Chi-Luen Feng
AV-SUPERB: A Multi-Task Evaluation Benchmark for Audio-Visual Representation Models
Sep 19, 2023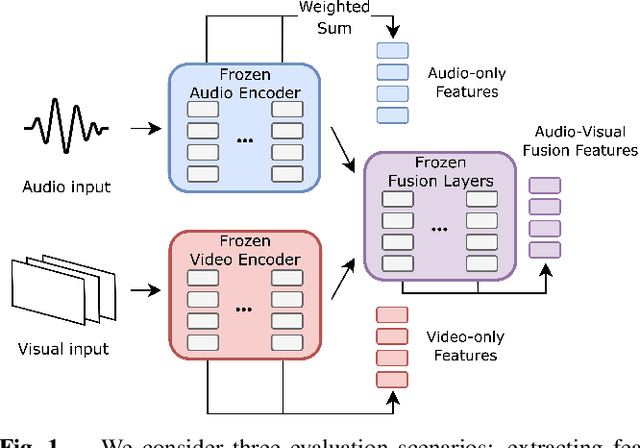
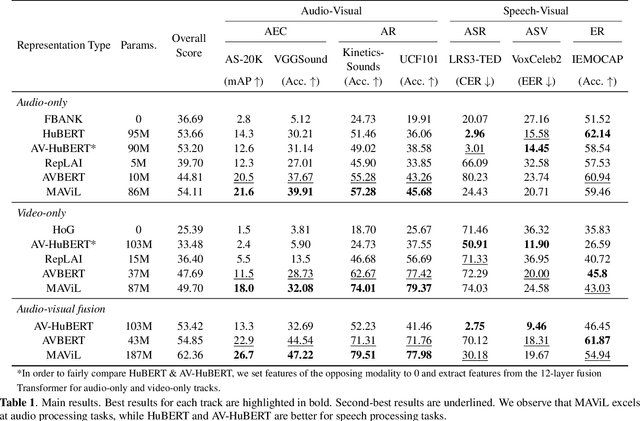
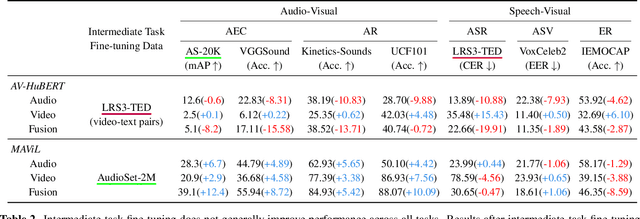
Abstract:Audio-visual representation learning aims to develop systems with human-like perception by utilizing correlation between auditory and visual information. However, current models often focus on a limited set of tasks, and generalization abilities of learned representations are unclear. To this end, we propose the AV-SUPERB benchmark that enables general-purpose evaluation of unimodal audio/visual and bimodal fusion representations on 7 datasets covering 5 audio-visual tasks in speech and audio processing. We evaluate 5 recent self-supervised models and show that none of these models generalize to all tasks, emphasizing the need for future study on improving universal model performance. In addition, we show that representations may be improved with intermediate-task fine-tuning and audio event classification with AudioSet serves as a strong intermediate task. We release our benchmark with evaluation code and a model submission platform to encourage further research in audio-visual learning.
On the Utility of Self-supervised Models for Prosody-related Tasks
Oct 13, 2022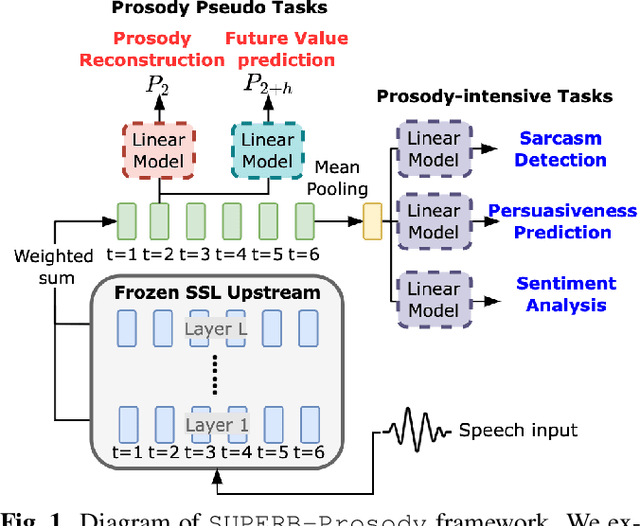
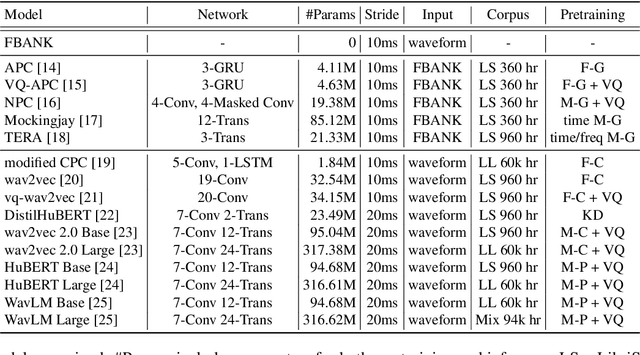
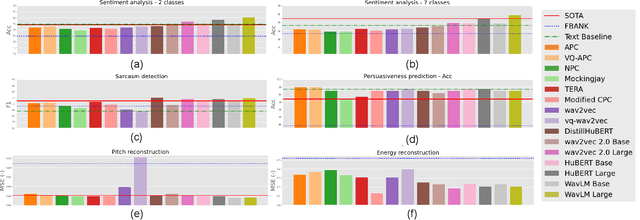
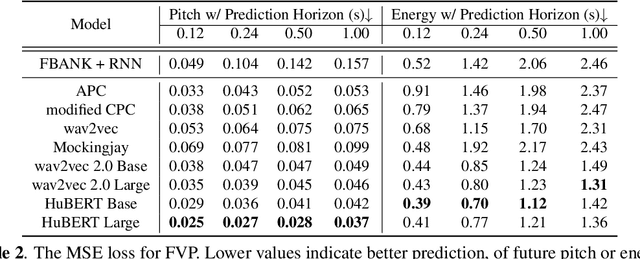
Abstract:Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) from speech data has produced models that have achieved remarkable performance in many tasks, and that are known to implicitly represent many aspects of information latently present in speech signals. However, relatively little is known about the suitability of such models for prosody-related tasks or the extent to which they encode prosodic information. We present a new evaluation framework, SUPERB-prosody, consisting of three prosody-related downstream tasks and two pseudo tasks. We find that 13 of the 15 SSL models outperformed the baseline on all the prosody-related tasks. We also show good performance on two pseudo tasks: prosody reconstruction and future prosody prediction. We further analyze the layerwise contributions of the SSL models. Overall we conclude that SSL speech models are highly effective for prosody-related tasks.
Silence is Sweeter Than Speech: Self-Supervised Model Using Silence to Store Speaker Information
May 08, 2022
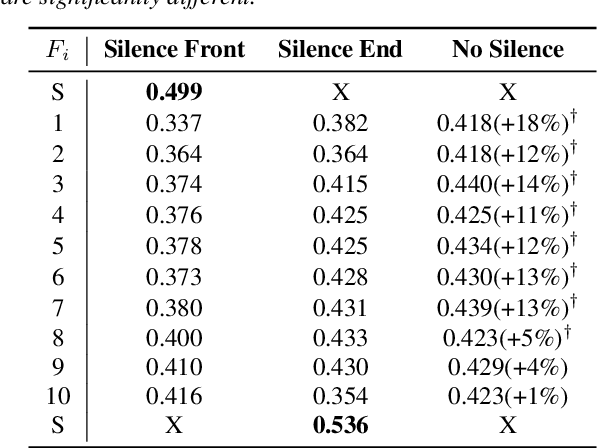

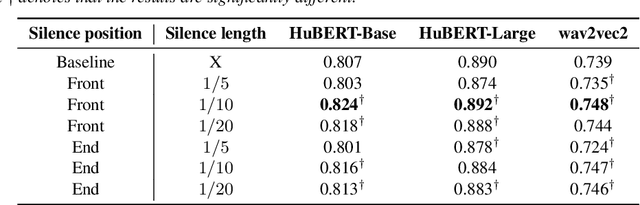
Abstract:Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has made great strides recently. SSL speech models achieve decent performance on a wide range of downstream tasks, suggesting that they extract different aspects of information from speech. However, how SSL models store various information in hidden representations without interfering is still poorly understood. Taking the recently successful SSL model, HuBERT, as an example, we explore how the SSL model processes and stores speaker information in the representation. We found that HuBERT stores speaker information in representations whose positions correspond to silences in a waveform. There are several pieces of evidence. (1) We find that the utterances with more silent parts in the waveforms have better Speaker Identification (SID) accuracy. (2) If we use the whole utterances for SID, the silence part always contributes more to the SID task. (3) If we only use the representation of a part of the utterance for SID, the silenced part has higher accuracy than the other parts. Our findings not only contribute to a better understanding of SSL models but also improve performance. By simply adding silence to the original waveform, HuBERT improved its accuracy on SID by nearly 2%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge