William P. McCarthy
mrCAD: Multimodal Refinement of Computer-aided Designs
Apr 28, 2025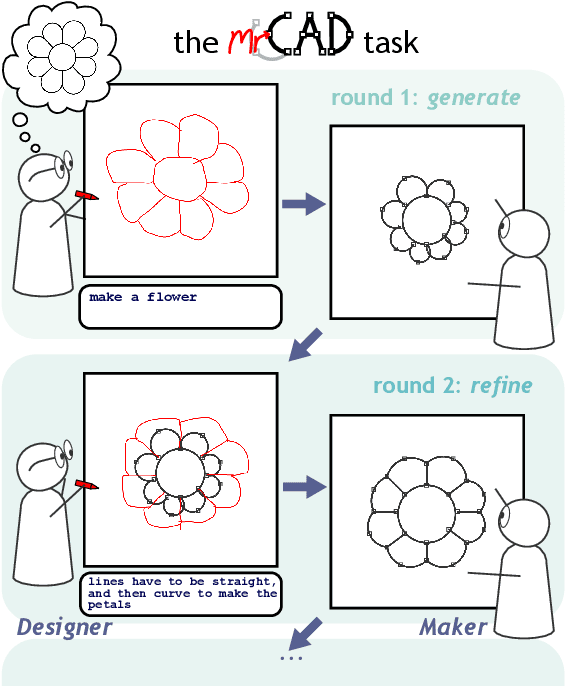
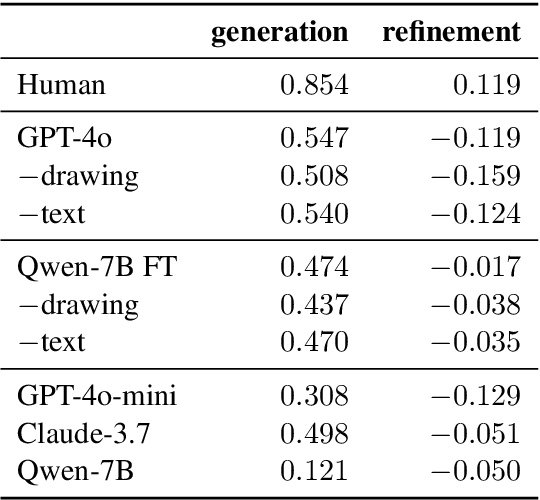
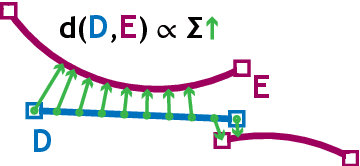
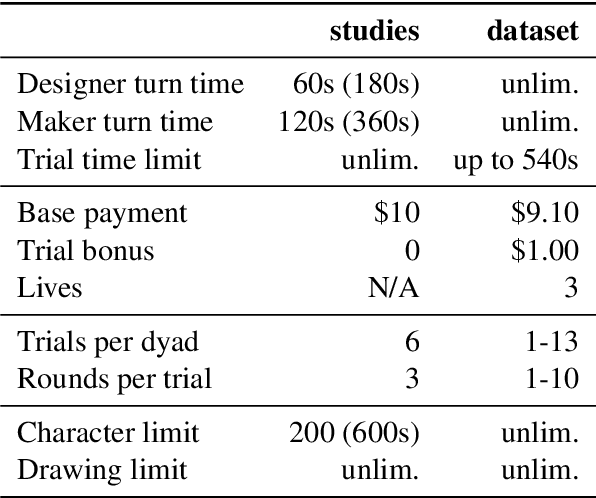
Abstract:A key feature of human collaboration is the ability to iteratively refine the concepts we have communicated. In contrast, while generative AI excels at the \textit{generation} of content, it often struggles to make specific language-guided \textit{modifications} of its prior outputs. To bridge the gap between how humans and machines perform edits, we present mrCAD, a dataset of multimodal instructions in a communication game. In each game, players created computer aided designs (CADs) and refined them over several rounds to match specific target designs. Only one player, the Designer, could see the target, and they must instruct the other player, the Maker, using text, drawing, or a combination of modalities. mrCAD consists of 6,082 communication games, 15,163 instruction-execution rounds, played between 1,092 pairs of human players. We analyze the dataset and find that generation and refinement instructions differ in their composition of drawing and text. Using the mrCAD task as a benchmark, we find that state-of-the-art VLMs are better at following generation instructions than refinement instructions. These results lay a foundation for analyzing and modeling a multimodal language of refinement that is not represented in previous datasets.
Identifying concept libraries from language about object structure
May 11, 2022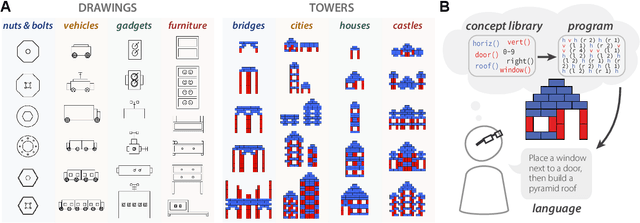
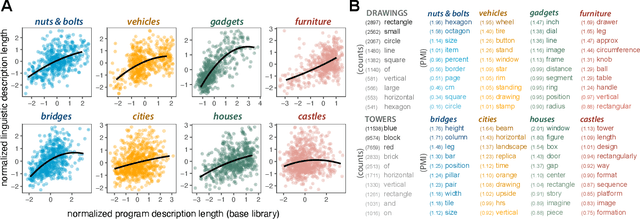
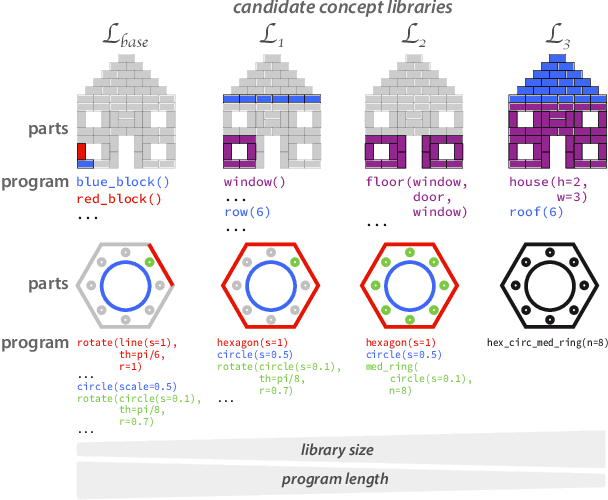
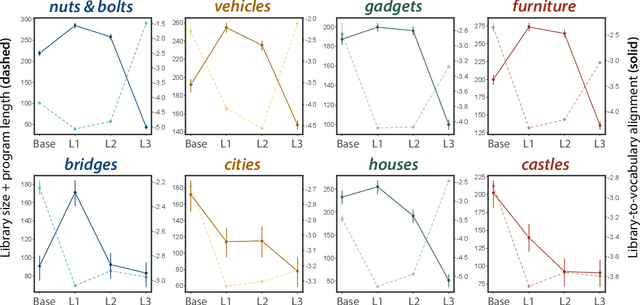
Abstract:Our understanding of the visual world goes beyond naming objects, encompassing our ability to parse objects into meaningful parts, attributes, and relations. In this work, we leverage natural language descriptions for a diverse set of 2K procedurally generated objects to identify the parts people use and the principles leading these parts to be favored over others. We formalize our problem as search over a space of program libraries that contain different part concepts, using tools from machine translation to evaluate how well programs expressed in each library align to human language. By combining naturalistic language at scale with structured program representations, we discover a fundamental information-theoretic tradeoff governing the part concepts people name: people favor a lexicon that allows concise descriptions of each object, while also minimizing the size of the lexicon itself.
Learning to communicate about shared procedural abstractions
Jun 30, 2021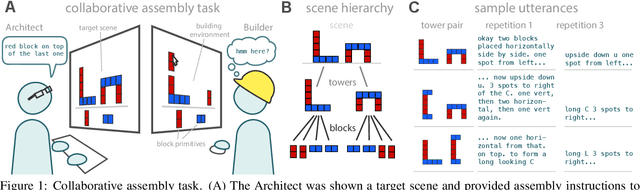
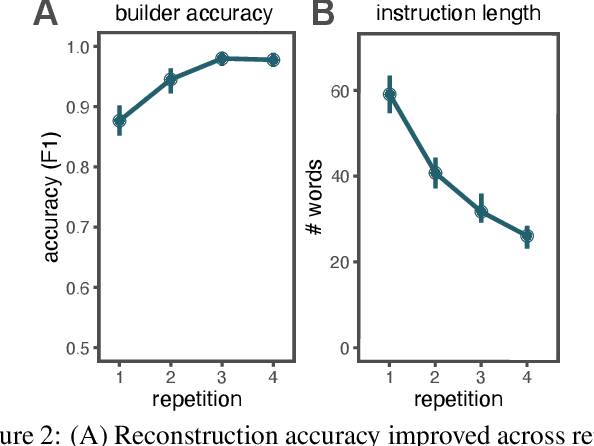
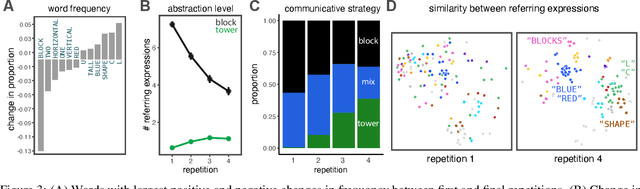
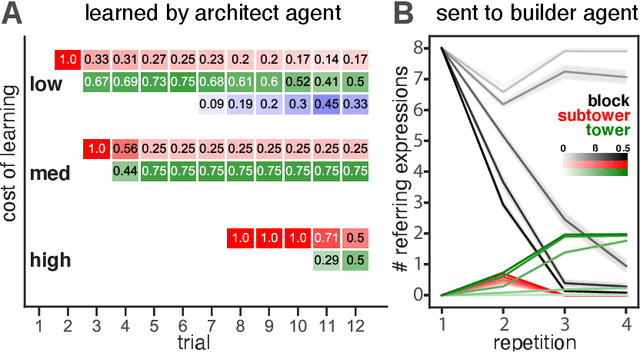
Abstract:Many real-world tasks require agents to coordinate their behavior to achieve shared goals. Successful collaboration requires not only adopting the same communicative conventions, but also grounding these conventions in the same task-appropriate conceptual abstractions. We investigate how humans use natural language to collaboratively solve physical assembly problems more effectively over time. Human participants were paired up in an online environment to reconstruct scenes containing two block towers. One participant could see the target towers, and sent assembly instructions for the other participant to reconstruct. Participants provided increasingly concise instructions across repeated attempts on each pair of towers, using higher-level referring expressions that captured each scene's hierarchical structure. To explain these findings, we extend recent probabilistic models of ad-hoc convention formation with an explicit perceptual learning mechanism. These results shed light on the inductive biases that enable intelligent agents to coordinate upon shared procedural abstractions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge