Wenhao Deng
Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models for Missing Modality Completion in Product Catalogues
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Missing-modality information on e-commerce platforms, such as absent product images or textual descriptions, often arises from annotation errors or incomplete metadata, impairing both product presentation and downstream applications such as recommendation systems. Motivated by the multimodal generative capabilities of recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), this work investigates a fundamental yet underexplored question: can MLLMs generate missing modalities for products in e-commerce scenarios? We propose the Missing Modality Product Completion Benchmark (MMPCBench), which consists of two sub-benchmarks: a Content Quality Completion Benchmark and a Recommendation Benchmark. We further evaluate six state-of-the-art MLLMs from the Qwen2.5-VL and Gemma-3 model families across nine real-world e-commerce categories, focusing on image-to-text and text-to-image completion tasks. Experimental results show that while MLLMs can capture high-level semantics, they struggle with fine-grained word-level and pixel- or patch-level alignment. In addition, performance varies substantially across product categories and model scales, and we observe no trivial correlation between model size and performance, in contrast to trends commonly reported in mainstream benchmarks. We also explore Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to better align MLLMs with this task. GRPO improves image-to-text completion but does not yield gains for text-to-image completion. Overall, these findings expose the limitations of current MLLMs in real-world cross-modal generation and represent an early step toward more effective missing-modality product completion.
GenCP: Towards Generative Modeling Paradigm of Coupled Physics
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Real-world physical systems are inherently complex, often involving the coupling of multiple physics, making their simulation both highly valuable and challenging. Many mainstream approaches face challenges when dealing with decoupled data. Besides, they also suffer from low efficiency and fidelity in strongly coupled spatio-temporal physical systems. Here we propose GenCP, a novel and elegant generative paradigm for coupled multiphysics simulation. By formulating coupled-physics modeling as a probability modeling problem, our key innovation is to integrate probability density evolution in generative modeling with iterative multiphysics coupling, thereby enabling training on data from decoupled simulation and inferring coupled physics during sampling. We also utilize operator-splitting theory in the space of probability evolution to establish error controllability guarantees for this "conditional-to-joint" sampling scheme. We evaluate our paradigm on a synthetic setting and three challenging multi-physics scenarios to demonstrate both principled insight and superior application performance of GenCP. Code is available at this repo: github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/GenCP.
RealPDEBench: A Benchmark for Complex Physical Systems with Real-World Data
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Predicting the evolution of complex physical systems remains a central problem in science and engineering. Despite rapid progress in scientific Machine Learning (ML) models, a critical bottleneck is the lack of expensive real-world data, resulting in most current models being trained and validated on simulated data. Beyond limiting the development and evaluation of scientific ML, this gap also hinders research into essential tasks such as sim-to-real transfer. We introduce RealPDEBench, the first benchmark for scientific ML that integrates real-world measurements with paired numerical simulations. RealPDEBench consists of five datasets, three tasks, eight metrics, and ten baselines. We first present five real-world measured datasets with paired simulated datasets across different complex physical systems. We further define three tasks, which allow comparisons between real-world and simulated data, and facilitate the development of methods to bridge the two. Moreover, we design eight evaluation metrics, spanning data-oriented and physics-oriented metrics, and finally benchmark ten representative baselines, including state-of-the-art models, pretrained PDE foundation models, and a traditional method. Experiments reveal significant discrepancies between simulated and real-world data, while showing that pretraining with simulated data consistently improves both accuracy and convergence. In this work, we hope to provide insights from real-world data, advancing scientific ML toward bridging the sim-to-real gap and real-world deployment. Our benchmark, datasets, and instructions are available at https://realpdebench.github.io/.
From Uncertain to Safe: Conformal Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Models for Safe PDE Control
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:The application of deep learning for partial differential equation (PDE)-constrained control is gaining increasing attention. However, existing methods rarely consider safety requirements crucial in real-world applications. To address this limitation, we propose Safe Diffusion Models for PDE Control (SafeDiffCon), which introduce the uncertainty quantile as model uncertainty quantification to achieve optimal control under safety constraints through both post-training and inference phases. Firstly, our approach post-trains a pre-trained diffusion model to generate control sequences that better satisfy safety constraints while achieving improved control objectives via a reweighted diffusion loss, which incorporates the uncertainty quantile estimated using conformal prediction. Secondly, during inference, the diffusion model dynamically adjusts both its generation process and parameters through iterative guidance and fine-tuning, conditioned on control targets while simultaneously integrating the estimated uncertainty quantile. We evaluate SafeDiffCon on three control tasks: 1D Burgers' equation, 2D incompressible fluid, and controlled nuclear fusion problem. Results demonstrate that SafeDiffCon is the only method that satisfies all safety constraints, whereas other classical and deep learning baselines fail. Furthermore, while adhering to safety constraints, SafeDiffCon achieves the best control performance.
On the Guidance of Flow Matching
Feb 04, 2025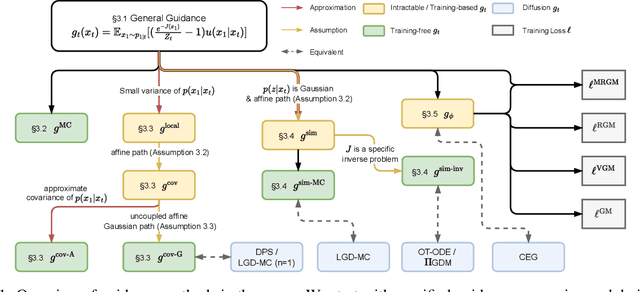
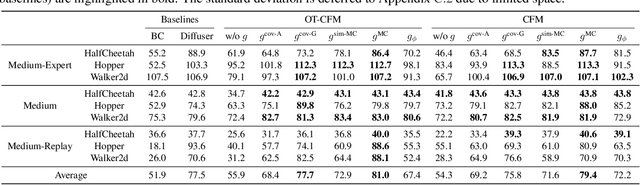
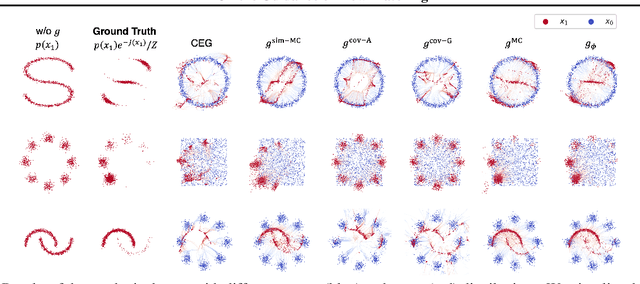
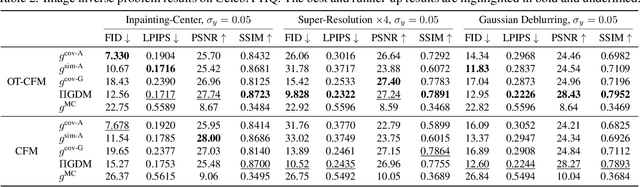
Abstract:Flow matching has shown state-of-the-art performance in various generative tasks, ranging from image generation to decision-making, where guided generation is pivotal. However, the guidance of flow matching is more general than and thus substantially different from that of its predecessor, diffusion models. Therefore, the challenge in guidance for general flow matching remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we propose the first framework of general guidance for flow matching. From this framework, we derive a family of guidance techniques that can be applied to general flow matching. These include a new training-free asymptotically exact guidance, novel training losses for training-based guidance, and two classes of approximate guidance that cover classical gradient guidance methods as special cases. We theoretically investigate these different methods to give a practical guideline for choosing suitable methods in different scenarios. Experiments on synthetic datasets, image inverse problems, and offline reinforcement learning demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed guidance methods and verify the correctness of our flow matching guidance framework. Code to reproduce the experiments can be found at https://github.com/AI4Science-WestlakeU/flow_guidance.
Exploring the Upper Limits of Text-Based Collaborative Filtering Using Large Language Models: Discoveries and Insights
May 19, 2023Abstract:Text-based collaborative filtering (TCF) has become the mainstream approach for text and news recommendation, utilizing text encoders, also known as language models (LMs), to represent items. However, existing TCF models primarily focus on using small or medium-sized LMs. It remains uncertain what impact replacing the item encoder with one of the largest and most powerful LMs, such as the 175-billion parameter GPT-3 model, would have on recommendation performance. Can we expect unprecedented results? To this end, we conduct an extensive series of experiments aimed at exploring the performance limits of the TCF paradigm. Specifically, we increase the size of item encoders from one hundred million to one hundred billion to reveal the scaling limits of the TCF paradigm. We then examine whether these extremely large LMs could enable a universal item representation for the recommendation task. Furthermore, we compare the performance of the TCF paradigm utilizing the most powerful LMs to the currently dominant ID embedding-based paradigm and investigate the transferability of this TCF paradigm. Finally, we compare TCF with the recently popularized prompt-based recommendation using ChatGPT. Our research findings have not only yielded positive results but also uncovered some surprising and previously unknown negative outcomes, which can inspire deeper reflection and innovative thinking regarding text-based recommender systems. Codes and datasets will be released for further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge