Wenxin Ding
Towards Scalable and Robust Model Versioning
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:As the deployment of deep learning models continues to expand across industries, the threat of malicious incursions aimed at gaining access to these deployed models is on the rise. Should an attacker gain access to a deployed model, whether through server breaches, insider attacks, or model inversion techniques, they can then construct white-box adversarial attacks to manipulate the model's classification outcomes, thereby posing significant risks to organizations that rely on these models for critical tasks. Model owners need mechanisms to protect themselves against such losses without the necessity of acquiring fresh training data - a process that typically demands substantial investments in time and capital. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of generating multiple versions of a model that possess different attack properties, without acquiring new training data or changing model architecture. The model owner can deploy one version at a time and replace a leaked version immediately with a new version. The newly deployed model version can resist adversarial attacks generated leveraging white-box access to one or all previously leaked versions. We show theoretically that this can be accomplished by incorporating parameterized hidden distributions into the model training data, forcing the model to learn task-irrelevant features uniquely defined by the chosen data. Additionally, optimal choices of hidden distributions can produce a sequence of model versions capable of resisting compound transferability attacks over time. Leveraging our analytical insights, we design and implement a practical model versioning method for DNN classifiers, which leads to significant robustness improvements over existing methods. We believe our work presents a promising direction for safeguarding DNN services beyond their initial deployment.
A Two-stage Personalized Virtual Try-on Framework with Shape Control and Texture Guidance
Dec 24, 2023Abstract:The Diffusion model has a strong ability to generate wild images. However, the model can just generate inaccurate images with the guidance of text, which makes it very challenging to directly apply the text-guided generative model for virtual try-on scenarios. Taking images as guiding conditions of the diffusion model, this paper proposes a brand new personalized virtual try-on model (PE-VITON), which uses the two stages (shape control and texture guidance) to decouple the clothing attributes. Specifically, the proposed model adaptively matches the clothing to human body parts through the Shape Control Module (SCM) to mitigate the misalignment of the clothing and the human body parts. The semantic information of the input clothing is parsed by the Texture Guided Module (TGM), and the corresponding texture is generated by directional guidance. Therefore, this model can effectively solve the problems of weak reduction of clothing folds, poor generation effect under complex human posture, blurred edges of clothing, and unclear texture styles in traditional try-on methods. Meanwhile, the model can automatically enhance the generated clothing folds and textures according to the human posture, and improve the authenticity of virtual try-on. In this paper, qualitative and quantitative experiments are carried out on high-resolution paired and unpaired datasets, the results show that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art model.
Prompt-Specific Poisoning Attacks on Text-to-Image Generative Models
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:Data poisoning attacks manipulate training data to introduce unexpected behaviors into machine learning models at training time. For text-to-image generative models with massive training datasets, current understanding of poisoning attacks suggests that a successful attack would require injecting millions of poison samples into their training pipeline. In this paper, we show that poisoning attacks can be successful on generative models. We observe that training data per concept can be quite limited in these models, making them vulnerable to prompt-specific poisoning attacks, which target a model's ability to respond to individual prompts. We introduce Nightshade, an optimized prompt-specific poisoning attack where poison samples look visually identical to benign images with matching text prompts. Nightshade poison samples are also optimized for potency and can corrupt an Stable Diffusion SDXL prompt in <100 poison samples. Nightshade poison effects "bleed through" to related concepts, and multiple attacks can composed together in a single prompt. Surprisingly, we show that a moderate number of Nightshade attacks can destabilize general features in a text-to-image generative model, effectively disabling its ability to generate meaningful images. Finally, we propose the use of Nightshade` and similar tools as a last defense for content creators against web scrapers that ignore opt-out/do-not-crawl directives, and discuss possible implications for model trainers and content creators.
Characterizing the Optimal 0-1 Loss for Multi-class Classification with a Test-time Attacker
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:Finding classifiers robust to adversarial examples is critical for their safe deployment. Determining the robustness of the best possible classifier under a given threat model for a given data distribution and comparing it to that achieved by state-of-the-art training methods is thus an important diagnostic tool. In this paper, we find achievable information-theoretic lower bounds on loss in the presence of a test-time attacker for multi-class classifiers on any discrete dataset. We provide a general framework for finding the optimal 0-1 loss that revolves around the construction of a conflict hypergraph from the data and adversarial constraints. We further define other variants of the attacker-classifier game that determine the range of the optimal loss more efficiently than the full-fledged hypergraph construction. Our evaluation shows, for the first time, an analysis of the gap to optimal robustness for classifiers in the multi-class setting on benchmark datasets.
On the Privacy-Utility Tradeoff in Peer-Review Data Analysis
Jun 29, 2020
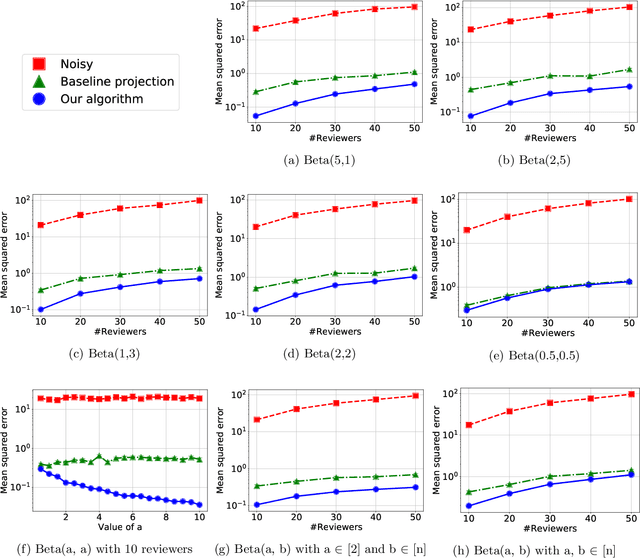
Abstract:A major impediment to research on improving peer review is the unavailability of peer-review data, since any release of such data must grapple with the sensitivity of the peer review data in terms of protecting identities of reviewers from authors. We posit the need to develop techniques to release peer-review data in a privacy-preserving manner. Identifying this problem, in this paper we propose a framework for privacy-preserving release of certain conference peer-review data -- distributions of ratings, miscalibration, and subjectivity -- with an emphasis on the accuracy (or utility) of the released data. The crux of the framework lies in recognizing that a part of the data pertaining to the reviews is already available in public, and we use this information to post-process the data released by any privacy mechanism in a manner that improves the accuracy (utility) of the data while retaining the privacy guarantees. Our framework works with any privacy-preserving mechanism that operates via releasing perturbed data. We present several positive and negative theoretical results, including a polynomial-time algorithm for improving on the privacy-utility tradeoff.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge