William Gray Roncal
Department of Computer Science, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD
SANTIAGO: Spine Association for Neuron Topology Improvement and Graph Optimization
Aug 08, 2016



Abstract:Developing automated and semi-automated solutions for reconstructing wiring diagrams of the brain from electron micrographs is important for advancing the field of connectomics. While the ultimate goal is to generate a graph of neuron connectivity, most prior automated methods have focused on volume segmentation rather than explicit graph estimation. In these approaches, one of the key, commonly occurring error modes is dendritic shaft-spine fragmentation. We posit that directly addressing this problem of connection identification may provide critical insight into estimating more accurate brain graphs. To this end, we develop a network-centric approach motivated by biological priors image grammars. We build a computer vision pipeline to reconnect fragmented spines to their parent dendrites using both fully-automated and semi-automated approaches. Our experiments show we can learn valid connections despite uncertain segmentation paths. We curate the first known reference dataset for analyzing the performance of various spine-shaft algorithms and demonstrate promising results that recover many previously lost connections. Our automated approach improves the local subgraph score by more than four times and the full graph score by 60 percent. These data, results, and evaluation tools are all available to the broader scientific community. This reframing of the connectomics problem illustrates a semantic, biologically inspired solution to remedy a major problem with neuron tracking.
Quantifying mesoscale neuroanatomy using X-ray microtomography
Jul 26, 2016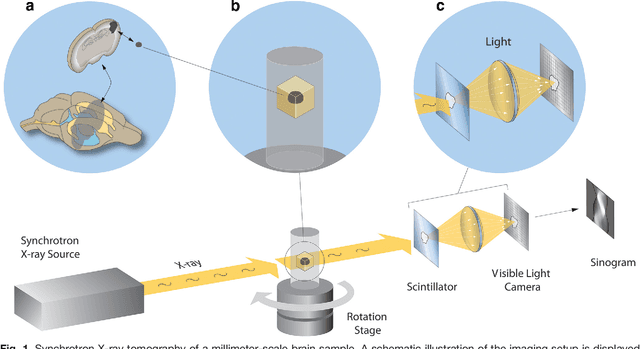
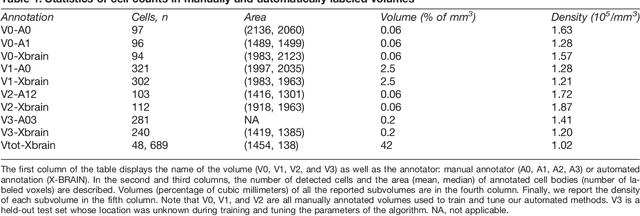
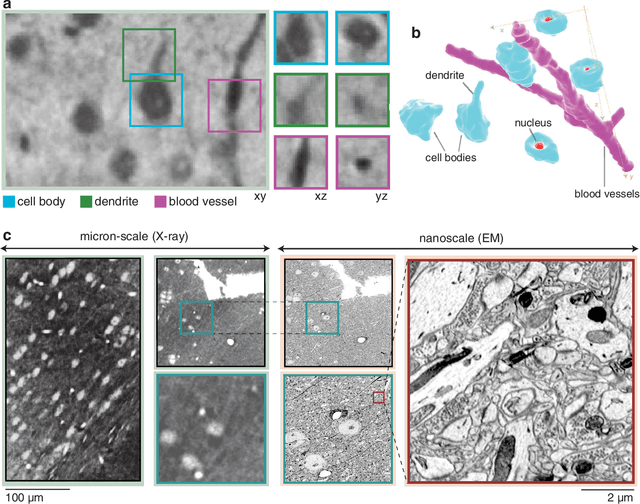
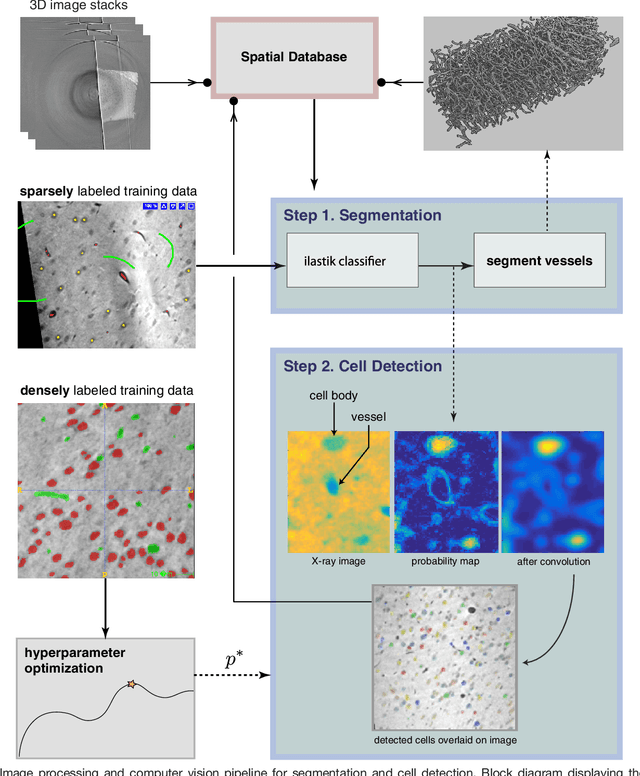
Abstract:Methods for resolving the 3D microstructure of the brain typically start by thinly slicing and staining the brain, and then imaging each individual section with visible light photons or electrons. In contrast, X-rays can be used to image thick samples, providing a rapid approach for producing large 3D brain maps without sectioning. Here we demonstrate the use of synchrotron X-ray microtomography ($\mu$CT) for producing mesoscale $(1~\mu m^3)$ resolution brain maps from millimeter-scale volumes of mouse brain. We introduce a pipeline for $\mu$CT-based brain mapping that combines methods for sample preparation, imaging, automated segmentation of image volumes into cells and blood vessels, and statistical analysis of the resulting brain structures. Our results demonstrate that X-ray tomography promises rapid quantification of large brain volumes, complementing other brain mapping and connectomics efforts.
VESICLE: Volumetric Evaluation of Synaptic Interfaces using Computer vision at Large Scale
Sep 07, 2015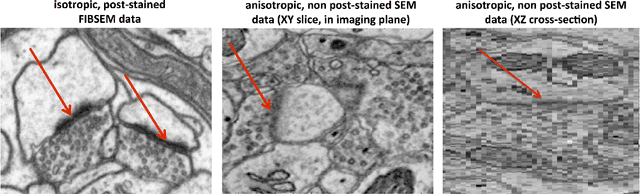
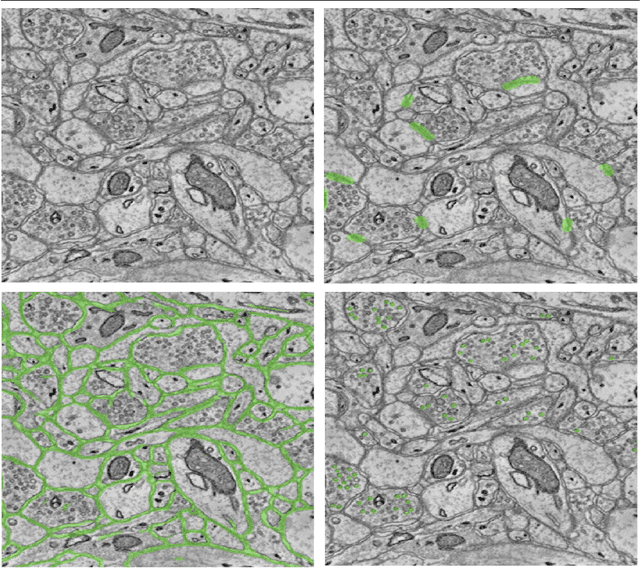
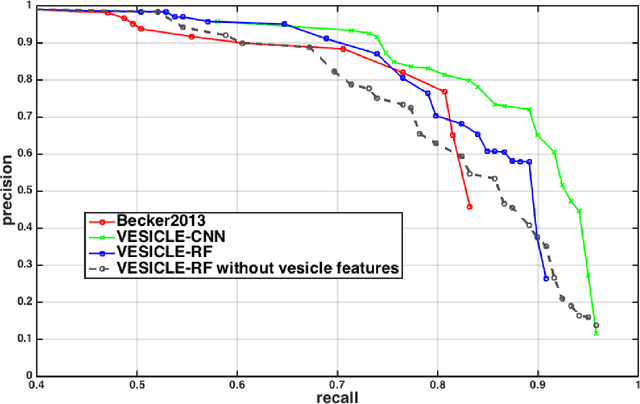
Abstract:An open challenge problem at the forefront of modern neuroscience is to obtain a comprehensive mapping of the neural pathways that underlie human brain function; an enhanced understanding of the wiring diagram of the brain promises to lead to new breakthroughs in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. Inferring brain structure from image data, such as that obtained via electron microscopy (EM), entails solving the problem of identifying biological structures in large data volumes. Synapses, which are a key communication structure in the brain, are particularly difficult to detect due to their small size and limited contrast. Prior work in automated synapse detection has relied upon time-intensive biological preparations (post-staining, isotropic slice thicknesses) in order to simplify the problem. This paper presents VESICLE, the first known approach designed for mammalian synapse detection in anisotropic, non-post-stained data. Our methods explicitly leverage biological context, and the results exceed existing synapse detection methods in terms of accuracy and scalability. We provide two different approaches - one a deep learning classifier (VESICLE-CNN) and one a lightweight Random Forest approach (VESICLE-RF) to offer alternatives in the performance-scalability space. Addressing this synapse detection challenge enables the analysis of high-throughput imaging data soon expected to reach petabytes of data, and provide tools for more rapid estimation of brain-graphs. Finally, to facilitate community efforts, we developed tools for large-scale object detection, and demonstrated this framework to find $\approx$ 50,000 synapses in 60,000 $\mu m ^3$ (220 GB on disk) of electron microscopy data.
* v4: added clarifying figures and updates for readability. v3: fixed metadata. 11 pp v2: Added CNN classifier, significant changes to improve performance and generalization
An Automated Images-to-Graphs Framework for High Resolution Connectomics
Apr 30, 2015


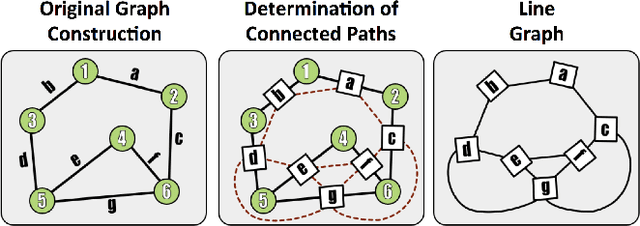
Abstract:Reconstructing a map of neuronal connectivity is a critical challenge in contemporary neuroscience. Recent advances in high-throughput serial section electron microscopy (EM) have produced massive 3D image volumes of nanoscale brain tissue for the first time. The resolution of EM allows for individual neurons and their synaptic connections to be directly observed. Recovering neuronal networks by manually tracing each neuronal process at this scale is unmanageable, and therefore researchers are developing automated image processing modules. Thus far, state-of-the-art algorithms focus only on the solution to a particular task (e.g., neuron segmentation or synapse identification). In this manuscript we present the first fully automated images-to-graphs pipeline (i.e., a pipeline that begins with an imaged volume of neural tissue and produces a brain graph without any human interaction). To evaluate overall performance and select the best parameters and methods, we also develop a metric to assess the quality of the output graphs. We evaluate a set of algorithms and parameters, searching possible operating points to identify the best available brain graph for our assessment metric. Finally, we deploy a reference end-to-end version of the pipeline on a large, publicly available data set. This provides a baseline result and framework for community analysis and future algorithm development and testing. All code and data derivatives have been made publicly available toward eventually unlocking new biofidelic computational primitives and understanding of neuropathologies.
Automatic Annotation of Axoplasmic Reticula in Pursuit of Connectomes using High-Resolution Neural EM Data
Apr 16, 2014

Abstract:Accurately estimating the wiring diagram of a brain, known as a connectome, at an ultrastructure level is an open research problem. Specifically, precisely tracking neural processes is difficult, especially across many image slices. Here, we propose a novel method to automatically identify and annotate small subcellular structures present in axons, known as axoplasmic reticula, through a 3D volume of high-resolution neural electron microscopy data. Our method produces high precision annotations, which can help improve automatic segmentation by using our results as seeds for segmentation, and as cues to aid segment merging.
Automatic Annotation of Axoplasmic Reticula in Pursuit of Connectomes
Apr 16, 2014

Abstract:In this paper, we present a new pipeline which automatically identifies and annotates axoplasmic reticula, which are small subcellular structures present only in axons. We run our algorithm on the Kasthuri11 dataset, which was color corrected using gradient-domain techniques to adjust contrast. We use a bilateral filter to smooth out the noise in this data while preserving edges, which highlights axoplasmic reticula. These axoplasmic reticula are then annotated using a morphological region growing algorithm. Additionally, we perform Laplacian sharpening on the bilaterally filtered data to enhance edges, and repeat the morphological region growing algorithm to annotate more axoplasmic reticula. We track our annotations through the slices to improve precision, and to create long objects to aid in segment merging. This method annotates axoplasmic reticula with high precision. Our algorithm can easily be adapted to annotate axoplasmic reticula in different sets of brain data by changing a few thresholds. The contribution of this work is the introduction of a straightforward and robust pipeline which annotates axoplasmic reticula with high precision, contributing towards advancements in automatic feature annotations in neural EM data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge