Tomer Michaeli
Illumination Angular Spectrum Encoding for Controlling the Functionality of Diffractive Networks
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Diffractive neural networks have recently emerged as a promising framework for all-optical computing. However, these networks are typically trained for a single task, limiting their potential adoption in systems requiring multiple functionalities. Existing approaches to achieving multi-task functionality either modify the mechanical configuration of the network per task or use a different illumination wavelength or polarization state for each task. In this work, we propose a new control mechanism, which is based on the illumination's angular spectrum. Specifically, we shape the illumination using an amplitude mask that selectively controls its angular spectrum. We employ different illumination masks for achieving different network functionalities, so that the mask serves as a unique task encoder. Interestingly, we show that effective control can be achieved over a very narrow angular range, within the paraxial regime. We numerically illustrate the proposed approach by training a single diffractive network to perform multiple image-to-image translation tasks. In particular, we demonstrate translating handwritten digits into typeset digits of different values, and translating handwritten English letters into typeset numbers and typeset Greek letters, where the type of the output is determined by the illumination's angular components. As we show, the proposed framework can work under different coherence conditions, and can be combined with existing control strategies, such as different wavelengths. Our results establish the illumination angular spectrum as a powerful degree of freedom for controlling diffractive networks, enabling a scalable and versatile framework for multi-task all-optical computing.
MineTheGap: Automatic Mining of Biases in Text-to-Image Models
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Image (TTI) models generate images based on text prompts, which often leave certain aspects of the desired image ambiguous. When faced with these ambiguities, TTI models have been shown to exhibit biases in their interpretations. These biases can have societal impacts, e.g., when showing only a certain race for a stated occupation. They can also affect user experience when creating redundancy within a set of generated images instead of spanning diverse possibilities. Here, we introduce MineTheGap - a method for automatically mining prompts that cause a TTI model to generate biased outputs. Our method goes beyond merely detecting bias for a given prompt. Rather, it leverages a genetic algorithm to iteratively refine a pool of prompts, seeking for those that expose biases. This optimization process is driven by a novel bias score, which ranks biases according to their severity, as we validate on a dataset with known biases. For a given prompt, this score is obtained by comparing the distribution of generated images to the distribution of LLM-generated texts that constitute variations on the prompt. Code and examples are available on the project's webpage.
Turbo-DDCM: Fast and Flexible Zero-Shot Diffusion-Based Image Compression
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:While zero-shot diffusion-based compression methods have seen significant progress in recent years, they remain notoriously slow and computationally demanding. This paper presents an efficient zero-shot diffusion-based compression method that runs substantially faster than existing methods, while maintaining performance that is on par with the state-of-the-art techniques. Our method builds upon the recently proposed Denoising Diffusion Codebook Models (DDCMs) compression scheme. Specifically, DDCM compresses an image by sequentially choosing the diffusion noise vectors from reproducible random codebooks, guiding the denoiser's output to reconstruct the target image. We modify this framework with Turbo-DDCM, which efficiently combines a large number of noise vectors at each denoising step, thereby significantly reducing the number of required denoising operations. This modification is also coupled with an improved encoding protocol. Furthermore, we introduce two flexible variants of Turbo-DDCM, a priority-aware variant that prioritizes user-specified regions and a distortion-controlled variant that compresses an image based on a target PSNR rather than a target BPP. Comprehensive experiments position Turbo-DDCM as a compelling, practical, and flexible image compression scheme.
When Diffusion Models Memorize: Inductive Biases in Probability Flow of Minimum-Norm Shallow Neural Nets
Jun 23, 2025Abstract:While diffusion models generate high-quality images via probability flow, the theoretical understanding of this process remains incomplete. A key question is when probability flow converges to training samples or more general points on the data manifold. We analyze this by studying the probability flow of shallow ReLU neural network denoisers trained with minimal $\ell^2$ norm. For intuition, we introduce a simpler score flow and show that for orthogonal datasets, both flows follow similar trajectories, converging to a training point or a sum of training points. However, early stopping by the diffusion time scheduler allows probability flow to reach more general manifold points. This reflects the tendency of diffusion models to both memorize training samples and generate novel points that combine aspects of multiple samples, motivating our study of such behavior in simplified settings. We extend these results to obtuse simplex data and, through simulations in the orthogonal case, confirm that probability flow converges to a training point, a sum of training points, or a manifold point. Moreover, memorization decreases when the number of training samples grows, as fewer samples accumulate near training points.
InvFussion: Bridging Supervised and Zero-shot Diffusion for Inverse Problems
Apr 02, 2025
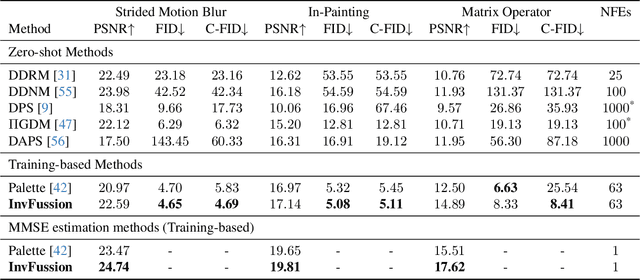

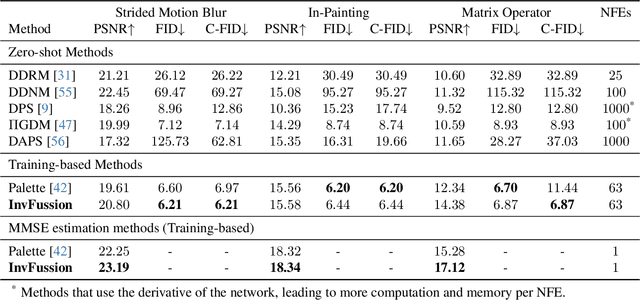
Abstract:Diffusion Models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling inverse problems, offering high-quality posterior-sampling-based solutions. Despite significant advances, a fundamental trade-off persists, regarding the way the conditioned synthesis is employed: Training-based methods achieve high quality results, while zero-shot approaches trade this with flexibility. This work introduces a framework that combines the best of both worlds -- the strong performance of supervised approaches and the flexibility of zero-shot methods. This is achieved through a novel architectural design that seamlessly integrates the degradation operator directly into the denoiser. In each block, our proposed architecture applies the degradation operator on the network activations and conditions the output using the attention mechanism, enabling adaptation to diverse degradation scenarios while maintaining high performance. Our work demonstrates the versatility of the proposed architecture, operating as a general MMSE estimator, a posterior sampler, or a Neural Posterior Principal Component estimator. This flexibility enables a wide range of downstream tasks, highlighting the broad applicability of our framework. The proposed modification of the denoiser network offers a versatile, accurate, and computationally efficient solution, demonstrating the advantages of dedicated network architectures for complex inverse problems. Experimental results on the FFHQ and ImageNet datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art posterior-sampling performance, surpassing both training-based and zero-shot alternatives.
Compressed Image Generation with Denoising Diffusion Codebook Models
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We present a novel generative approach based on Denoising Diffusion Models (DDMs), which produces high-quality image samples along with their losslessly compressed bit-stream representations. This is obtained by replacing the standard Gaussian noise sampling in the reverse diffusion with a selection of noise samples from pre-defined codebooks of fixed iid Gaussian vectors. Surprisingly, we find that our method, termed Denoising Diffusion Codebook Model (DDCM), retains sample quality and diversity of standard DDMs, even for extremely small codebooks. We leverage DDCM and pick the noises from the codebooks that best match a given image, converting our generative model into a highly effective lossy image codec achieving state-of-the-art perceptual image compression results. More generally, by setting other noise selections rules, we extend our compression method to any conditional image generation task (e.g., image restoration), where the generated images are produced jointly with their condensed bit-stream representations. Our work is accompanied by a mathematical interpretation of the proposed compressed conditional generation schemes, establishing a connection with score-based approximations of posterior samplers for the tasks considered.
TokenVerse: Versatile Multi-concept Personalization in Token Modulation Space
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:We present TokenVerse -- a method for multi-concept personalization, leveraging a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model. Our framework can disentangle complex visual elements and attributes from as little as a single image, while enabling seamless plug-and-play generation of combinations of concepts extracted from multiple images. As opposed to existing works, TokenVerse can handle multiple images with multiple concepts each, and supports a wide-range of concepts, including objects, accessories, materials, pose, and lighting. Our work exploits a DiT-based text-to-image model, in which the input text affects the generation through both attention and modulation (shift and scale). We observe that the modulation space is semantic and enables localized control over complex concepts. Building on this insight, we devise an optimization-based framework that takes as input an image and a text description, and finds for each word a distinct direction in the modulation space. These directions can then be used to generate new images that combine the learned concepts in a desired configuration. We demonstrate the effectiveness of TokenVerse in challenging personalization settings, and showcase its advantages over existing methods. project's webpage in https://token-verse.github.io/
FlowEdit: Inversion-Free Text-Based Editing Using Pre-Trained Flow Models
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Editing real images using a pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) diffusion/flow model often involves inverting the image into its corresponding noise map. However, inversion by itself is typically insufficient for obtaining satisfactory results, and therefore many methods additionally intervene in the sampling process. Such methods achieve improved results but are not seamlessly transferable between model architectures. Here, we introduce FlowEdit, a text-based editing method for pre-trained T2I flow models, which is inversion-free, optimization-free and model agnostic. Our method constructs an ODE that directly maps between the source and target distributions (corresponding to the source and target text prompts) and achieves a lower transport cost than the inversion approach. This leads to state-of-the-art results, as we illustrate with Stable Diffusion 3 and FLUX. Code and examples are available on the project's webpage.
Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow: Towards Minimum MSE Photo-Realistic Image Restoration
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Photo-realistic image restoration algorithms are typically evaluated by distortion measures (e.g., PSNR, SSIM) and by perceptual quality measures (e.g., FID, NIQE), where the desire is to attain the lowest possible distortion without compromising on perceptual quality. To achieve this goal, current methods typically attempt to sample from the posterior distribution, or to optimize a weighted sum of a distortion loss (e.g., MSE) and a perceptual quality loss (e.g., GAN). Unlike previous works, this paper is concerned specifically with the optimal estimator that minimizes the MSE under a constraint of perfect perceptual index, namely where the distribution of the reconstructed images is equal to that of the ground-truth ones. A recent theoretical result shows that such an estimator can be constructed by optimally transporting the posterior mean prediction (MMSE estimate) to the distribution of the ground-truth images. Inspired by this result, we introduce Posterior-Mean Rectified Flow (PMRF), a simple yet highly effective algorithm that approximates this optimal estimator. In particular, PMRF first predicts the posterior mean, and then transports the result to a high-quality image using a rectified flow model that approximates the desired optimal transport map. We investigate the theoretical utility of PMRF and demonstrate that it consistently outperforms previous methods on a variety of image restoration tasks.
Coherence Awareness in Diffractive Neural Networks
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:Diffractive neural networks hold great promise for applications requiring intensive computational processing. Considerable attention has focused on diffractive networks for either spatially coherent or spatially incoherent illumination. Here we illustrate that, as opposed to imaging systems, in diffractive networks the degree of spatial coherence has a dramatic effect. In particular, we show that when the spatial coherence length on the object is comparable to the minimal feature size preserved by the optical system, neither the incoherent nor the coherent extremes serve as acceptable approximations. Importantly, this situation is inherent to many settings involving active illumination, including reflected light microscopy, autonomous vehicles and smartphones. Following this observation, we propose a general framework for training diffractive networks for any specified degree of spatial and temporal coherence, supporting all types of linear and nonlinear layers. Using our method, we numerically optimize networks for image classification, and thoroughly investigate their performance dependence on the illumination coherence properties. We further introduce the concept of coherence-blind networks, which have enhanced resilience to changes in illumination conditions. Our findings serve as a steppingstone toward adopting all-optical neural networks in real-world applications, leveraging nothing but natural light.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge