Tianran Sun
Reasoning in Trees: Improving Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Multi-Hop Question Answering
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has demonstrated significant effectiveness in enhancing large language models (LLMs) for complex multi-hop question answering (QA). For multi-hop QA tasks, current iterative approaches predominantly rely on LLMs to self-guide and plan multi-step exploration paths during retrieval, leading to substantial challenges in maintaining reasoning coherence across steps from inaccurate query decomposition and error propagation. To address these issues, we introduce Reasoning Tree Guided RAG (RT-RAG), a novel hierarchical framework for complex multi-hop QA. RT-RAG systematically decomposes multi-hop questions into explicit reasoning trees, minimizing inaccurate decomposition through structured entity analysis and consensus-based tree selection that clearly separates core queries, known entities, and unknown entities. Subsequently, a bottom-up traversal strategy employs iterative query rewriting and refinement to collect high-quality evidence, thereby mitigating error propagation. Comprehensive experiments show that RT-RAG substantially outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.0% F1 and 6.0% EM, demonstrating the effectiveness of RT-RAG in complex multi-hop QA.
Astra: A Multi-Agent System for GPU Kernel Performance Optimization
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:GPU kernel optimization has long been a central challenge at the intersection of high-performance computing and machine learning. Efficient kernels are crucial for accelerating large language model (LLM) training and serving, yet attaining high performance typically requires extensive manual tuning. Compiler-based systems reduce some of this burden, but still demand substantial manual design and engineering effort. Recently, researchers have explored using LLMs for GPU kernel generation, though prior work has largely focused on translating high-level PyTorch modules into CUDA code. In this work, we introduce Astra, the first LLM-based multi-agent system for GPU kernel optimization. Unlike previous approaches, Astra starts from existing CUDA implementations extracted from SGLang, a widely deployed framework for serving LLMs, rather than treating PyTorch modules as the specification. Within Astra, specialized LLM agents collaborate through iterative code generation, testing, profiling, and planning to produce kernels that are both correct and high-performance. On kernels from SGLang, Astra achieves an average speedup of 1.32x using zero-shot prompting with OpenAI o4-mini. A detailed case study further demonstrates that LLMs can autonomously apply loop transformations, optimize memory access patterns, exploit CUDA intrinsics, and leverage fast math operations to yield substantial performance gains. Our work highlights multi-agent LLM systems as a promising new paradigm for GPU kernel optimization.
AttentionRAG: Attention-Guided Context Pruning in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:While RAG demonstrates remarkable capabilities in LLM applications, its effectiveness is hindered by the ever-increasing length of retrieved contexts, which introduces information redundancy and substantial computational overhead. Existing context pruning methods, such as LLMLingua, lack contextual awareness and offer limited flexibility in controlling compression rates, often resulting in either insufficient pruning or excessive information loss. In this paper, we propose AttentionRAG, an attention-guided context pruning method for RAG systems. The core idea of AttentionRAG lies in its attention focus mechanism, which reformulates RAG queries into a next-token prediction paradigm. This mechanism isolates the query's semantic focus to a single token, enabling precise and efficient attention calculation between queries and retrieved contexts. Extensive experiments on LongBench and Babilong benchmarks show that AttentionRAG achieves up to 6.3$\times$ context compression while outperforming LLMLingua methods by around 10\% in key metrics.
Building A Proof-Oriented Programmer That Is 64% Better Than GPT-4o Under Data Scarsity
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Existing LMs struggle with proof-oriented programming due to data scarcity, which manifest in two key ways: (1) a lack of sufficient corpora for proof-oriented programming languages such as F*, and (2) the absence of large-scale, project-level proof-oriented implementations that can teach the model the intricate reasoning process when performing proof-oriented programming. We present the first on synthetic data augmentation for project level proof oriented programming for both generation and repair. Our method addresses data scarcity by synthesizing basic proof-oriented programming problems for proficiency in that language; incorporating diverse coding data for reasoning capability elicitation and creating new proofs and repair data within existing repositories. This approach enables language models to both synthesize and repair proofs for function- and repository-level code. We show that our fine-tuned 14B parameter model, PoPilot, can exceed the performance of the models that outperforms GPT-4o in project-level proof-oriented programming by 64% relative margin, and can improve GPT-4o's performance by 54% by repairing its outputs over GPT-4o's self-repair.
Multi-layer Attention Mechanism for Speech Keyword Recognition
Jul 10, 2019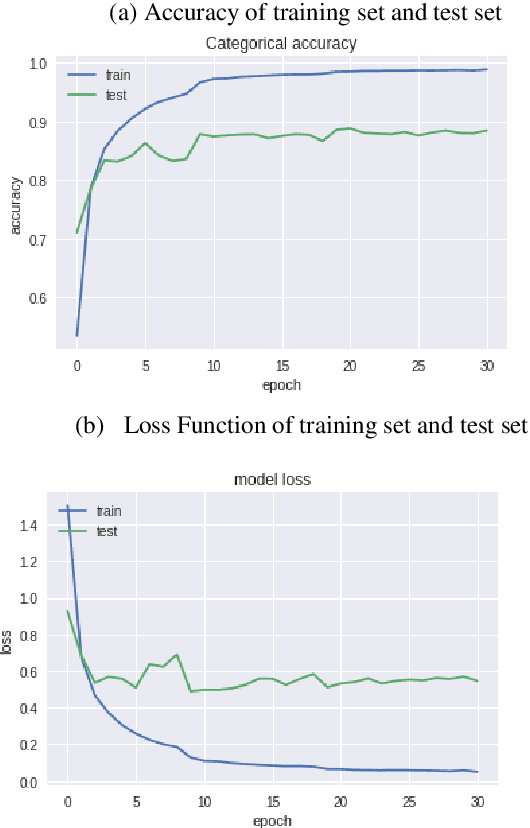
Abstract:As an important part of speech recognition technology, automatic speech keyword recognition has been intensively studied in recent years. Such technology becomes especially pivotal under situations with limited infrastructures and computational resources, such as voice command recognition in vehicles and robot interaction. At present, the mainstream methods in automatic speech keyword recognition are based on long short-term memory (LSTM) networks with attention mechanism. However, due to inevitable information losses for the LSTM layer caused during feature extraction, the calculated attention weights are biased. In this paper, a novel approach, namely Multi-layer Attention Mechanism, is proposed to handle the inaccurate attention weights problem. The key idea is that, in addition to the conventional attention mechanism, information of layers prior to feature extraction and LSTM are introduced into attention weights calculations. Therefore, the attention weights are more accurate because the overall model can have more precise and focused areas. We conduct a comprehensive comparison and analysis on the keyword spotting performances on convolution neural network, bi-directional LSTM cyclic neural network, and cyclic neural network with the proposed attention mechanism on Google Speech Command datasets V2 datasets. Experimental results indicate favorable results for the proposed method and demonstrate the validity of the proposed method. The proposed multi-layer attention methods can be useful for other researches related to object spotting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge