Valentin Macé
QDax: A Library for Quality-Diversity and Population-based Algorithms with Hardware Acceleration
Aug 07, 2023Abstract:QDax is an open-source library with a streamlined and modular API for Quality-Diversity (QD) optimization algorithms in Jax. The library serves as a versatile tool for optimization purposes, ranging from black-box optimization to continuous control. QDax offers implementations of popular QD, Neuroevolution, and Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms, supported by various examples. All the implementations can be just-in-time compiled with Jax, facilitating efficient execution across multiple accelerators, including GPUs and TPUs. These implementations effectively demonstrate the framework's flexibility and user-friendliness, easing experimentation for research purposes. Furthermore, the library is thoroughly documented and tested with 95\% coverage.
The Quality-Diversity Transformer: Generating Behavior-Conditioned Trajectories with Decision Transformers
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:In the context of neuroevolution, Quality-Diversity algorithms have proven effective in generating repertoires of diverse and efficient policies by relying on the definition of a behavior space. A natural goal induced by the creation of such a repertoire is trying to achieve behaviors on demand, which can be done by running the corresponding policy from the repertoire. However, in uncertain environments, two problems arise. First, policies can lack robustness and repeatability, meaning that multiple episodes under slightly different conditions often result in very different behaviors. Second, due to the discrete nature of the repertoire, solutions vary discontinuously. Here we present a new approach to achieve behavior-conditioned trajectory generation based on two mechanisms: First, MAP-Elites Low-Spread (ME-LS), which constrains the selection of solutions to those that are the most consistent in the behavior space. Second, the Quality-Diversity Transformer (QDT), a Transformer-based model conditioned on continuous behavior descriptors, which trains on a dataset generated by policies from a ME-LS repertoire and learns to autoregressively generate sequences of actions that achieve target behaviors. Results show that ME-LS produces consistent and robust policies, and that its combination with the QDT yields a single policy capable of achieving diverse behaviors on demand with high accuracy.
Assessing Quality-Diversity Neuro-Evolution Algorithms Performance in Hard Exploration Problems
Nov 24, 2022Abstract:A fascinating aspect of nature lies in its ability to produce a collection of organisms that are all high-performing in their niche. Quality-Diversity (QD) methods are evolutionary algorithms inspired by this observation, that obtained great results in many applications, from wing design to robot adaptation. Recently, several works demonstrated that these methods could be applied to perform neuro-evolution to solve control problems in large search spaces. In such problems, diversity can be a target in itself. Diversity can also be a way to enhance exploration in tasks exhibiting deceptive reward signals. While the first aspect has been studied in depth in the QD community, the latter remains scarcer in the literature. Exploration is at the heart of several domains trying to solve control problems such as Reinforcement Learning and QD methods are promising candidates to overcome the challenges associated. Therefore, we believe that standardized benchmarks exhibiting control problems in high dimension with exploration difficulties are of interest to the QD community. In this paper, we highlight three candidate benchmarks and explain why they appear relevant for systematic evaluation of QD algorithms. We also provide open-source implementations in Jax allowing practitioners to run fast and numerous experiments on few compute resources.
Neuroevolution is a Competitive Alternative to Reinforcement Learning for Skill Discovery
Oct 06, 2022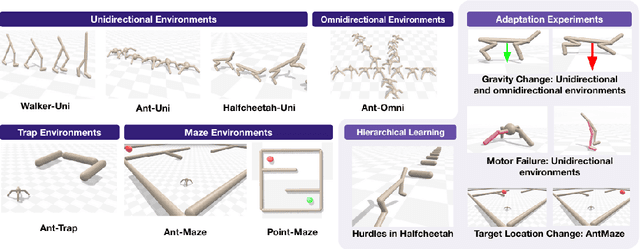
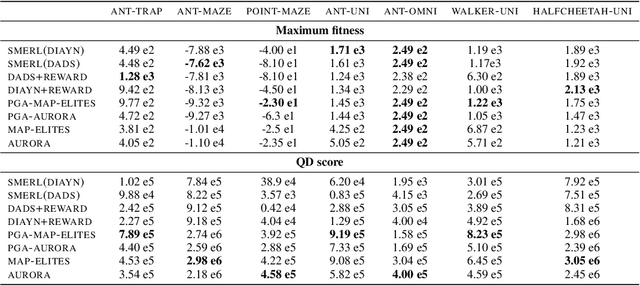
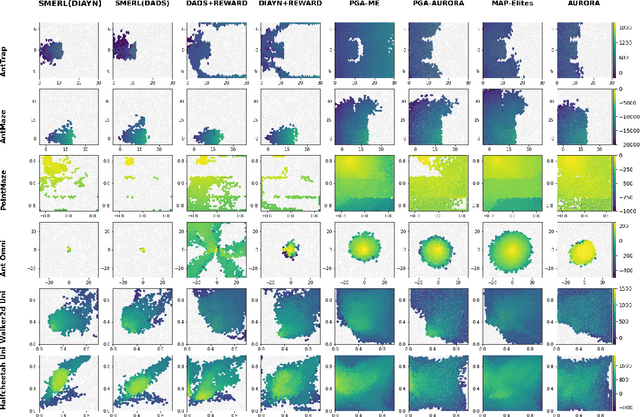
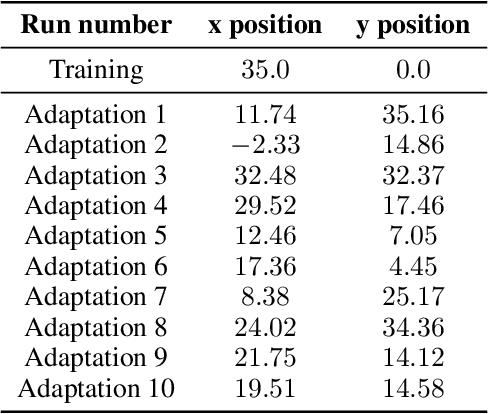
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for training neural policies to solve complex control tasks. However, these policies tend to be overfit to the exact specifications of the task and environment they were trained on, and thus do not perform well when conditions deviate slightly or when composed hierarchically to solve even more complex tasks. Recent work has shown that training a mixture of policies, as opposed to a single one, that are driven to explore different regions of the state-action space can address this shortcoming by generating a diverse set of behaviors, referred to as skills, that can be collectively used to great effect in adaptation tasks or for hierarchical planning. This is typically realized by including a diversity term - often derived from information theory - in the objective function optimized by RL. However these approaches often require careful hyperparameter tuning to be effective. In this work, we demonstrate that less widely-used neuroevolution methods, specifically Quality Diversity (QD), are a competitive alternative to information-theory-augmented RL for skill discovery. Through an extensive empirical evaluation comparing eight state-of-the-art methods on the basis of (i) metrics directly evaluating the skills' diversity, (ii) the skills' performance on adaptation tasks, and (iii) the skills' performance when used as primitives for hierarchical planning; QD methods are found to provide equal, and sometimes improved, performance whilst being less sensitive to hyperparameters and more scalable. As no single method is found to provide near-optimal performance across all environments, there is a rich scope for further research which we support by proposing future directions and providing optimized open-source implementations.
Using Whole Document Context in Neural Machine Translation
Oct 16, 2019
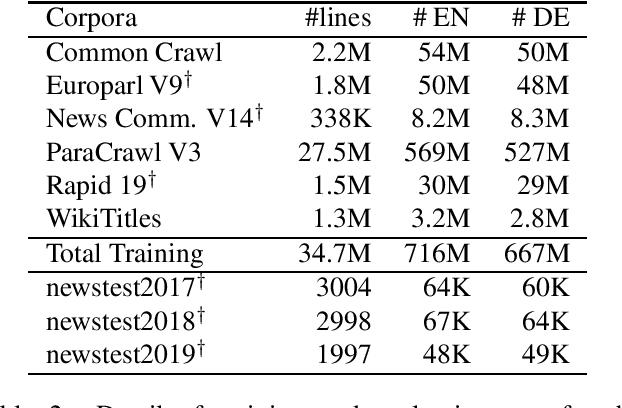
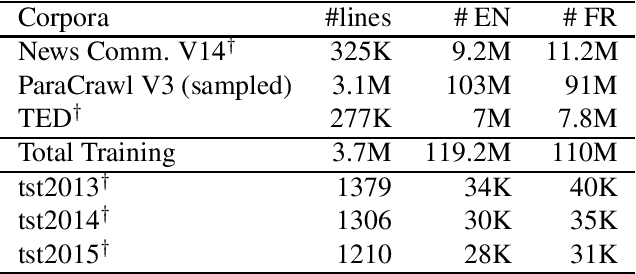
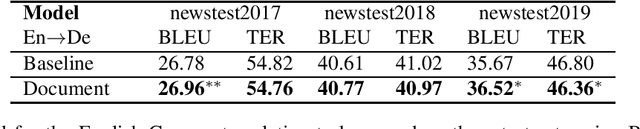
Abstract:In Machine Translation, considering the document as a whole can help to resolve ambiguities and inconsistencies. In this paper, we propose a simple yet promising approach to add contextual information in Neural Machine Translation. We present a method to add source context that capture the whole document with accurate boundaries, taking every word into account. We provide this additional information to a Transformer model and study the impact of our method on three language pairs. The proposed approach obtains promising results in the English-German, English-French and French-English document-level translation tasks. We observe interesting cross-sentential behaviors where the model learns to use document-level information to improve translation coherence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge