William Gantt
Small Models Are (Still) Effective Cross-Domain Argument Extractors
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Effective ontology transfer has been a major goal of recent work on event argument extraction (EAE). Two methods in particular -- question answering (QA) and template infilling (TI) -- have emerged as promising approaches to this problem. However, detailed explorations of these techniques' ability to actually enable this transfer are lacking. In this work, we provide such a study, exploring zero-shot transfer using both techniques on six major EAE datasets at both the sentence and document levels. Further, we challenge the growing reliance on LLMs for zero-shot extraction, showing that vastly smaller models trained on an appropriate source ontology can yield zero-shot performance superior to that of GPT-3.5 or GPT-4.
Event-Keyed Summarization
Feb 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce event-keyed summarization (EKS), a novel task that marries traditional summarization and document-level event extraction, with the goal of generating a contextualized summary for a specific event, given a document and an extracted event structure. We introduce a dataset for this task, MUCSUM, consisting of summaries of all events in the classic MUC-4 dataset, along with a set of baselines that comprises both pretrained LM standards in the summarization literature, as well as larger frontier models. We show that ablations that reduce EKS to traditional summarization or structure-to-text yield inferior summaries of target events and that MUCSUM is a robust benchmark for this task. Lastly, we conduct a human evaluation of both reference and model summaries, and provide some detailed analysis of the results.
MultiMUC: Multilingual Template Filling on MUC-4
Jan 29, 2024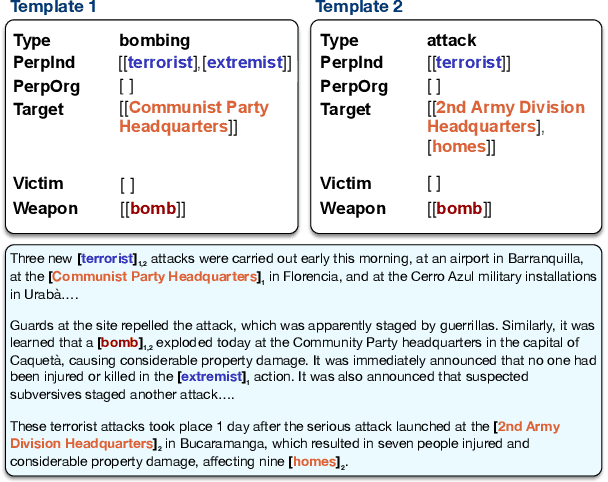
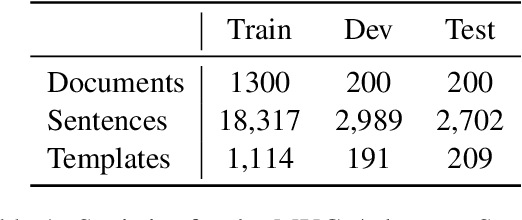

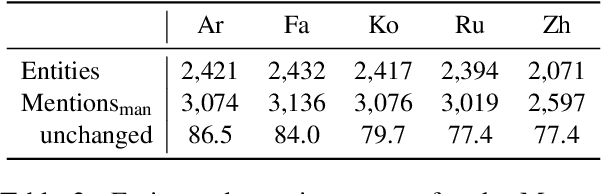
Abstract:We introduce MultiMUC, the first multilingual parallel corpus for template filling, comprising translations of the classic MUC-4 template filling benchmark into five languages: Arabic, Chinese, Farsi, Korean, and Russian. We obtain automatic translations from a strong multilingual machine translation system and manually project the original English annotations into each target language. For all languages, we also provide human translations for sentences in the dev and test splits that contain annotated template arguments. Finally, we present baselines on MultiMUC both with state-of-the-art template filling models and with ChatGPT.
FAMuS: Frames Across Multiple Sources
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Understanding event descriptions is a central aspect of language processing, but current approaches focus overwhelmingly on single sentences or documents. Aggregating information about an event \emph{across documents} can offer a much richer understanding. To this end, we present FAMuS, a new corpus of Wikipedia passages that \emph{report} on some event, paired with underlying, genre-diverse (non-Wikipedia) \emph{source} articles for the same event. Events and (cross-sentence) arguments in both report and source are annotated against FrameNet, providing broad coverage of different event types. We present results on two key event understanding tasks enabled by FAMuS: \emph{source validation} -- determining whether a document is a valid source for a target report event -- and \emph{cross-document argument extraction} -- full-document argument extraction for a target event from both its report and the correct source article. We release both FAMuS and our models to support further research.
A Unified View of Evaluation Metrics for Structured Prediction
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:We present a conceptual framework that unifies a variety of evaluation metrics for different structured prediction tasks (e.g. event and relation extraction, syntactic and semantic parsing). Our framework requires representing the outputs of these tasks as objects of certain data types, and derives metrics through matching of common substructures, possibly followed by normalization. We demonstrate how commonly used metrics for a number of tasks can be succinctly expressed by this framework, and show that new metrics can be naturally derived in a bottom-up way based on an output structure. We release a library that enables this derivation to create new metrics. Finally, we consider how specific characteristics of tasks motivate metric design decisions, and suggest possible modifications to existing metrics in line with those motivations.
On Event Individuation for Document-Level Information Extraction
Dec 19, 2022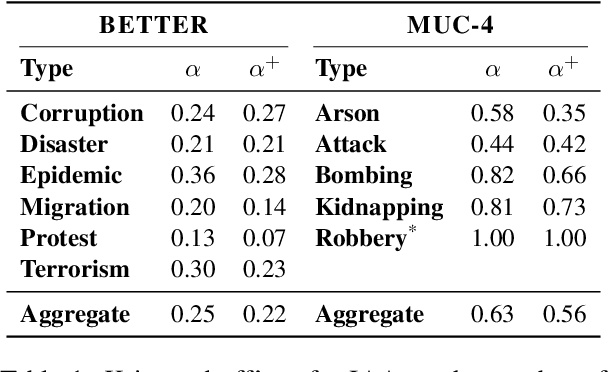

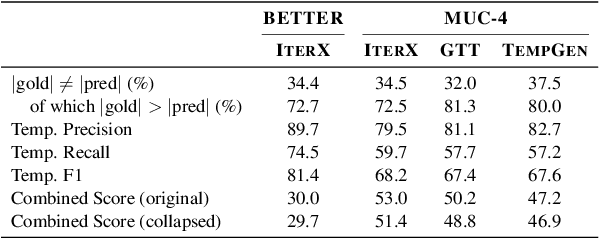
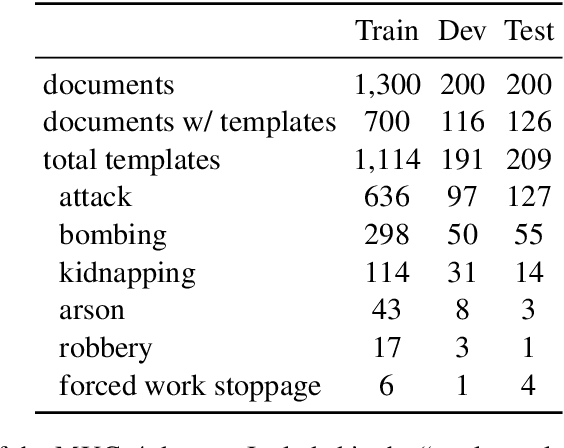
Abstract:As information extraction (IE) systems have grown more capable at whole-document extraction, the classic task of \emph{template filling} has seen renewed interest as a benchmark for evaluating them. In this position paper, we call into question the suitability of template filling for this purpose. We argue that the task demands definitive answers to thorny questions of \emph{event individuation} -- the problem of distinguishing distinct events -- about which even human experts disagree. We show through annotation studies and error analysis that this raises concerns about the usefulness of template filling evaluation metrics, the quality of datasets for the task, and the ability of models to learn it. Finally, we consider possible solutions.
Iterative Document-level Information Extraction via Imitation Learning
Oct 12, 2022
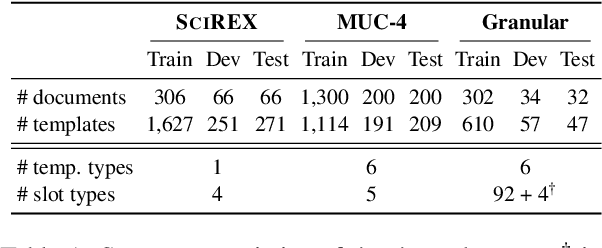

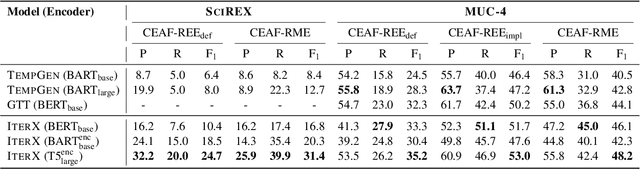
Abstract:We present a novel iterative extraction (IterX) model for extracting complex relations, or templates, i.e., N-tuples representing a mapping from named slots to spans of text contained within a document. Documents may support zero or more instances of a template of any particular type, leading to the tasks of identifying the templates in a document, and extracting each template's slot values. Our imitation learning approach relieves the need to use predefined template orders to train an extractor and leads to state-of-the-art results on two established benchmarks -- 4-ary relation extraction on SciREX and template extraction on MUC-4 -- as well as a strong baseline on the new BETTER Granular task.
Argument Linking: A Survey and Forecast
Jul 18, 2021



Abstract:Semantic role labeling (SRL) -- identifying the semantic relationships between a predicate and other constituents in the same sentence -- is a well-studied task in natural language understanding (NLU). However, many of these relationships are evident only at the level of the document, as a role for a predicate in one sentence may often be filled by an argument in a different one. This more general task, known as implicit semantic role labeling or argument linking, has received increased attention in recent years, as researchers have recognized its centrality to information extraction and NLU. This paper surveys the literature on argument linking and identifies several notable shortcomings of existing approaches that indicate the paths along which future research effort could most profitably be spent.
Decomposing and Recomposing Event Structure
Mar 18, 2021



Abstract:We present an event structure ontology empirically derived from inferential properties annotated on sentence- and document-level semantic graphs. We induce this ontology jointly with semantic role, entity type, and event-event relation ontologies using a document-level generative model, identifying sets of types that align closely with previous theoretically-motivated taxonomies.
Natural Language Inference with Mixed Effects
Oct 20, 2020
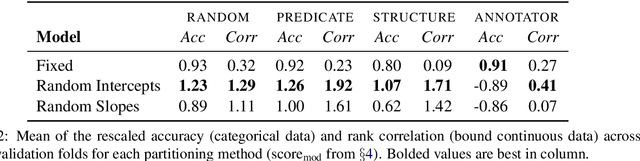
Abstract:There is growing evidence that the prevalence of disagreement in the raw annotations used to construct natural language inference datasets makes the common practice of aggregating those annotations to a single label problematic. We propose a generic method that allows one to skip the aggregation step and train on the raw annotations directly without subjecting the model to unwanted noise that can arise from annotator response biases. We demonstrate that this method, which generalizes the notion of a \textit{mixed effects model} by incorporating \textit{annotator random effects} into any existing neural model, improves performance over models that do not incorporate such effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge