Identifying concept libraries from language about object structure
Paper and Code
May 11, 2022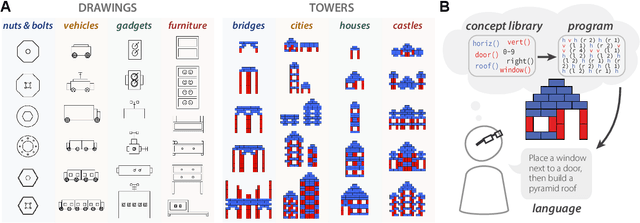
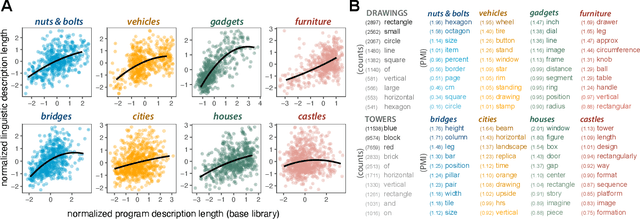
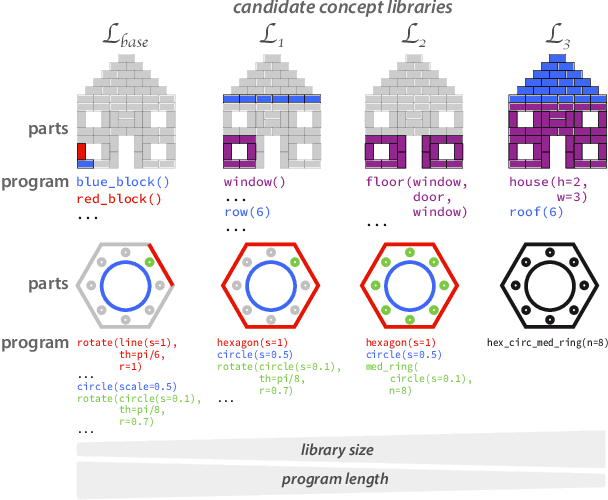
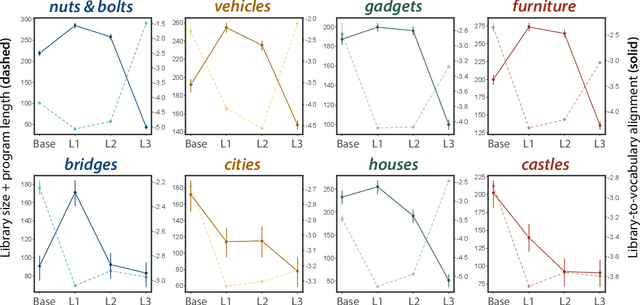
Our understanding of the visual world goes beyond naming objects, encompassing our ability to parse objects into meaningful parts, attributes, and relations. In this work, we leverage natural language descriptions for a diverse set of 2K procedurally generated objects to identify the parts people use and the principles leading these parts to be favored over others. We formalize our problem as search over a space of program libraries that contain different part concepts, using tools from machine translation to evaluate how well programs expressed in each library align to human language. By combining naturalistic language at scale with structured program representations, we discover a fundamental information-theoretic tradeoff governing the part concepts people name: people favor a lexicon that allows concise descriptions of each object, while also minimizing the size of the lexicon itself.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge