Vijay John
View-aware Cross-modal Distillation for Multi-view Action Recognition
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:The widespread use of multi-sensor systems has increased research in multi-view action recognition. While existing approaches in multi-view setups with fully overlapping sensors benefit from consistent view coverage, partially overlapping settings where actions are visible in only a subset of views remain underexplored. This challenge becomes more severe in real-world scenarios, as many systems provide only limited input modalities and rely on sequence-level annotations instead of dense frame-level labels. In this study, we propose View-aware Cross-modal Knowledge Distillation (ViCoKD), a framework that distills knowledge from a fully supervised multi-modal teacher to a modality- and annotation-limited student. ViCoKD employs a cross-modal adapter with cross-modal attention, allowing the student to exploit multi-modal correlations while operating with incomplete modalities. Moreover, we propose a View-aware Consistency module to address view misalignment, where the same action may appear differently or only partially across viewpoints. It enforces prediction alignment when the action is co-visible across views, guided by human-detection masks and confidence-weighted Jensen-Shannon divergence between their predicted class distributions. Experiments on the real-world MultiSensor-Home dataset show that ViCoKD consistently outperforms competitive distillation methods across multiple backbones and environments, delivering significant gains and surpassing the teacher model under limited conditions.
MultiSensor-Home: A Wide-area Multi-modal Multi-view Dataset for Action Recognition and Transformer-based Sensor Fusion
Apr 03, 2025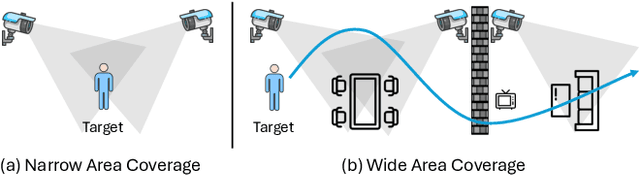
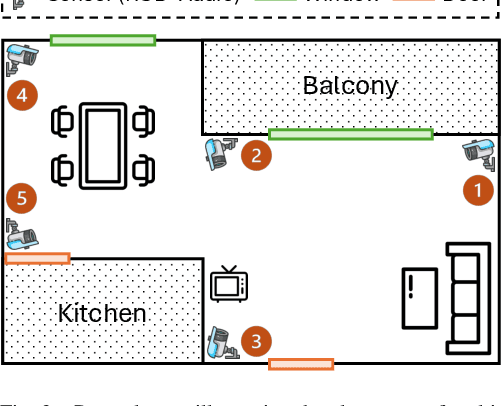

Abstract:Multi-modal multi-view action recognition is a rapidly growing field in computer vision, offering significant potential for applications in surveillance. However, current datasets often fail to address real-world challenges such as wide-area environmental conditions, asynchronous data streams, and the lack of frame-level annotations. Furthermore, existing methods face difficulties in effectively modeling inter-view relationships and enhancing spatial feature learning. In this study, we propose the Multi-modal Multi-view Transformer-based Sensor Fusion (MultiTSF) method and introduce the MultiSensor-Home dataset, a novel benchmark designed for comprehensive action recognition in home environments. The MultiSensor-Home dataset features untrimmed videos captured by distributed sensors, providing high-resolution RGB and audio data along with detailed multi-view frame-level action labels. The proposed MultiTSF method leverages a Transformer-based fusion mechanism to dynamically model inter-view relationships. Furthermore, the method also integrates a external human detection module to enhance spatial feature learning. Experiments on MultiSensor-Home and MM-Office datasets demonstrate the superiority of MultiTSF over the state-of-the-art methods. The quantitative and qualitative results highlight the effectiveness of the proposed method in advancing real-world multi-modal multi-view action recognition.
MultiTSF: Transformer-based Sensor Fusion for Human-Centric Multi-view and Multi-modal Action Recognition
Apr 03, 2025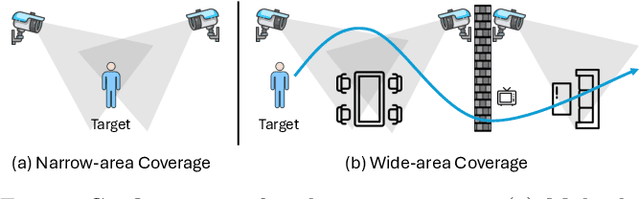

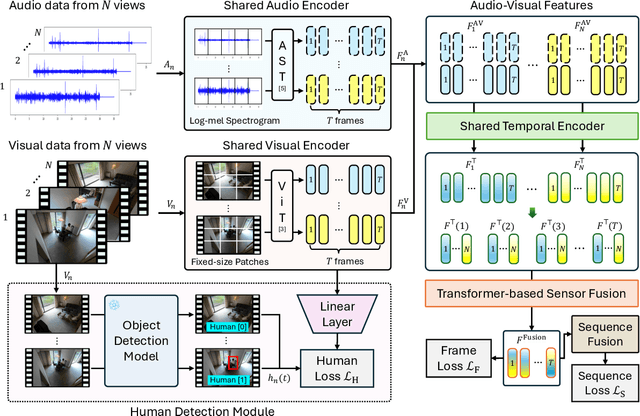
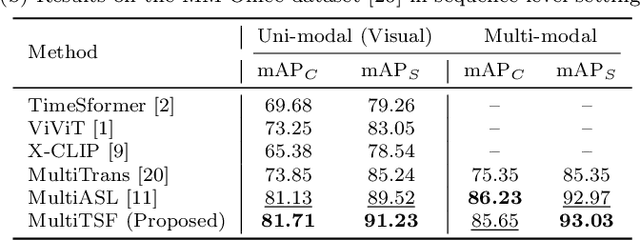
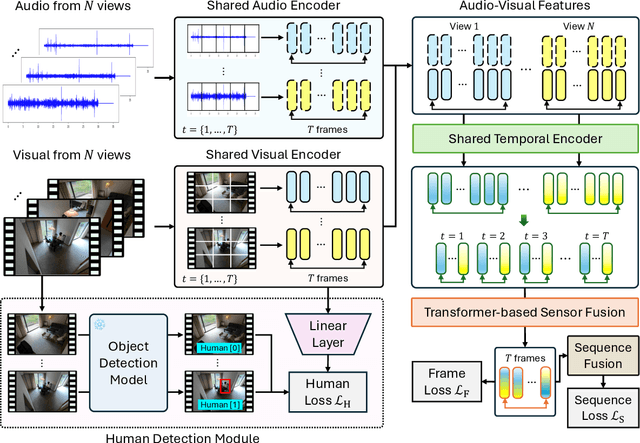
Abstract:Action recognition from multi-modal and multi-view observations holds significant potential for applications in surveillance, robotics, and smart environments. However, existing methods often fall short of addressing real-world challenges such as diverse environmental conditions, strict sensor synchronization, and the need for fine-grained annotations. In this study, we propose the Multi-modal Multi-view Transformer-based Sensor Fusion (MultiTSF). The proposed method leverages a Transformer-based to dynamically model inter-view relationships and capture temporal dependencies across multiple views. Additionally, we introduce a Human Detection Module to generate pseudo-ground-truth labels, enabling the model to prioritize frames containing human activity and enhance spatial feature learning. Comprehensive experiments conducted on our in-house MultiSensor-Home dataset and the existing MM-Office dataset demonstrate that MultiTSF outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both video sequence-level and frame-level action recognition settings.
Multi-View Video-Based Learning: Leveraging Weak Labels for Frame-Level Perception
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:For training a video-based action recognition model that accepts multi-view video, annotating frame-level labels is tedious and difficult. However, it is relatively easy to annotate sequence-level labels. This kind of coarse annotations are called as weak labels. However, training a multi-view video-based action recognition model with weak labels for frame-level perception is challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel learning framework, where the weak labels are first used to train a multi-view video-based base model, which is subsequently used for downstream frame-level perception tasks. The base model is trained to obtain individual latent embeddings for each view in the multi-view input. For training the model using the weak labels, we propose a novel latent loss function. We also propose a model that uses the view-specific latent embeddings for downstream frame-level action recognition and detection tasks. The proposed framework is evaluated using the MM Office dataset by comparing several baseline algorithms. The results show that the proposed base model is effectively trained using weak labels and the latent embeddings help the downstream models improve accuracy.
Principal Model Analysis Based on Partial Least Squares
Feb 06, 2019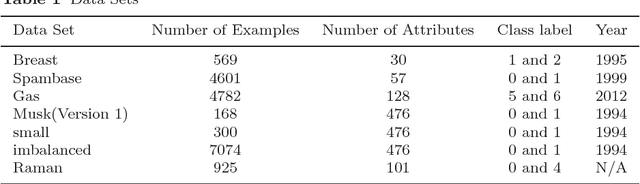
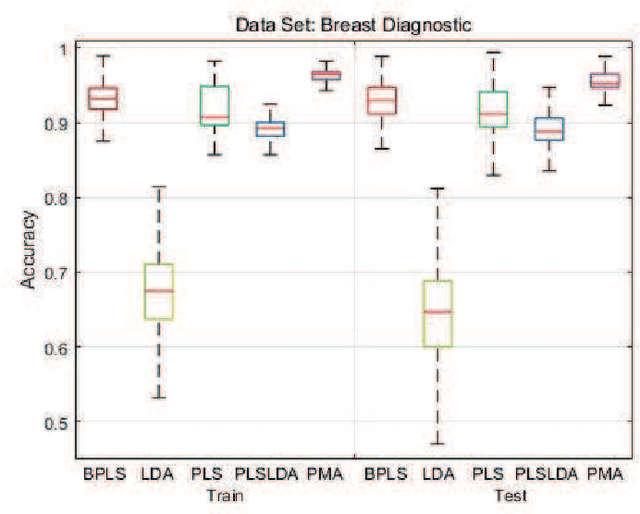
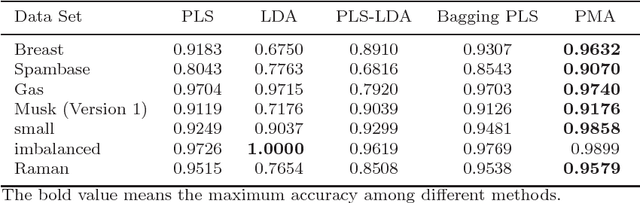
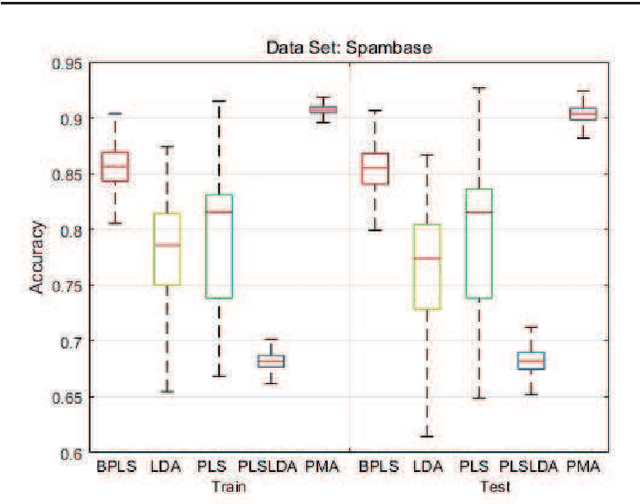
Abstract:Motivated by the Bagging Partial Least Squares (PLS) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) algorithms, we propose a Principal Model Analysis (PMA) method in this paper. In the proposed PMA algorithm, the PCA and the PLS are combined. In the method, multiple PLS models are trained on sub-training sets, derived from the original training set based on the random sampling with replacement method. The regression coefficients of all the sub-PLS models are fused in a joint regression coefficient matrix. The final projection direction is then estimated by performing the PCA on the joint regression coefficient matrix. The proposed PMA method is compared with other traditional dimension reduction methods, such as PLS, Bagging PLS, Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and PLS-LDA. Experimental results on six public datasets show that our proposed method can achieve better classification performance and is usually more stable.
IR2VI: Enhanced Night Environmental Perception by Unsupervised Thermal Image Translation
Jun 25, 2018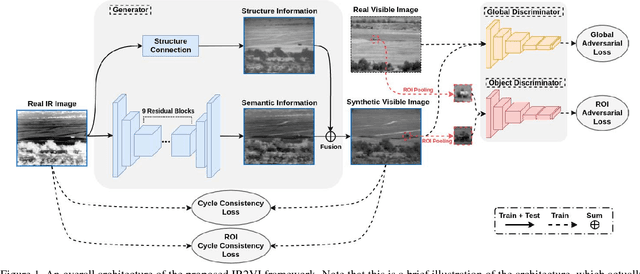

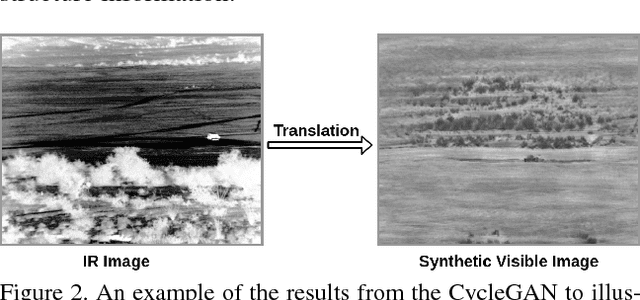
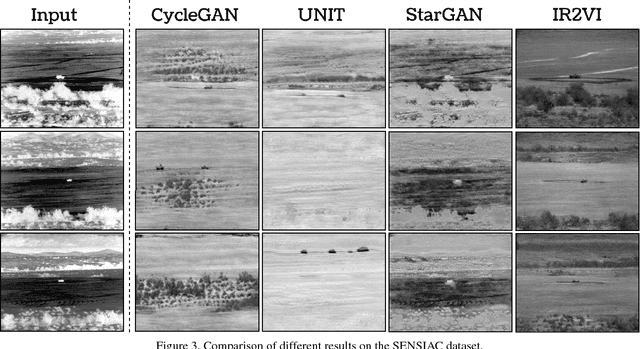
Abstract:Context enhancement is critical for night vision (NV) applications, especially for the dark night situation without any artificial lights. In this paper, we present the infrared-to-visual (IR2VI) algorithm, a novel unsupervised thermal-to-visible image translation framework based on generative adversarial networks (GANs). IR2VI is able to learn the intrinsic characteristics from VI images and integrate them into IR images. Since the existing unsupervised GAN-based image translation approaches face several challenges, such as incorrect mapping and lack of fine details, we propose a structure connection module and a region-of-interest (ROI) focal loss method to address the current limitations. Experimental results show the superiority of the IR2VI algorithm over baseline methods.
A Tutorial On Autonomous Vehicle Steering Controller Design, Simulation and Implementation
Mar 10, 2018



Abstract:In this tutorial, we detailed simple controllers for autonomous parking and path following for self-driving cars and provided practical methods for curvature computation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge