Cameron Holdaway
Learning to communicate about shared procedural abstractions
Jun 30, 2021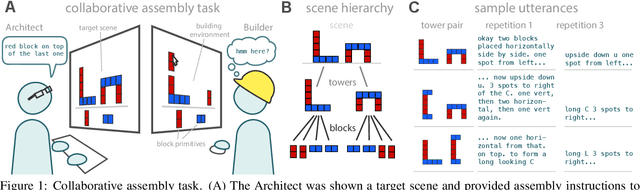
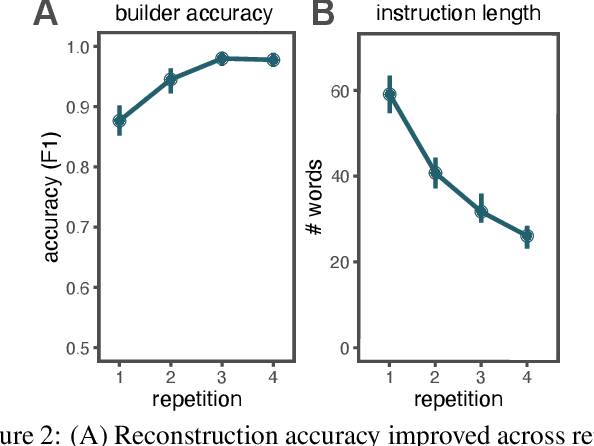
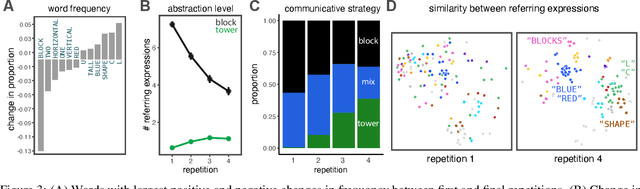
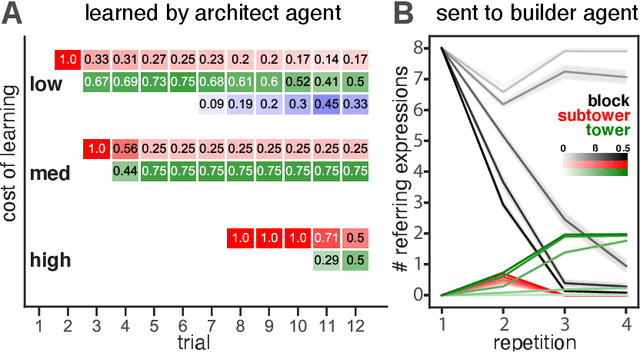
Abstract:Many real-world tasks require agents to coordinate their behavior to achieve shared goals. Successful collaboration requires not only adopting the same communicative conventions, but also grounding these conventions in the same task-appropriate conceptual abstractions. We investigate how humans use natural language to collaboratively solve physical assembly problems more effectively over time. Human participants were paired up in an online environment to reconstruct scenes containing two block towers. One participant could see the target towers, and sent assembly instructions for the other participant to reconstruct. Participants provided increasingly concise instructions across repeated attempts on each pair of towers, using higher-level referring expressions that captured each scene's hierarchical structure. To explain these findings, we extend recent probabilistic models of ad-hoc convention formation with an explicit perceptual learning mechanism. These results shed light on the inductive biases that enable intelligent agents to coordinate upon shared procedural abstractions.
Physion: Evaluating Physical Prediction from Vision in Humans and Machines
Jun 17, 2021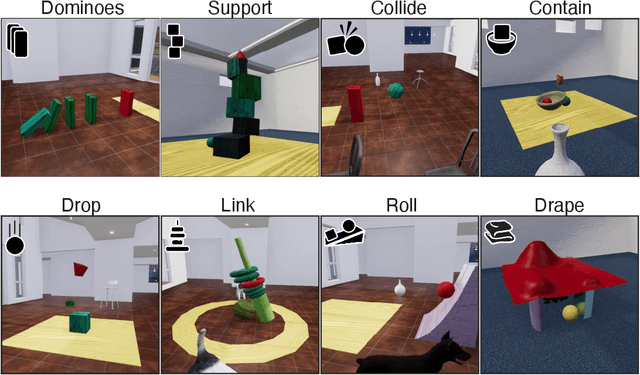
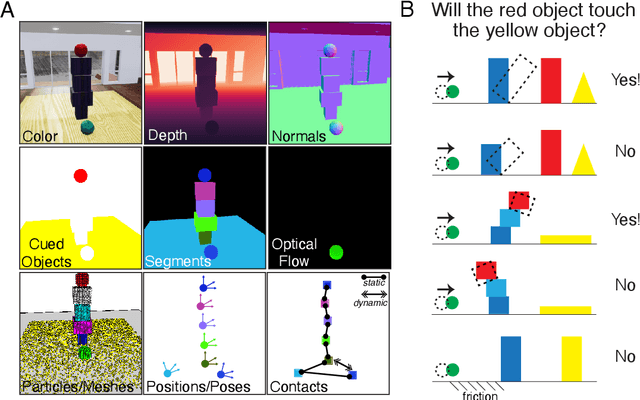
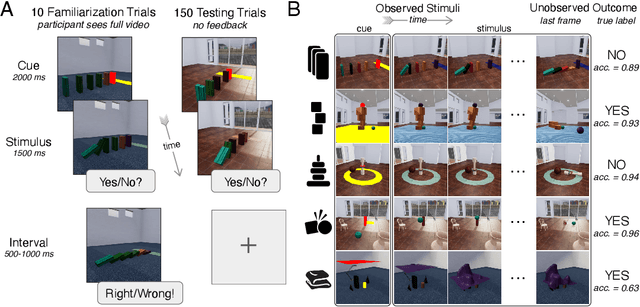
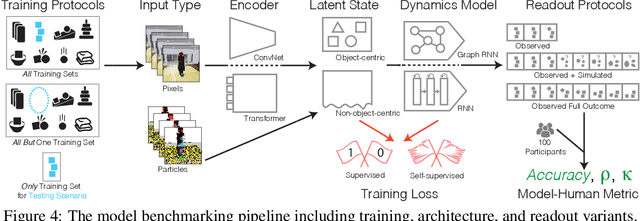
Abstract:While machine learning algorithms excel at many challenging visual tasks, it is unclear that they can make predictions about commonplace real world physical events. Here, we present a visual and physical prediction benchmark that precisely measures this capability. In realistically simulating a wide variety of physical phenomena -- rigid and soft-body collisions, stable multi-object configurations, rolling and sliding, projectile motion -- our dataset presents a more comprehensive challenge than existing benchmarks. Moreover, we have collected human responses for our stimuli so that model predictions can be directly compared to human judgments. We compare an array of algorithms -- varying in their architecture, learning objective, input-output structure, and training data -- on their ability to make diverse physical predictions. We find that graph neural networks with access to the physical state best capture human behavior, whereas among models that receive only visual input, those with object-centric representations or pretraining do best but fall far short of human accuracy. This suggests that extracting physically meaningful representations of scenes is the main bottleneck to achieving human-like visual prediction. We thus demonstrate how our benchmark can identify areas for improvement and measure progress on this key aspect of physical understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge