Miao Du
Fully Dense Neural Network for the Automatic Modulation Recognition
Dec 07, 2019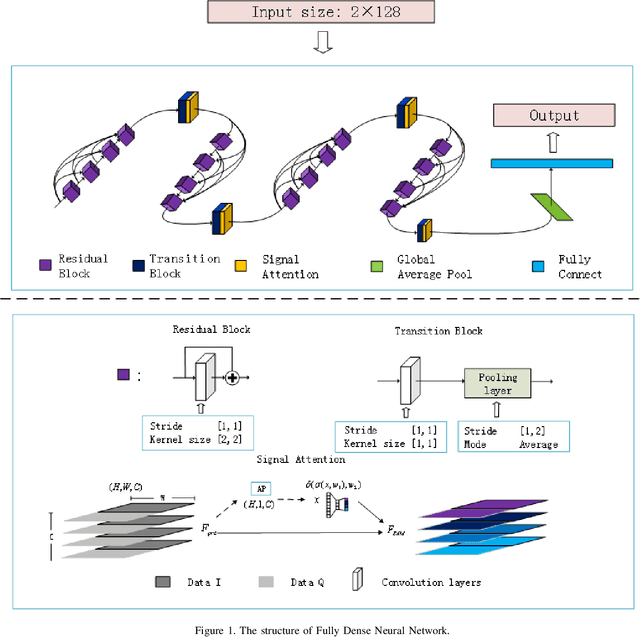
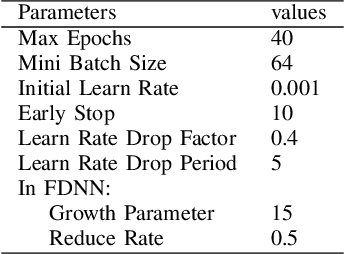
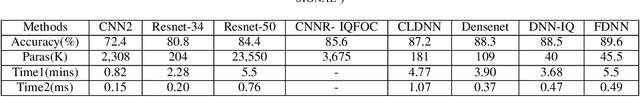
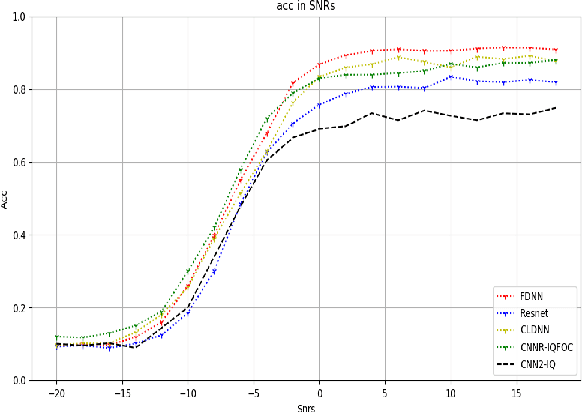
Abstract:Nowadays, we mainly use various convolution neural network (CNN) structures to extract features from radio data or spectrogram in AMR. Based on expert experience and spectrograms, they not only increase the difficulty of preprocessing, but also consume a lot of memory. In order to directly use in-phase and quadrature (IQ) data obtained by the receiver and enhance the efficiency of network extraction features to improve the recognition rate of modulation mode, this paper proposes a new network structure called Fully Dense Neural Network (FDNN). This network uses residual blocks to extract features, dense connect to reduce model size, and adds attentions mechanism to recalibrate. Experiments on RML2016.10a show that this network has a higher recognition rate and lower model complexity. And it shows that the FDNN model with dense connections can not only extract features effectively but also greatly reduce model parameters, which also provides a significant contribution for the application of deep learning to the intelligent radio system.
Multi-layer Attention Mechanism for Speech Keyword Recognition
Jul 10, 2019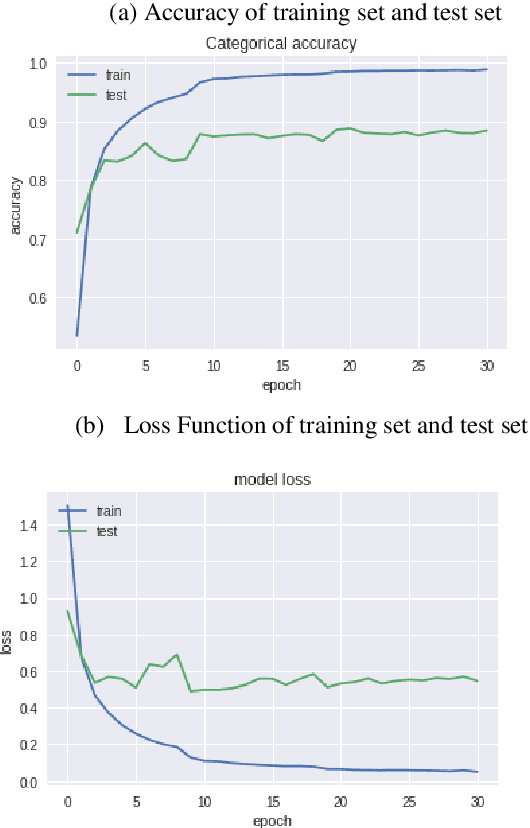
Abstract:As an important part of speech recognition technology, automatic speech keyword recognition has been intensively studied in recent years. Such technology becomes especially pivotal under situations with limited infrastructures and computational resources, such as voice command recognition in vehicles and robot interaction. At present, the mainstream methods in automatic speech keyword recognition are based on long short-term memory (LSTM) networks with attention mechanism. However, due to inevitable information losses for the LSTM layer caused during feature extraction, the calculated attention weights are biased. In this paper, a novel approach, namely Multi-layer Attention Mechanism, is proposed to handle the inaccurate attention weights problem. The key idea is that, in addition to the conventional attention mechanism, information of layers prior to feature extraction and LSTM are introduced into attention weights calculations. Therefore, the attention weights are more accurate because the overall model can have more precise and focused areas. We conduct a comprehensive comparison and analysis on the keyword spotting performances on convolution neural network, bi-directional LSTM cyclic neural network, and cyclic neural network with the proposed attention mechanism on Google Speech Command datasets V2 datasets. Experimental results indicate favorable results for the proposed method and demonstrate the validity of the proposed method. The proposed multi-layer attention methods can be useful for other researches related to object spotting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge