Tomer D. Ullman
In-Context Learning Dynamics with Random Binary Sequences
Oct 26, 2023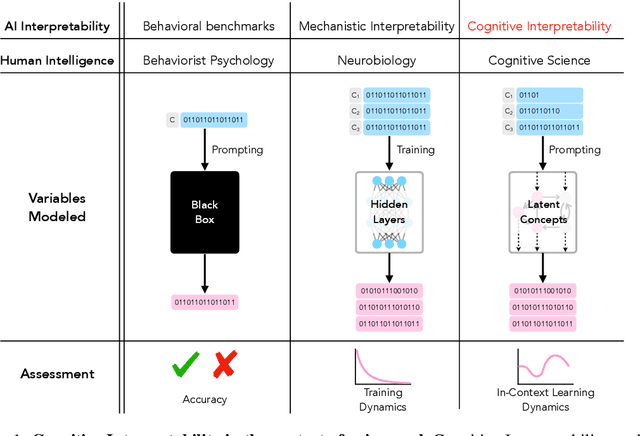
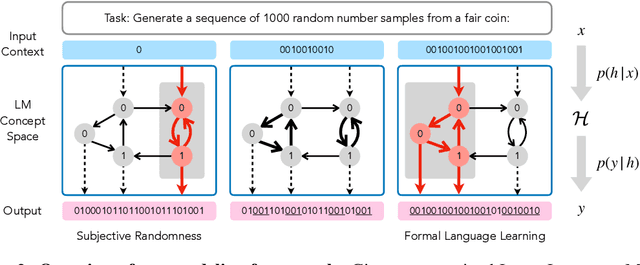
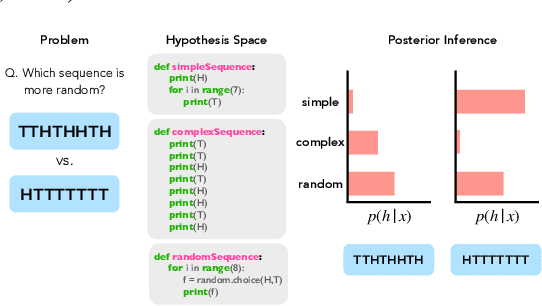
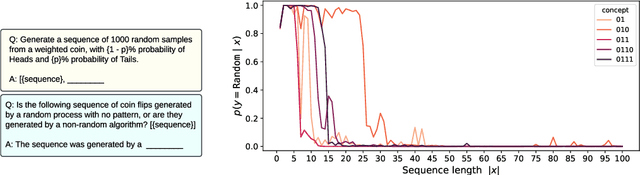
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) trained on huge corpora of text datasets demonstrate complex, emergent capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art performance on tasks they were not explicitly trained for. The precise nature of LLM capabilities is often mysterious, and different prompts can elicit different capabilities through in-context learning. We propose a Cognitive Interpretability framework that enables us to analyze in-context learning dynamics to understand latent concepts in LLMs underlying behavioral patterns. This provides a more nuanced understanding than success-or-failure evaluation benchmarks, but does not require observing internal activations as a mechanistic interpretation of circuits would. Inspired by the cognitive science of human randomness perception, we use random binary sequences as context and study dynamics of in-context learning by manipulating properties of context data, such as sequence length. In the latest GPT-3.5+ models, we find emergent abilities to generate pseudo-random numbers and learn basic formal languages, with striking in-context learning dynamics where model outputs transition sharply from pseudo-random behaviors to deterministic repetition.
Temporal and Object Quantification Networks
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:We present Temporal and Object Quantification Networks (TOQ-Nets), a new class of neuro-symbolic networks with a structural bias that enables them to learn to recognize complex relational-temporal events. This is done by including reasoning layers that implement finite-domain quantification over objects and time. The structure allows them to generalize directly to input instances with varying numbers of objects in temporal sequences of varying lengths. We evaluate TOQ-Nets on input domains that require recognizing event-types in terms of complex temporal relational patterns. We demonstrate that TOQ-Nets can generalize from small amounts of data to scenarios containing more objects than were present during training and to temporal warpings of input sequences.
AGENT: A Benchmark for Core Psychological Reasoning
Feb 25, 2021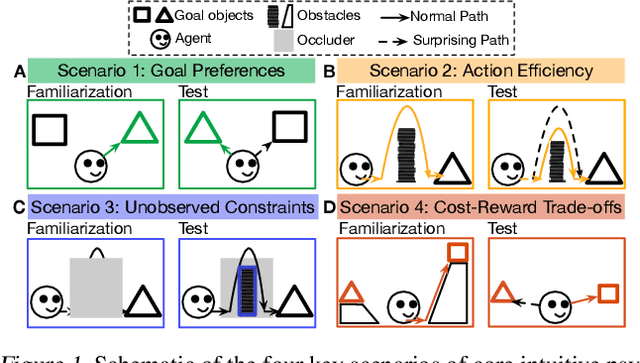

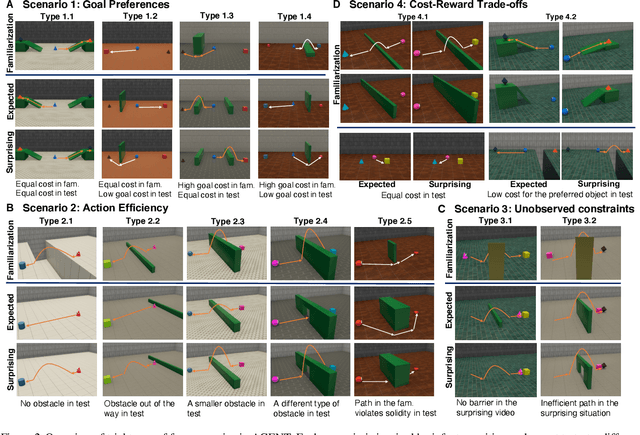
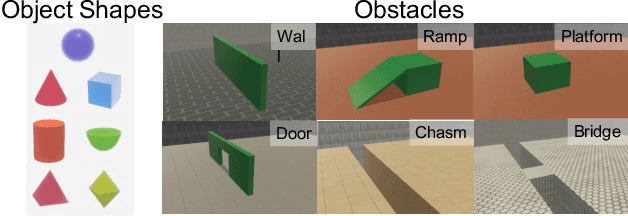
Abstract:For machine agents to successfully interact with humans in real-world settings, they will need to develop an understanding of human mental life. Intuitive psychology, the ability to reason about hidden mental variables that drive observable actions, comes naturally to people: even pre-verbal infants can tell agents from objects, expecting agents to act efficiently to achieve goals given constraints. Despite recent interest in machine agents that reason about other agents, it is not clear if such agents learn or hold the core psychology principles that drive human reasoning. Inspired by cognitive development studies on intuitive psychology, we present a benchmark consisting of a large dataset of procedurally generated 3D animations, AGENT (Action, Goal, Efficiency, coNstraint, uTility), structured around four scenarios (goal preferences, action efficiency, unobserved constraints, and cost-reward trade-offs) that probe key concepts of core intuitive psychology. We validate AGENT with human-ratings, propose an evaluation protocol emphasizing generalization, and compare two strong baselines built on Bayesian inverse planning and a Theory of Mind neural network. Our results suggest that to pass the designed tests of core intuitive psychology at human levels, a model must acquire or have built-in representations of how agents plan, combining utility computations and core knowledge of objects and physics.
Building Machines That Learn and Think Like People
Nov 02, 2016



Abstract:Recent progress in artificial intelligence (AI) has renewed interest in building systems that learn and think like people. Many advances have come from using deep neural networks trained end-to-end in tasks such as object recognition, video games, and board games, achieving performance that equals or even beats humans in some respects. Despite their biological inspiration and performance achievements, these systems differ from human intelligence in crucial ways. We review progress in cognitive science suggesting that truly human-like learning and thinking machines will have to reach beyond current engineering trends in both what they learn, and how they learn it. Specifically, we argue that these machines should (a) build causal models of the world that support explanation and understanding, rather than merely solving pattern recognition problems; (b) ground learning in intuitive theories of physics and psychology, to support and enrich the knowledge that is learned; and (c) harness compositionality and learning-to-learn to rapidly acquire and generalize knowledge to new tasks and situations. We suggest concrete challenges and promising routes towards these goals that can combine the strengths of recent neural network advances with more structured cognitive models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge