking style is more useful on downstream recognition tasks. A unified training objective with APC and MPC provided 8.46% relative error reduction on streaming model trained on HKUST. Also, the combination of target data adaption and layer-wise discriminative training helped the knowledge transfer of MPC, which achieved 3.99% relative error reduction on AISHELL over a strong baseline.
Improving Transformer-based Speech Recognition Using Unsupervised Pre-training
Oct 31, 2019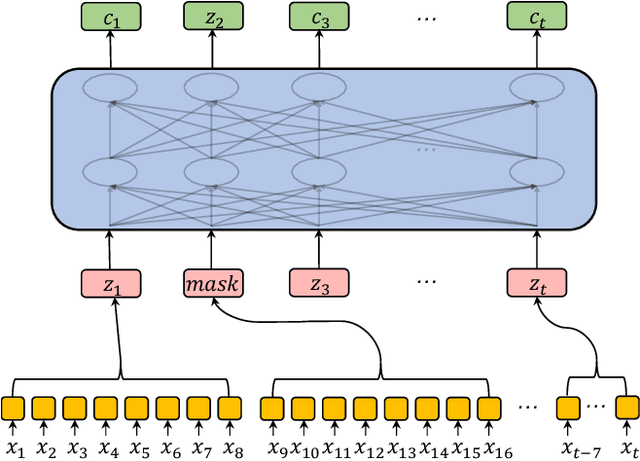
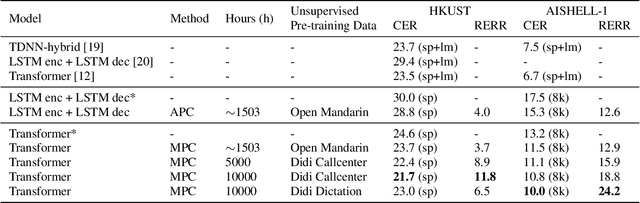
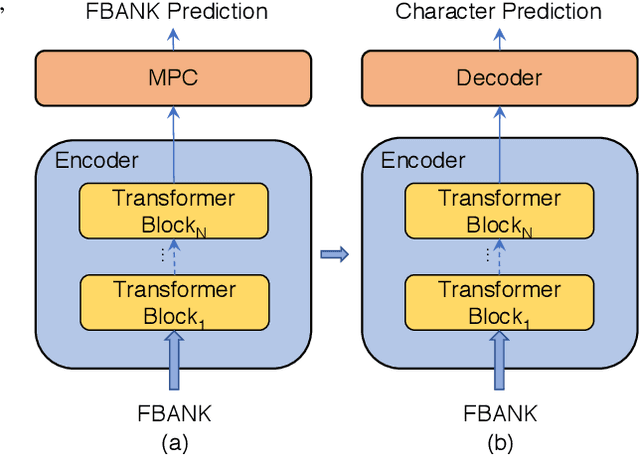
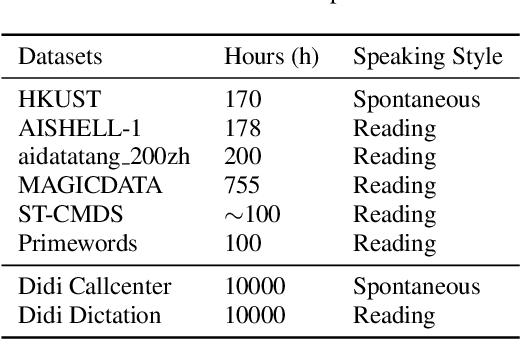
Abstract:Speech recognition technologies are gaining enormous popularity in various industrial applications. However, building a good speech recognition system usually requires large amounts of transcribed data, which is expensive to collect. To tackle this problem, an unsupervised pre-training method called Masked Predictive Coding is proposed, which can be applied for unsupervised pre-training with Transformer based model. Experiments on HKUST show that using the same training data, we can achieve CER 23.3%, exceeding the best end-to-end model by over 0.2% absolute CER. With more pre-training data, we can further reduce the CER to 21.0%, or a 11.8% relative CER reduction over baseline.
TCT: A Cross-supervised Learning Method for Multimodal Sequence Representation
Oct 23, 2019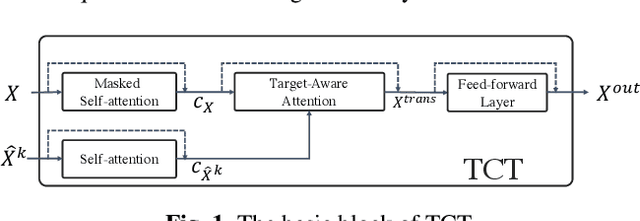
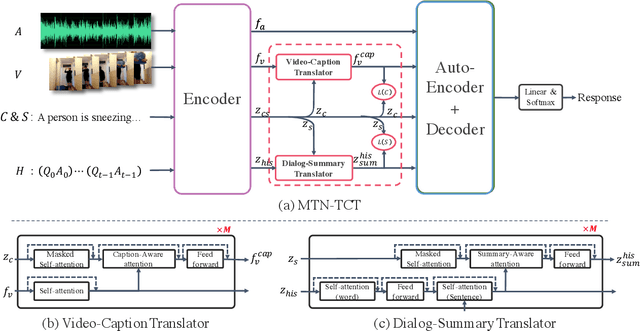
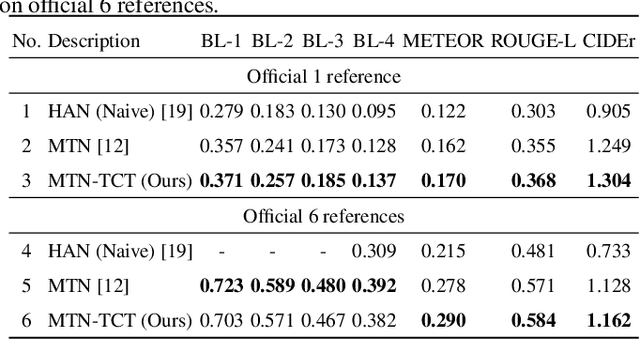
Abstract:Multimodalities provide promising performance than unimodality in most tasks. However, learning the semantic of the representations from multimodalities efficiently is extremely challenging. To tackle this, we propose the Transformer based Cross-modal Translator (TCT) to learn unimodal sequence representations by translating from other related multimodal sequences on a supervised learning method. Combined TCT with Multimodal Transformer Network (MTN), we evaluate MTN-TCT on the video-grounded dialogue which uses multimodality. The proposed method reports new state-of-the-art performance on video-grounded dialogue which indicates representations learned by TCT are more semantics compared to directly use unimodality.
A Multi-Modal Chinese Poetry Generation Model
Jun 26, 2018
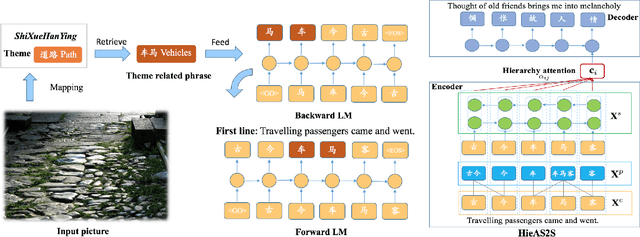


Abstract:Recent studies in sequence-to-sequence learning demonstrate that RNN encoder-decoder structure can successfully generate Chinese poetry. However, existing methods can only generate poetry with a given first line or user's intent theme. In this paper, we proposed a three-stage multi-modal Chinese poetry generation approach. Given a picture, the first line, the title and the other lines of the poem are successively generated in three stages. According to the characteristics of Chinese poems, we propose a hierarchy-attention seq2seq model which can effectively capture character, phrase, and sentence information between contexts and improve the symmetry delivered in poems. In addition, the Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model is utilized for title generation and improve the relevance of the whole poem and the title. Compared with strong baseline, the experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, using machine evaluations as well as human judgments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge