Tzu-Han Lin
AdaSearch: Balancing Parametric Knowledge and Search in Large Language Models via Reinforcement Learning
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Equipping large language models (LLMs) with search engines via reinforcement learning (RL) has emerged as an effective approach for building search agents. However, overreliance on search introduces unnecessary cost and risks exposure to noisy or malicious content, while relying solely on parametric knowledge risks hallucination. The central challenge is to develop agents that adaptively balance parametric knowledge with external search, invoking search only when necessary. Prior work mitigates search overuse by shaping rewards around the number of tool calls. However, these penalties require substantial reward engineering, provide ambiguous credit assignment, and can be exploited by agents that superficially reduce calls. Moreover, evaluating performance solely through call counts conflates necessary and unnecessary search, obscuring the measurement of true adaptive behavior. To address these limitations, we first quantify the self-knowledge awareness of existing search agents via an F1-based decision metric, revealing that methods such as Search-R1 often overlook readily available parametric knowledge. Motivated by these findings, we propose AdaSearch, a simple two-stage, outcome-driven RL framework that disentangles problem solving from the decision of whether to invoke search, and makes this decision process explicit and interpretable. This transparency is crucial for high-stakes domains such as finance and medical question answering, yet is largely neglected by prior approaches. Experiments across multiple model families and sizes demonstrate that AdaSearch substantially improves knowledge-boundary awareness, reduces unnecessary search calls, preserves strong task performance, and offers more transparent, interpretable decision behaviors.
When Silence Matters: The Impact of Irrelevant Audio on Text Reasoning in Large Audio-Language Models
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Large audio-language models (LALMs) unify speech and text processing, but their robustness in noisy real-world settings remains underexplored. We investigate how irrelevant audio, such as silence, synthetic noise, and environmental sounds, affects text reasoning tasks where audio is unnecessary. Across three text-based benchmarks, we find that even non-informative audio reduces accuracy and increases prediction volatility; the severity of interference scales with longer durations, higher amplitudes, and elevated decoding temperatures. Silence, often assumed neutral, destabilizes outputs as strongly as synthetic noise. While larger models show greater resilience, vulnerabilities persist across all evaluated systems. We further test mitigation strategies and find that prompting shows limited effectiveness, whereas self-consistency improves stability at the cost of increased computation. Our results reveal cross-modal interference as a key robustness challenge and highlight the need for efficient fusion strategies that preserve reasoning performance in the presence of irrelevant inputs.
Transferring Textual Preferences to Vision-Language Understanding through Model Merging
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) perform outstandingly across various multimodal tasks. However, their ability to evaluate generated content remains limited, and training vision-language reward models (VLRMs) with preference data is computationally expensive. This paper explores a training-free alternative by merging text-based reward models (RMs) with LVLMs to create VLRMs. Our approach shows that integrating these models leads to improved performance over LVLMs' scoring and text-based RMs, offering an efficient method for incorporating textual preferences into LVLMs.
DogeRM: Equipping Reward Models with Domain Knowledge through Model Merging
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) is a popular strategy for aligning large language models (LLMs) with desired behaviors. Reward modeling is a crucial step in RLHF. However, collecting paired preference data for training reward models is often costly and time-consuming, especially for domain-specific preferences requiring expert annotation. To address this challenge, we propose the \textbf{Do}main knowled\textbf{ge} merged \textbf{R}eward \textbf{M}odel (DogeRM), a novel framework that integrates domain-specific knowledge into a general reward model by model merging. The experiments demonstrate that DogeRM enhances performance across different benchmarks and provide a detailed analysis showcasing the effects of model merging, showing the great potential of facilitating model alignment.
Editing the Mind of Giants: An In-Depth Exploration of Pitfalls of Knowledge Editing in Large Language Models
Jun 03, 2024Abstract:Knowledge editing is a rising technique for efficiently updating factual knowledge in Large Language Models (LLMs) with minimal alteration of parameters. However, recent studies have identified concerning side effects, such as knowledge distortion and the deterioration of general abilities, that have emerged after editing. This survey presents a comprehensive study of these side effects, providing a unified view of the challenges associated with knowledge editing in LLMs. We discuss related works and summarize potential research directions to overcome these limitations. Our work highlights the limitations of current knowledge editing methods, emphasizing the need for deeper understanding of inner knowledge structures of LLMs and improved knowledge editing methods. To foster future research, we have released the complementary materials such as paper collection publicly at https://github.com/MiuLab/EditLLM-Survey
PEFT for Speech: Unveiling Optimal Placement, Merging Strategies, and Ensemble Techniques
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) is increasingly recognized as an effective method in speech processing. However, the optimal approach and the placement of PEFT methods remain inconclusive. Our study conducts extensive experiments to compare different PEFT methods and their layer-wise placement adapting Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS). We also explore the use of ensemble learning to leverage diverse PEFT strategies. The results reveal that DARTS does not outperform the baseline approach, which involves inserting the same PEFT method into all layers of a Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) model. In contrast, an ensemble learning approach, particularly one employing majority voting, demonstrates superior performance. Our statistical evidence indicates that different PEFT methods learn in varied ways. This variation might explain why the synergistic integration of various PEFT methods through ensemble learning can harness their unique learning capabilities more effectively compared to individual layer-wise optimization.
On the Utility of Self-supervised Models for Prosody-related Tasks
Oct 13, 2022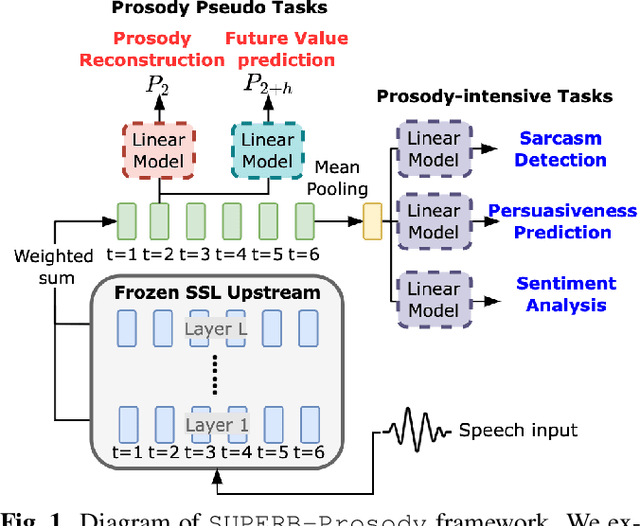
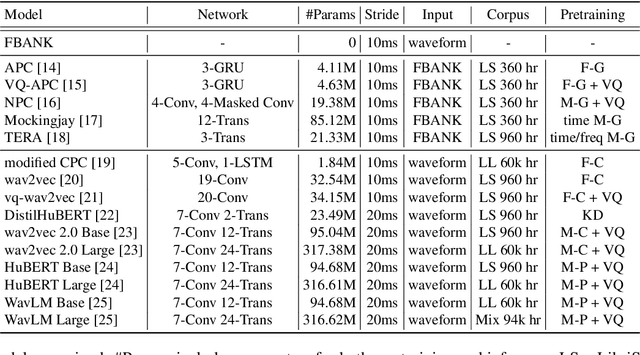
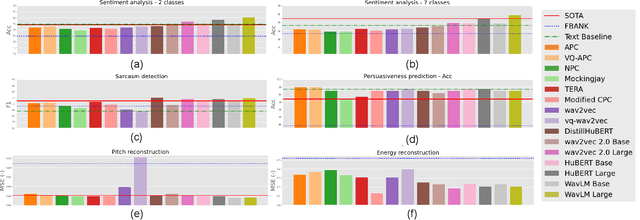
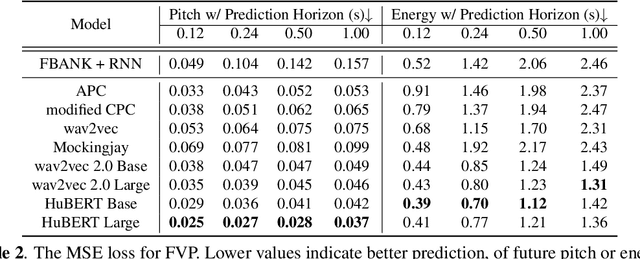
Abstract:Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) from speech data has produced models that have achieved remarkable performance in many tasks, and that are known to implicitly represent many aspects of information latently present in speech signals. However, relatively little is known about the suitability of such models for prosody-related tasks or the extent to which they encode prosodic information. We present a new evaluation framework, SUPERB-prosody, consisting of three prosody-related downstream tasks and two pseudo tasks. We find that 13 of the 15 SSL models outperformed the baseline on all the prosody-related tasks. We also show good performance on two pseudo tasks: prosody reconstruction and future prosody prediction. We further analyze the layerwise contributions of the SSL models. Overall we conclude that SSL speech models are highly effective for prosody-related tasks.
The Ability of Self-Supervised Speech Models for Audio Representations
Sep 28, 2022
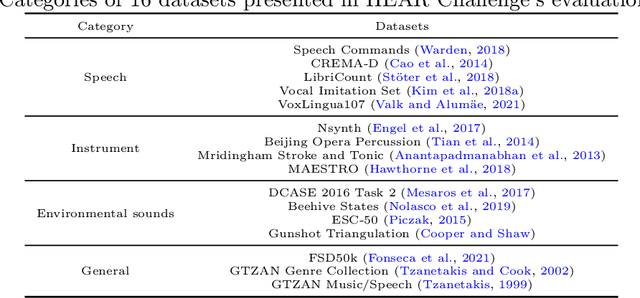
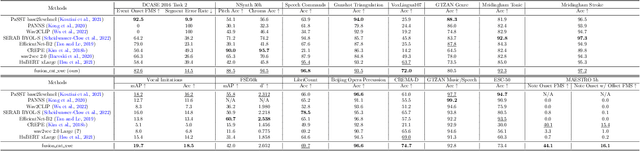
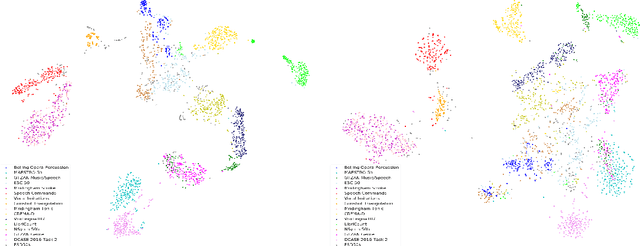
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) speech models have achieved unprecedented success in speech representation learning, but some questions regarding their representation ability remain unanswered. This paper addresses two of them: (1) Can SSL speech models deal with non-speech audio?; (2) Would different SSL speech models have insights into diverse aspects of audio features? To answer the two questions, we conduct extensive experiments on abundant speech and non-speech audio datasets to evaluate the representation ability of currently state-of-the-art SSL speech models, which are wav2vec 2.0 and HuBERT in this paper. These experiments are carried out during NeurIPS 2021 HEAR Challenge as a standard evaluation pipeline provided by competition officials. Results show that (1) SSL speech models could extract meaningful features of a wide range of non-speech audio, while they may also fail on certain types of datasets; (2) different SSL speech models have insights into different aspects of audio features. The two conclusions provide a foundation for the ensemble of representation models. We further propose an ensemble framework to fuse speech representation models' embeddings. Our framework outperforms state-of-the-art SSL speech/audio models and has generally superior performance on abundant datasets compared with other teams in HEAR Challenge. Our code is available at https://github.com/tony10101105/HEAR-2021-NeurIPS-Challenge -- NTU-GURA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge