Tomasz Pieciak
Federated Learning: A new frontier in the exploration of multi-institutional medical imaging data
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Artificial intelligence has transformed the perspective of medical imaging, leading to a genuine technological revolution in modern computer-assisted healthcare systems. However, ubiquitously featured deep learning (DL) systems require access to a considerable amount of data, facilitating proper knowledge extraction and generalization. Admission to such extensive resources may be hindered due to the time and effort required to convey ethical agreements, set up and carry the acquisition procedures through, and manage the datasets adequately with a particular emphasis on proper anonymization. One of the pivotal challenges in the DL field is data integration from various sources acquired using different hardware vendors, diverse acquisition protocols, experimental setups, and even inter-operator variabilities. In this paper, we review the federated learning (FL) concept that fosters the integration of large-scale heterogeneous datasets from multiple institutions in training DL models. In contrast to a centralized approach, the decentralized FL procedure promotes training DL models while preserving data privacy at each institution involved. We formulate the FL principle and comprehensively review general and dedicated medical imaging aggregation and learning algorithms, enabling the generation of a globally generalized model. We meticulously go through the challenges in constructing FL-based systems, such as data heterogeneity across the institutions, resilience to potential attacks on data privacy, and the variability in computational and communication resources among the entangled sites that might induce efficiency issues of the entire system. Finally, we explore the up-to-date open frameworks for rapid FL-based algorithm prototyping and shed light on future directions in this intensively growing field.
Multi-compartment diffusion-relaxation MR signal representation in the spherical 3D-SHORE basis
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Modelling the diffusion-relaxation magnetic resonance (MR) signal obtained from multi-parametric sequences has recently gained immense interest in the community due to new techniques significantly reducing data acquisition time. A preferred approach for examining the diffusion-relaxation MR data is to follow the continuum modelling principle that employs kernels to represent the tissue features, such as the relaxations or diffusion properties. However, constructing reasonable dictionaries with predefined signal components depends on the sampling density of model parameter space, thus leading to a geometrical increase in the number of atoms per extra tissue parameter considered in the model. That makes estimating the contributions from each atom in the signal challenging, especially considering diffusion features beyond the mono-exponential decay. This paper presents a new Multi-Compartment diffusion-relaxation MR signal representation based on the Simple Harmonic Oscillator-based Reconstruction and Estimation (MC-SHORE) representation, compatible with scattered acquisitions. The proposed technique imposes sparsity constraint on the solution via the $\ell_1$ norm and enables the estimation of the microstructural measures, such as the return-to-the-origin probability, and the orientation distribution function, depending on the compartments considered in a single voxel. The procedure has been verified with in silico and in vivo data and enabled the approximation of the diffusion-relaxation MR signal more accurately than single-compartment non-Gaussian representations and multi-compartment mono-exponential decay techniques, maintaining a low number of atoms in the dictionary. Ultimately, the MC-SHORE procedure allows for separating intra-/extra-axonal and free water contributions from the signal, thus reducing the partial volume effect observable in the boundaries of the tissues.
MICCAI-CDMRI 2023 QuantConn Challenge Findings on Achieving Robust Quantitative Connectivity through Harmonized Preprocessing of Diffusion MRI
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:White matter alterations are increasingly implicated in neurological diseases and their progression. International-scale studies use diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) to qualitatively identify changes in white matter microstructure and connectivity. Yet, quantitative analysis of DW-MRI data is hindered by inconsistencies stemming from varying acquisition protocols. There is a pressing need to harmonize the preprocessing of DW-MRI datasets to ensure the derivation of robust quantitative diffusion metrics across acquisitions. In the MICCAI-CDMRI 2023 QuantConn challenge, participants were provided raw data from the same individuals collected on the same scanner but with two different acquisitions and tasked with preprocessing the DW-MRI to minimize acquisition differences while retaining biological variation. Submissions are evaluated on the reproducibility and comparability of cross-acquisition bundle-wise microstructure measures, bundle shape features, and connectomics. The key innovations of the QuantConn challenge are that (1) we assess bundles and tractography in the context of harmonization for the first time, (2) we assess connectomics in the context of harmonization for the first time, and (3) we have 10x additional subjects over prior harmonization challenge, MUSHAC and 100x over SuperMUDI. We find that bundle surface area, fractional anisotropy, connectome assortativity, betweenness centrality, edge count, modularity, nodal strength, and participation coefficient measures are most biased by acquisition and that machine learning voxel-wise correction, RISH mapping, and NeSH methods effectively reduce these biases. In addition, microstructure measures AD, MD, RD, bundle length, connectome density, efficiency, and path length are least biased by these acquisition differences.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024/019
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Glioma Classification Using Multimodal Radiology and Histology Data
Nov 10, 2020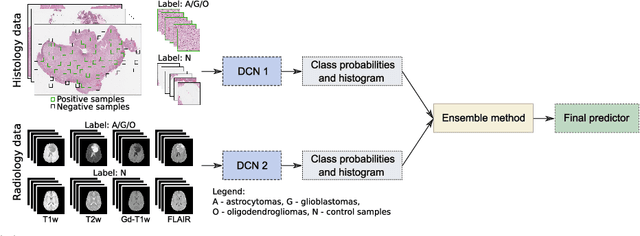
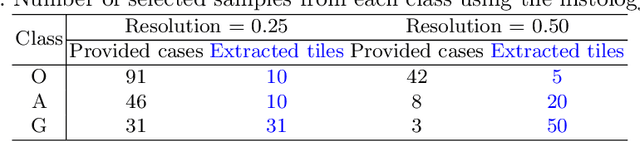
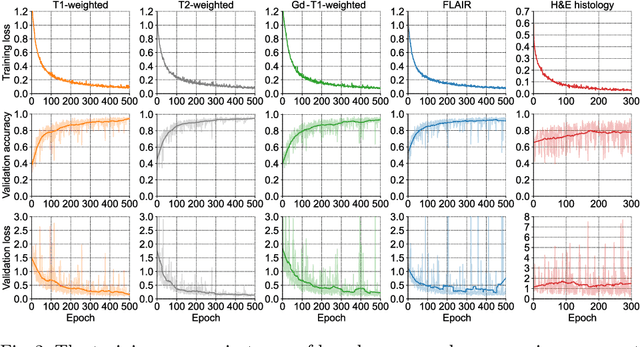
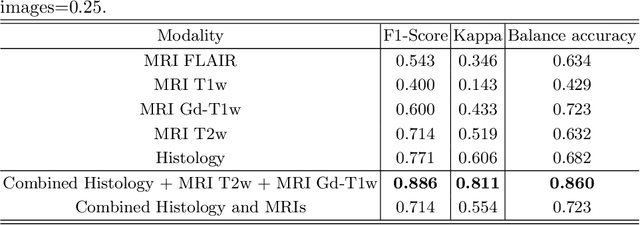
Abstract:Gliomas are brain tumours with a high mortality rate. There are various grades and sub-types of this tumour, and the treatment procedure varies accordingly. Clinicians and oncologists diagnose and categorise these tumours based on visual inspection of radiology and histology data. However, this process can be time-consuming and subjective. The computer-assisted methods can help clinicians to make better and faster decisions. In this paper, we propose a pipeline for automatic classification of gliomas into three sub-types: oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, and glioblastoma, using both radiology and histopathology images. The proposed approach implements distinct classification models for radiographic and histologic modalities and combines them through an ensemble method. The classification algorithm initially carries out tile-level (for histology) and slice-level (for radiology) classification via a deep learning method, then tile/slice-level latent features are combined for a whole-slide and whole-volume sub-type prediction. The classification algorithm was evaluated using the data set provided in the CPM-RadPath 2020 challenge. The proposed pipeline achieved the F1-Score of 0.886, Cohen's Kappa score of 0.811 and Balance accuracy of 0.860. The ability of the proposed model for end-to-end learning of diverse features enables it to give a comparable prediction of glioma tumour sub-types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge