Tianyang Zhan
Mitigating LLM Hallucination via Behaviorally Calibrated Reinforcement Learning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:LLM deployment in critical domains is currently impeded by persistent hallucinations--generating plausible but factually incorrect assertions. While scaling laws drove significant improvements in general capabilities, theoretical frameworks suggest hallucination is not merely stochastic error but a predictable statistical consequence of training objectives prioritizing mimicking data distribution over epistemic honesty. Standard RLVR paradigms, utilizing binary reward signals, inadvertently incentivize models as good test-takers rather than honest communicators, encouraging guessing whenever correctness probability exceeds zero. This paper presents an exhaustive investigation into behavioral calibration, which incentivizes models to stochastically admit uncertainty by abstaining when not confident, aligning model behavior with accuracy. Synthesizing recent advances, we propose and evaluate training interventions optimizing strictly proper scoring rules for models to output a calibrated probability of correctness. Our methods enable models to either abstain from producing a complete response or flag individual claims where uncertainty remains. Utilizing Qwen3-4B-Instruct, empirical analysis reveals behavior-calibrated reinforcement learning allows smaller models to surpass frontier models in uncertainty quantification--a transferable meta-skill decouplable from raw predictive accuracy. Trained on math reasoning tasks, our model's log-scale Accuracy-to-Hallucination Ratio gain (0.806) exceeds GPT-5's (0.207) in a challenging in-domain evaluation (BeyondAIME). Moreover, in cross-domain factual QA (SimpleQA), our 4B LLM achieves zero-shot calibration error on par with frontier models including Grok-4 and Gemini-2.5-Pro, even though its factual accuracy is much lower.
Seed-Prover 1.5: Mastering Undergraduate-Level Theorem Proving via Learning from Experience
Dec 19, 2025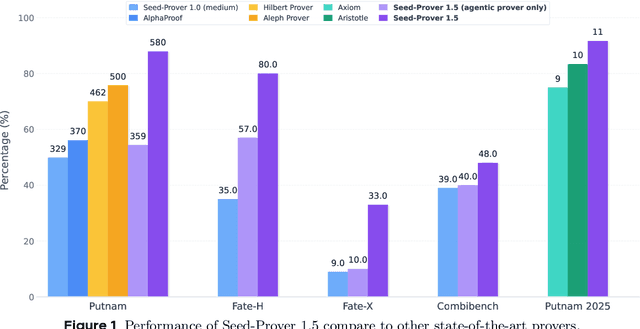

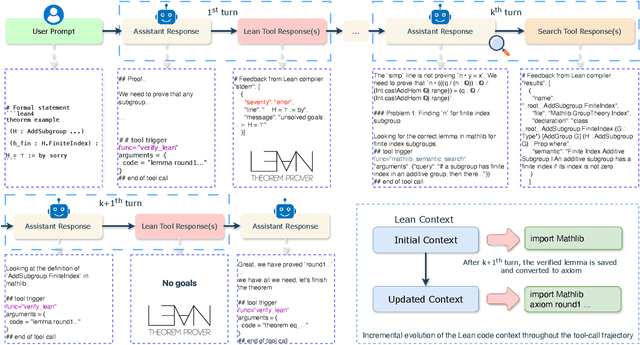
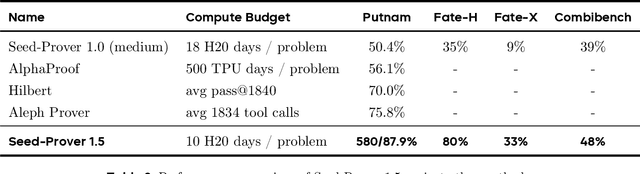
Abstract:Large language models have recently made significant progress to generate rigorous mathematical proofs. In contrast, utilizing LLMs for theorem proving in formal languages (such as Lean) remains challenging and computationally expensive, particularly when addressing problems at the undergraduate level and beyond. In this work, we present \textbf{Seed-Prover 1.5}, a formal theorem-proving model trained via large-scale agentic reinforcement learning, alongside an efficient test-time scaling (TTS) workflow. Through extensive interactions with Lean and other tools, the model continuously accumulates experience during the RL process, substantially enhancing the capability and efficiency of formal theorem proving. Furthermore, leveraging recent advancements in natural language proving, our TTS workflow efficiently bridges the gap between natural and formal languages. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, Seed-Prover 1.5 achieves superior performance with a smaller compute budget. It solves \textbf{88\% of PutnamBench} (undergraduate-level), \textbf{80\% of Fate-H} (graduate-level), and \textbf{33\% of Fate-X} (PhD-level) problems. Notably, using our system, we solved \textbf{11 out of 12 problems} from Putnam 2025 within 9 hours. Our findings suggest that scaling learning from experience, driven by high-quality formal feedback, holds immense potential for the future of formal mathematical reasoning.
StructVRM: Aligning Multimodal Reasoning with Structured and Verifiable Reward Models
Aug 07, 2025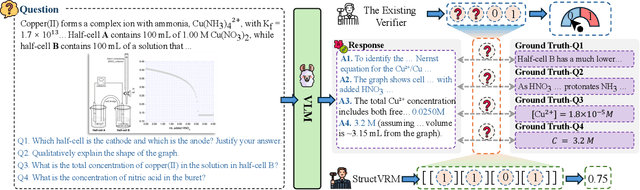

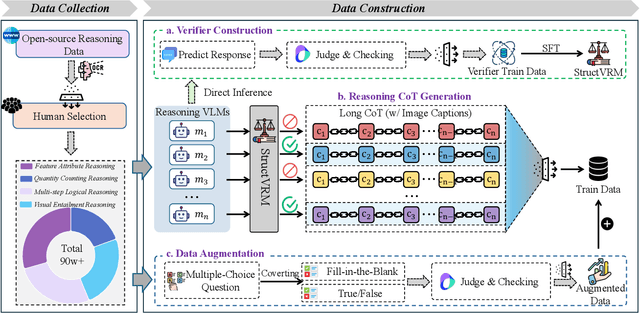
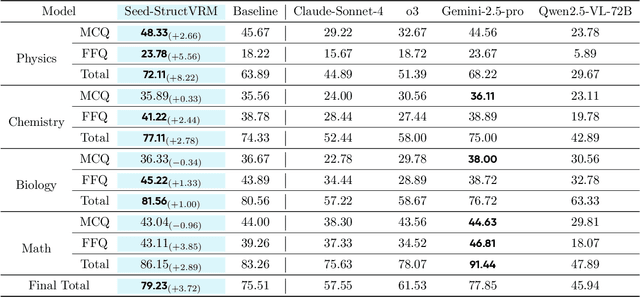
Abstract:Existing Vision-Language Models often struggle with complex, multi-question reasoning tasks where partial correctness is crucial for effective learning. Traditional reward mechanisms, which provide a single binary score for an entire response, are too coarse to guide models through intricate problems with multiple sub-parts. To address this, we introduce StructVRM, a method that aligns multimodal reasoning with Structured and Verifiable Reward Models. At its core is a model-based verifier trained to provide fine-grained, sub-question-level feedback, assessing semantic and mathematical equivalence rather than relying on rigid string matching. This allows for nuanced, partial credit scoring in previously intractable problem formats. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of StructVRM. Our trained model, Seed-StructVRM, achieves state-of-the-art performance on six out of twelve public multimodal benchmarks and our newly curated, high-difficulty STEM-Bench. The success of StructVRM validates that training with structured, verifiable rewards is a highly effective approach for advancing the capabilities of multimodal models in complex, real-world reasoning domains.
Seed-Prover: Deep and Broad Reasoning for Automated Theorem Proving
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:LLMs have demonstrated strong mathematical reasoning abilities by leveraging reinforcement learning with long chain-of-thought, yet they continue to struggle with theorem proving due to the lack of clear supervision signals when solely using natural language. Dedicated domain-specific languages like Lean provide clear supervision via formal verification of proofs, enabling effective training through reinforcement learning. In this work, we propose \textbf{Seed-Prover}, a lemma-style whole-proof reasoning model. Seed-Prover can iteratively refine its proof based on Lean feedback, proved lemmas, and self-summarization. To solve IMO-level contest problems, we design three test-time inference strategies that enable both deep and broad reasoning. Seed-Prover proves $78.1\%$ of formalized past IMO problems, saturates MiniF2F, and achieves over 50\% on PutnamBench, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art by a large margin. To address the lack of geometry support in Lean, we introduce a geometry reasoning engine \textbf{Seed-Geometry}, which outperforms previous formal geometry engines. We use these two systems to participate in IMO 2025 and fully prove 5 out of 6 problems. This work represents a significant advancement in automated mathematical reasoning, demonstrating the effectiveness of formal verification with long chain-of-thought reasoning.
SuperGPQA: Scaling LLM Evaluation across 285 Graduate Disciplines
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in mainstream academic disciplines such as mathematics, physics, and computer science. However, human knowledge encompasses over 200 specialized disciplines, far exceeding the scope of existing benchmarks. The capabilities of LLMs in many of these specialized fields-particularly in light industry, agriculture, and service-oriented disciplines-remain inadequately evaluated. To address this gap, we present SuperGPQA, a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates graduate-level knowledge and reasoning capabilities across 285 disciplines. Our benchmark employs a novel Human-LLM collaborative filtering mechanism to eliminate trivial or ambiguous questions through iterative refinement based on both LLM responses and expert feedback. Our experimental results reveal significant room for improvement in the performance of current state-of-the-art LLMs across diverse knowledge domains (e.g., the reasoning-focused model DeepSeek-R1 achieved the highest accuracy of 61.82% on SuperGPQA), highlighting the considerable gap between current model capabilities and artificial general intelligence. Additionally, we present comprehensive insights from our management of a large-scale annotation process, involving over 80 expert annotators and an interactive Human-LLM collaborative system, offering valuable methodological guidance for future research initiatives of comparable scope.
Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training with Unified Modality Masking for Visual Document Understanding
May 16, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents GenDoc, a general sequence-to-sequence document understanding model pre-trained with unified masking across three modalities: text, image, and layout. The proposed model utilizes an encoder-decoder architecture, which allows for increased adaptability to a wide range of downstream tasks with diverse output formats, in contrast to the encoder-only models commonly employed in document understanding. In addition to the traditional text infilling task used in previous encoder-decoder models, our pre-training extends to include tasks of masked image token prediction and masked layout prediction. We also design modality-specific instruction and adopt both disentangled attention and the mixture-of-modality-experts strategy to effectively capture the information leveraged by each modality. Evaluation of the proposed model through extensive experiments on several downstream tasks in document understanding demonstrates its ability to achieve superior or competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art approaches. Our analysis further suggests that GenDoc is more robust than the encoder-only models in scenarios where the OCR quality is imperfect.
Variational Autoencoder with Disentanglement Priors for Low-Resource Task-Specific Natural Language Generation
Mar 15, 2022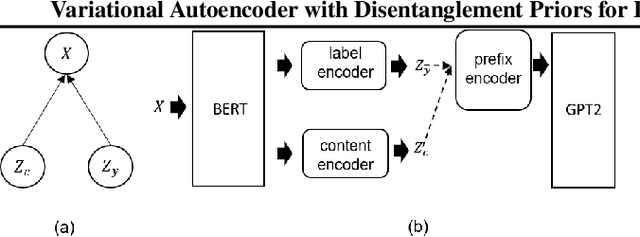
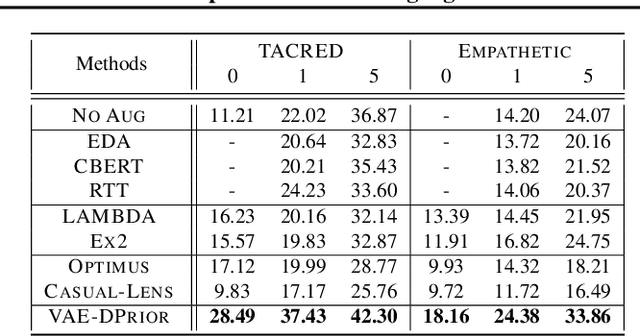
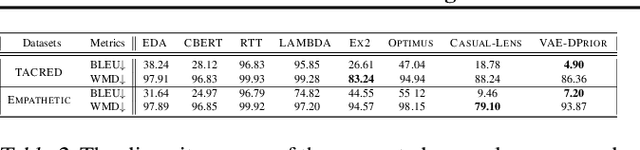
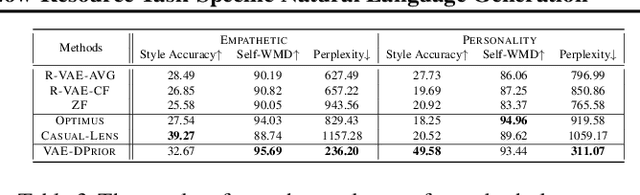
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a variational autoencoder with disentanglement priors, VAE-DPRIOR, for conditional natural language generation with none or a handful of task-specific labeled examples. In order to improve compositional generalization, our model performs disentangled representation learning by introducing a prior for the latent content space and another prior for the latent label space. We show both empirically and theoretically that the conditional priors can already disentangle representations even without specific regularizations as in the prior work. We can also sample diverse content representations from the content space without accessing data of the seen tasks, and fuse them with the representations of novel tasks for generating diverse texts in the low-resource settings. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our model over competitive baselines in terms of i) data augmentation in continuous zero/few-shot learning, and ii) text style transfer in both zero/few-shot settings.
A Framework for Deep Constrained Clustering
Jan 07, 2021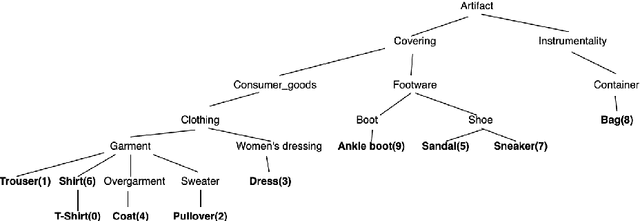
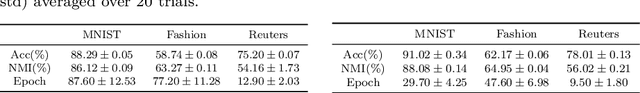
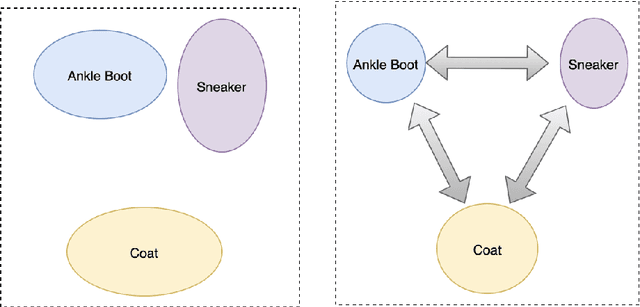
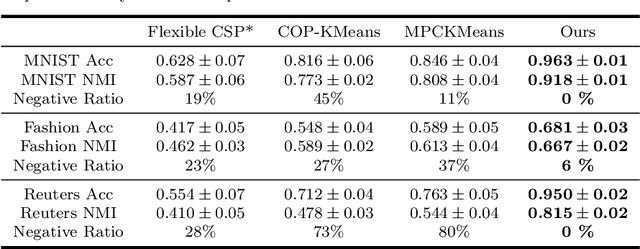
Abstract:The area of constrained clustering has been extensively explored by researchers and used by practitioners. Constrained clustering formulations exist for popular algorithms such as k-means, mixture models, and spectral clustering but have several limitations. A fundamental strength of deep learning is its flexibility, and here we explore a deep learning framework for constrained clustering and in particular explore how it can extend the field of constrained clustering. We show that our framework can not only handle standard together/apart constraints (without the well documented negative effects reported earlier) generated from labeled side information but more complex constraints generated from new types of side information such as continuous values and high-level domain knowledge. Furthermore, we propose an efficient training paradigm that is generally applicable to these four types of constraints. We validate the effectiveness of our approach by empirical results on both image and text datasets. We also study the robustness of our framework when learning with noisy constraints and show how different components of our framework contribute to the final performance. Our source code is available at $\href{https://github.com/blueocean92/deep_constrained_clustering}{\text{URL}}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge