On the Utility of Self-supervised Models for Prosody-related Tasks
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2022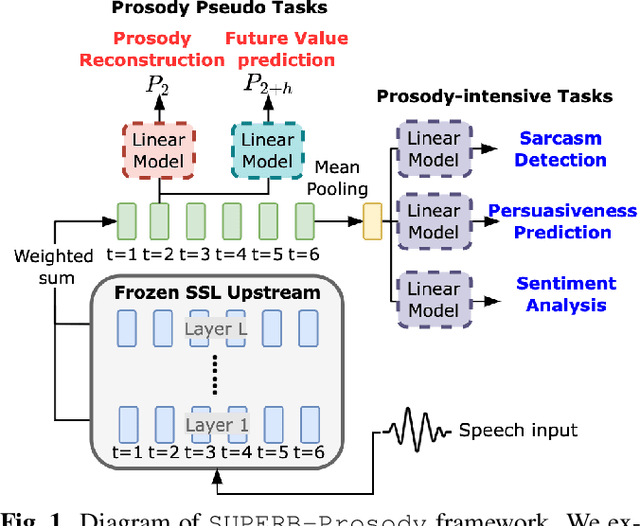
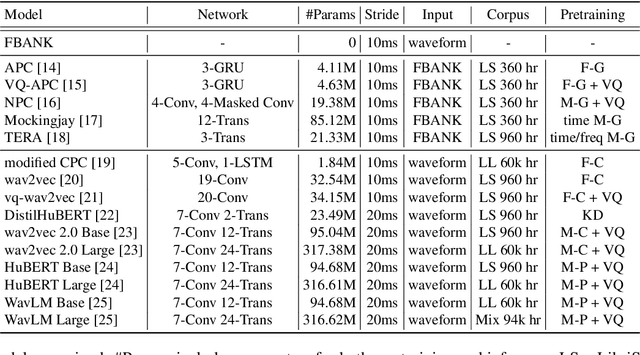
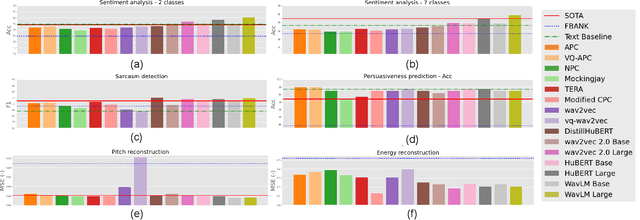
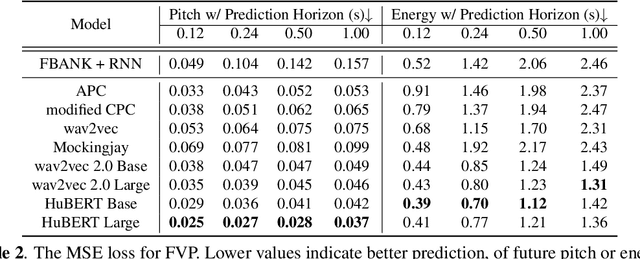
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) from speech data has produced models that have achieved remarkable performance in many tasks, and that are known to implicitly represent many aspects of information latently present in speech signals. However, relatively little is known about the suitability of such models for prosody-related tasks or the extent to which they encode prosodic information. We present a new evaluation framework, SUPERB-prosody, consisting of three prosody-related downstream tasks and two pseudo tasks. We find that 13 of the 15 SSL models outperformed the baseline on all the prosody-related tasks. We also show good performance on two pseudo tasks: prosody reconstruction and future prosody prediction. We further analyze the layerwise contributions of the SSL models. Overall we conclude that SSL speech models are highly effective for prosody-related tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge