Wenjing Liao
Data-Driven Model Reduction using WeldNet: Windowed Encoders for Learning Dynamics
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Many problems in science and engineering involve time-dependent, high dimensional datasets arising from complex physical processes, which are costly to simulate. In this work, we propose WeldNet: Windowed Encoders for Learning Dynamics, a data-driven nonlinear model reduction framework to build a low-dimensional surrogate model for complex evolution systems. Given time-dependent training data, we split the time domain into multiple overlapping windows, within which nonlinear dimension reduction is performed by auto-encoders to capture latent codes. Once a low-dimensional representation of the data is learned, a propagator network is trained to capture the evolution of the latent codes in each window, and a transcoder is trained to connect the latent codes between adjacent windows. The proposed windowed decomposition significantly simplifies propagator training by breaking long-horizon dynamics into multiple short, manageable segments, while the transcoders ensure consistency across windows. In addition to the algorithmic framework, we develop a mathematical theory establishing the representation power of WeldNet under the manifold hypothesis, justifying the success of nonlinear model reduction via deep autoencoder-based architectures. Our numerical experiments on various differential equations indicate that WeldNet can capture nonlinear latent structures and their underlying dynamics, outperforming both traditional projection-based approaches and recently developed nonlinear model reduction methods.
Understanding In-Context Learning on Structured Manifolds: Bridging Attention to Kernel Methods
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:While in-context learning (ICL) has achieved remarkable success in natural language and vision domains, its theoretical understanding--particularly in the context of structured geometric data--remains unexplored. In this work, we initiate a theoretical study of ICL for regression of H\"older functions on manifolds. By establishing a novel connection between the attention mechanism and classical kernel methods, we derive generalization error bounds in terms of the prompt length and the number of training tasks. When a sufficient number of training tasks are observed, transformers give rise to the minimax regression rate of H\"older functions on manifolds, which scales exponentially with the intrinsic dimension of the manifold, rather than the ambient space dimension. Our result also characterizes how the generalization error scales with the number of training tasks, shedding light on the complexity of transformers as in-context algorithm learners. Our findings provide foundational insights into the role of geometry in ICL and novels tools to study ICL of nonlinear models.
Single-shot prediction of parametric partial differential equations
May 14, 2025Abstract:We introduce Flexi-VAE, a data-driven framework for efficient single-shot forecasting of nonlinear parametric partial differential equations (PDEs), eliminating the need for iterative time-stepping while maintaining high accuracy and stability. Flexi-VAE incorporates a neural propagator that advances latent representations forward in time, aligning latent evolution with physical state reconstruction in a variational autoencoder setting. We evaluate two propagation strategies, the Direct Concatenation Propagator (DCP) and the Positional Encoding Propagator (PEP), and demonstrate, through representation-theoretic analysis, that DCP offers superior long-term generalization by fostering disentangled and physically meaningful latent spaces. Geometric diagnostics, including Jacobian spectral analysis, reveal that propagated latent states reside in regions of lower decoder sensitivity and more stable local geometry than those derived via direct encoding, enhancing robustness for long-horizon predictions. We validate Flexi-VAE on canonical PDE benchmarks, the 1D viscous Burgers equation and the 2D advection-diffusion equation, achieving accurate forecasts across wide parametric ranges. The model delivers over 50x CPU and 90x GPU speedups compared to autoencoder-LSTM baselines for large temporal shifts. These results position Flexi-VAE as a scalable and interpretable surrogate modeling tool for accelerating high-fidelity simulations in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and other parametric PDE-driven applications, with extensibility to higher-dimensional and more complex systems.
Transformers for Learning on Noisy and Task-Level Manifolds: Approximation and Generalization Insights
May 06, 2025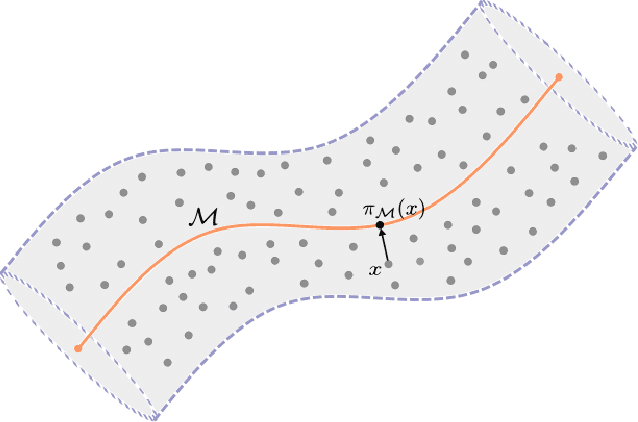
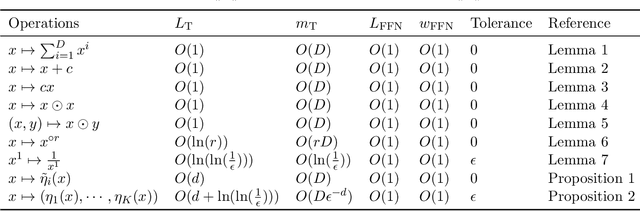
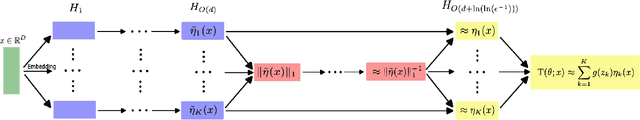

Abstract:Transformers serve as the foundational architecture for large language and video generation models, such as GPT, BERT, SORA and their successors. Empirical studies have demonstrated that real-world data and learning tasks exhibit low-dimensional structures, along with some noise or measurement error. The performance of transformers tends to depend on the intrinsic dimension of the data/tasks, though theoretical understandings remain largely unexplored for transformers. This work establishes a theoretical foundation by analyzing the performance of transformers for regression tasks involving noisy input data on a manifold. Specifically, the input data are in a tubular neighborhood of a manifold, while the ground truth function depends on the projection of the noisy data onto the manifold. We prove approximation and generalization errors which crucially depend on the intrinsic dimension of the manifold. Our results demonstrate that transformers can leverage low-complexity structures in learning task even when the input data are perturbed by high-dimensional noise. Our novel proof technique constructs representations of basic arithmetic operations by transformers, which may hold independent interest.
Coefficient-to-Basis Network: A Fine-Tunable Operator Learning Framework for Inverse Problems with Adaptive Discretizations and Theoretical Guarantees
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:We propose a Coefficient-to-Basis Network (C2BNet), a novel framework for solving inverse problems within the operator learning paradigm. C2BNet efficiently adapts to different discretizations through fine-tuning, using a pre-trained model to significantly reduce computational cost while maintaining high accuracy. Unlike traditional approaches that require retraining from scratch for new discretizations, our method enables seamless adaptation without sacrificing predictive performance. Furthermore, we establish theoretical approximation and generalization error bounds for C2BNet by exploiting low-dimensional structures in the underlying datasets. Our analysis demonstrates that C2BNet adapts to low-dimensional structures without relying on explicit encoding mechanisms, highlighting its robustness and efficiency. To validate our theoretical findings, we conducted extensive numerical experiments that showcase the superior performance of C2BNet on several inverse problems. The results confirm that C2BNet effectively balances computational efficiency and accuracy, making it a promising tool to solve inverse problems in scientific computing and engineering applications.
Understanding Scaling Laws with Statistical and Approximation Theory for Transformer Neural Networks on Intrinsically Low-dimensional Data
Nov 11, 2024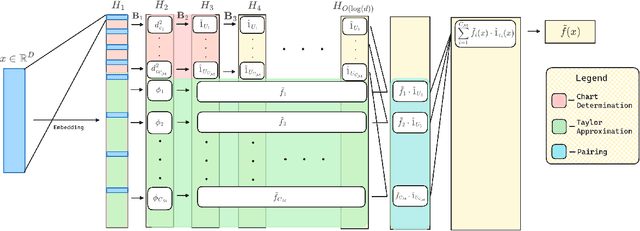
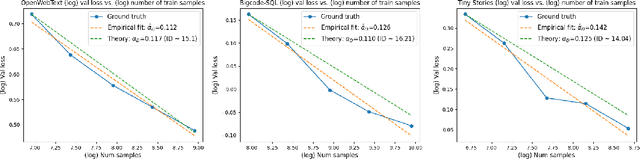
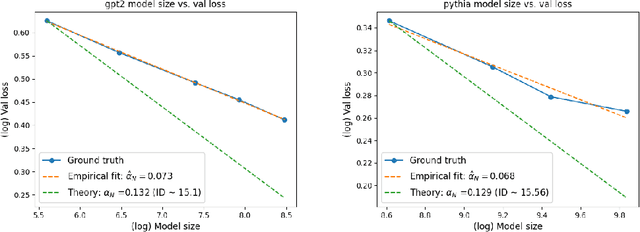
Abstract:When training deep neural networks, a model's generalization error is often observed to follow a power scaling law dependent both on the model size and the data size. Perhaps the best known example of such scaling laws are for transformer-based large language models, where networks with billions of parameters are trained on trillions of tokens of text. Yet, despite sustained widespread interest, a rigorous understanding of why transformer scaling laws exist is still missing. To answer this question, we establish novel statistical estimation and mathematical approximation theories for transformers when the input data are concentrated on a low-dimensional manifold. Our theory predicts a power law between the generalization error and both the training data size and the network size for transformers, where the power depends on the intrinsic dimension $d$ of the training data. Notably, the constructed model architecture is shallow, requiring only logarithmic depth in $d$. By leveraging low-dimensional data structures under a manifold hypothesis, we are able to explain transformer scaling laws in a way which respects the data geometry. Moreover, we test our theory with empirical observation by training LLMs on natural language datasets. We find the observed empirical data scaling laws closely agree with our theoretical predictions. Taken together, these results rigorously show the intrinsic dimension of data to be a crucial quantity affecting transformer scaling laws in both theory and practice.
Deep Neural Networks are Adaptive to Function Regularity and Data Distribution in Approximation and Estimation
Jun 08, 2024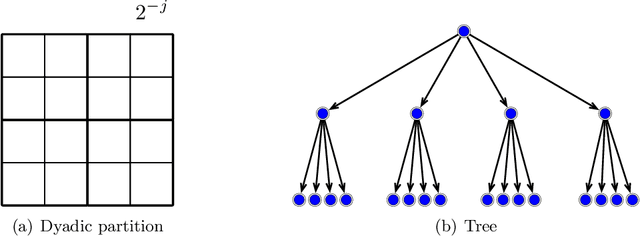
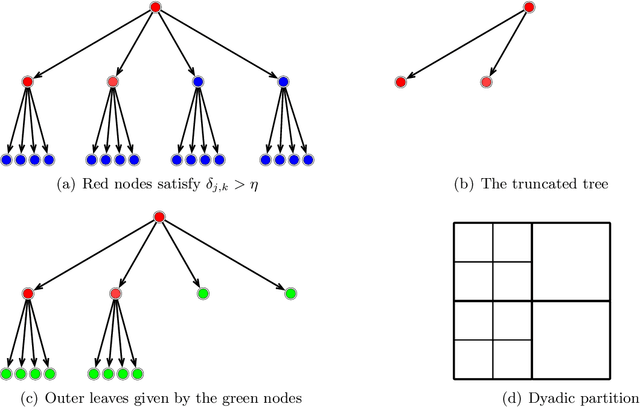
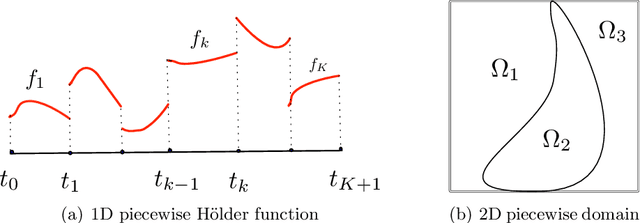
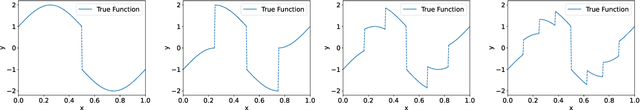
Abstract:Deep learning has exhibited remarkable results across diverse areas. To understand its success, substantial research has been directed towards its theoretical foundations. Nevertheless, the majority of these studies examine how well deep neural networks can model functions with uniform regularity. In this paper, we explore a different angle: how deep neural networks can adapt to different regularity in functions across different locations and scales and nonuniform data distributions. More precisely, we focus on a broad class of functions defined by nonlinear tree-based approximation. This class encompasses a range of function types, such as functions with uniform regularity and discontinuous functions. We develop nonparametric approximation and estimation theories for this function class using deep ReLU networks. Our results show that deep neural networks are adaptive to different regularity of functions and nonuniform data distributions at different locations and scales. We apply our results to several function classes, and derive the corresponding approximation and generalization errors. The validity of our results is demonstrated through numerical experiments.
Generalization Error Guaranteed Auto-Encoder-Based Nonlinear Model Reduction for Operator Learning
Jan 19, 2024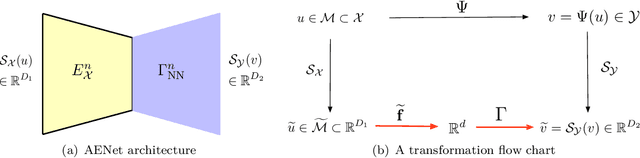
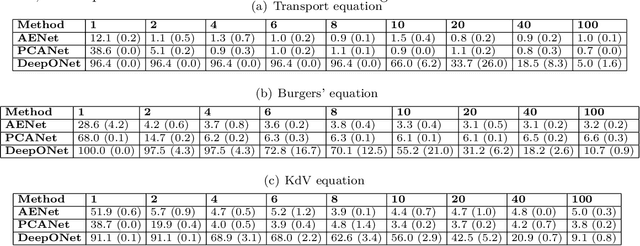
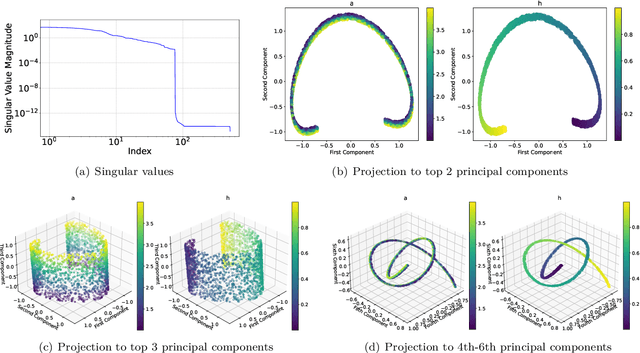
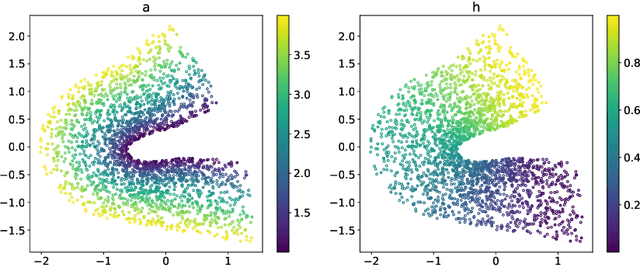
Abstract:Many physical processes in science and engineering are naturally represented by operators between infinite-dimensional function spaces. The problem of operator learning, in this context, seeks to extract these physical processes from empirical data, which is challenging due to the infinite or high dimensionality of data. An integral component in addressing this challenge is model reduction, which reduces both the data dimensionality and problem size. In this paper, we utilize low-dimensional nonlinear structures in model reduction by investigating Auto-Encoder-based Neural Network (AENet). AENet first learns the latent variables of the input data and then learns the transformation from these latent variables to corresponding output data. Our numerical experiments validate the ability of AENet to accurately learn the solution operator of nonlinear partial differential equations. Furthermore, we establish a mathematical and statistical estimation theory that analyzes the generalization error of AENet. Our theoretical framework shows that the sample complexity of training AENet is intricately tied to the intrinsic dimension of the modeled process, while also demonstrating the remarkable resilience of AENet to noise.
Effective Minkowski Dimension of Deep Nonparametric Regression: Function Approximation and Statistical Theories
Jun 26, 2023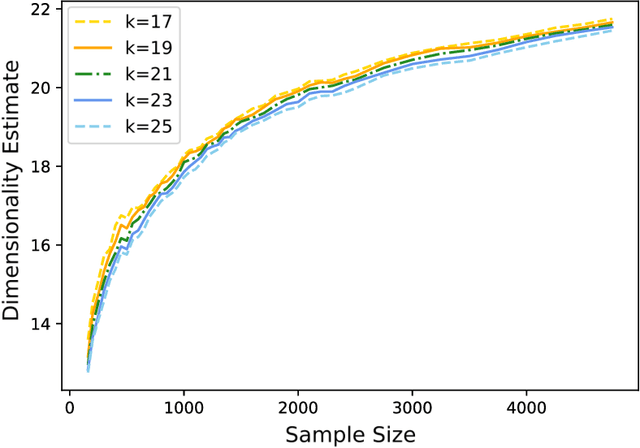
Abstract:Existing theories on deep nonparametric regression have shown that when the input data lie on a low-dimensional manifold, deep neural networks can adapt to the intrinsic data structures. In real world applications, such an assumption of data lying exactly on a low dimensional manifold is stringent. This paper introduces a relaxed assumption that the input data are concentrated around a subset of $\mathbb{R}^d$ denoted by $\mathcal{S}$, and the intrinsic dimension of $\mathcal{S}$ can be characterized by a new complexity notation -- effective Minkowski dimension. We prove that, the sample complexity of deep nonparametric regression only depends on the effective Minkowski dimension of $\mathcal{S}$ denoted by $p$. We further illustrate our theoretical findings by considering nonparametric regression with an anisotropic Gaussian random design $N(0,\Sigma)$, where $\Sigma$ is full rank. When the eigenvalues of $\Sigma$ have an exponential or polynomial decay, the effective Minkowski dimension of such an Gaussian random design is $p=\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{\log n})$ or $p=\mathcal{O}(n^\gamma)$, respectively, where $n$ is the sample size and $\gamma\in(0,1)$ is a small constant depending on the polynomial decay rate. Our theory shows that, when the manifold assumption does not hold, deep neural networks can still adapt to the effective Minkowski dimension of the data, and circumvent the curse of the ambient dimensionality for moderate sample sizes.
Deep Nonparametric Estimation of Intrinsic Data Structures by Chart Autoencoders: Generalization Error and Robustness
Mar 20, 2023
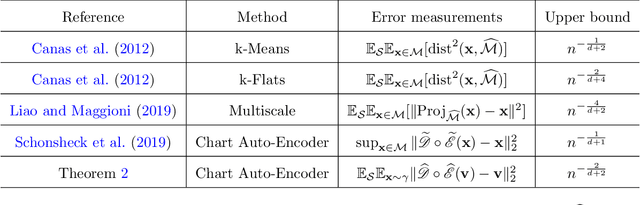
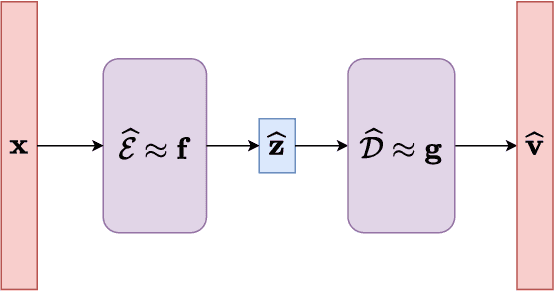
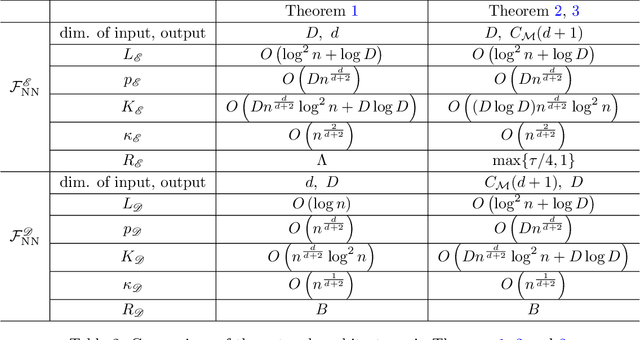
Abstract:Autoencoders have demonstrated remarkable success in learning low-dimensional latent features of high-dimensional data across various applications. Assuming that data are sampled near a low-dimensional manifold, we employ chart autoencoders, which encode data into low-dimensional latent features on a collection of charts, preserving the topology and geometry of the data manifold. Our paper establishes statistical guarantees on the generalization error of chart autoencoders, and we demonstrate their denoising capabilities by considering $n$ noisy training samples, along with their noise-free counterparts, on a $d$-dimensional manifold. By training autoencoders, we show that chart autoencoders can effectively denoise the input data with normal noise. We prove that, under proper network architectures, chart autoencoders achieve a squared generalization error in the order of $\displaystyle n^{-\frac{2}{d+2}}\log^4 n$, which depends on the intrinsic dimension of the manifold and only weakly depends on the ambient dimension and noise level. We further extend our theory on data with noise containing both normal and tangential components, where chart autoencoders still exhibit a denoising effect for the normal component. As a special case, our theory also applies to classical autoencoders, as long as the data manifold has a global parametrization. Our results provide a solid theoretical foundation for the effectiveness of autoencoders, which is further validated through several numerical experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge