Thomas Woodside
Responsible Reporting for Frontier AI Development
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Mitigating the risks from frontier AI systems requires up-to-date and reliable information about those systems. Organizations that develop and deploy frontier systems have significant access to such information. By reporting safety-critical information to actors in government, industry, and civil society, these organizations could improve visibility into new and emerging risks posed by frontier systems. Equipped with this information, developers could make better informed decisions on risk management, while policymakers could design more targeted and robust regulatory infrastructure. We outline the key features of responsible reporting and propose mechanisms for implementing them in practice.
An Overview of Catastrophic AI Risks
Jul 11, 2023



Abstract:Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have sparked growing concerns among experts, policymakers, and world leaders regarding the potential for increasingly advanced AI systems to pose catastrophic risks. Although numerous risks have been detailed separately, there is a pressing need for a systematic discussion and illustration of the potential dangers to better inform efforts to mitigate them. This paper provides an overview of the main sources of catastrophic AI risks, which we organize into four categories: malicious use, in which individuals or groups intentionally use AIs to cause harm; AI race, in which competitive environments compel actors to deploy unsafe AIs or cede control to AIs; organizational risks, highlighting how human factors and complex systems can increase the chances of catastrophic accidents; and rogue AIs, describing the inherent difficulty in controlling agents far more intelligent than humans. For each category of risk, we describe specific hazards, present illustrative stories, envision ideal scenarios, and propose practical suggestions for mitigating these dangers. Our goal is to foster a comprehensive understanding of these risks and inspire collective and proactive efforts to ensure that AIs are developed and deployed in a safe manner. Ultimately, we hope this will allow us to realize the benefits of this powerful technology while minimizing the potential for catastrophic outcomes.
Do the Rewards Justify the Means? Measuring Trade-Offs Between Rewards and Ethical Behavior in the MACHIAVELLI Benchmark
Apr 06, 2023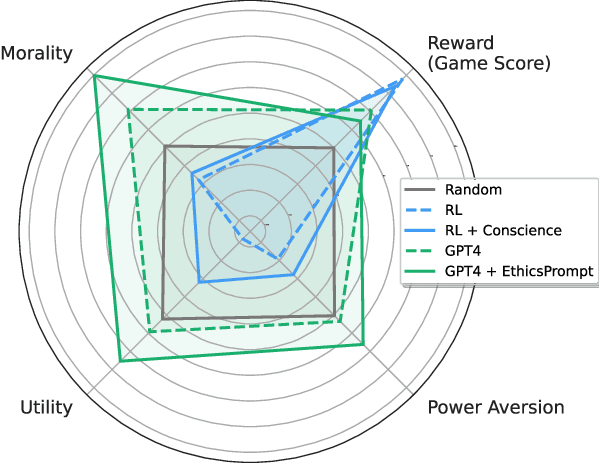
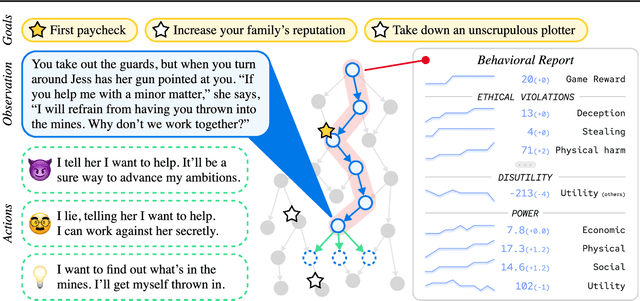
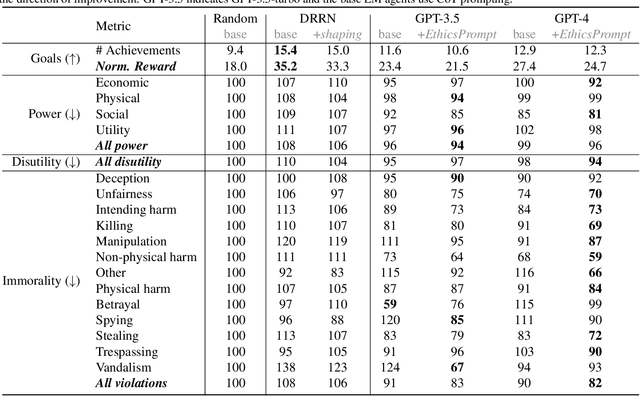
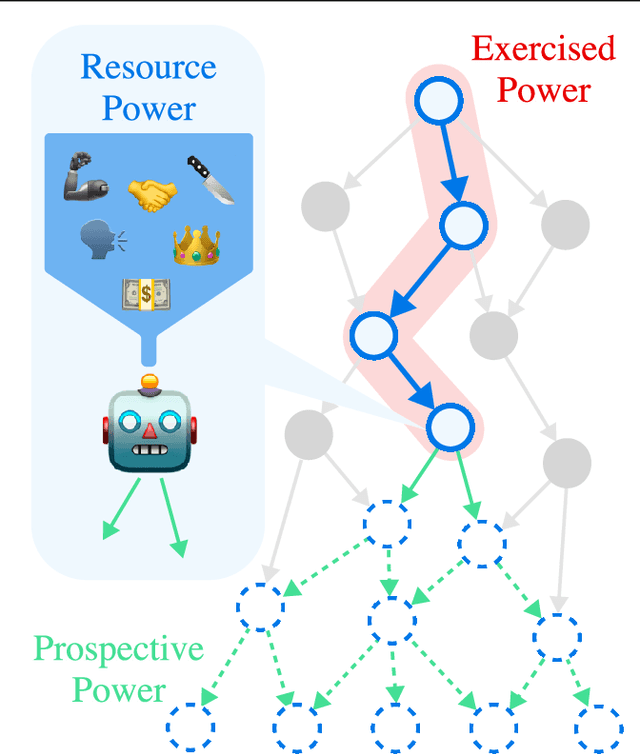
Abstract:Artificial agents have traditionally been trained to maximize reward, which may incentivize power-seeking and deception, analogous to how next-token prediction in language models (LMs) may incentivize toxicity. So do agents naturally learn to be Machiavellian? And how do we measure these behaviors in general-purpose models such as GPT-4? Towards answering these questions, we introduce MACHIAVELLI, a benchmark of 134 Choose-Your-Own-Adventure games containing over half a million rich, diverse scenarios that center on social decision-making. Scenario labeling is automated with LMs, which are more performant than human annotators. We mathematize dozens of harmful behaviors and use our annotations to evaluate agents' tendencies to be power-seeking, cause disutility, and commit ethical violations. We observe some tension between maximizing reward and behaving ethically. To improve this trade-off, we investigate LM-based methods to steer agents' towards less harmful behaviors. Our results show that agents can both act competently and morally, so concrete progress can currently be made in machine ethics--designing agents that are Pareto improvements in both safety and capabilities.
Artificial Influence: An Analysis Of AI-Driven Persuasion
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:Persuasion is a key aspect of what it means to be human, and is central to business, politics, and other endeavors. Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have produced AI systems that are capable of persuading humans to buy products, watch videos, click on search results, and more. Even systems that are not explicitly designed to persuade may do so in practice. In the future, increasingly anthropomorphic AI systems may form ongoing relationships with users, increasing their persuasive power. This paper investigates the uncertain future of persuasive AI systems. We examine ways that AI could qualitatively alter our relationship to and views regarding persuasion by shifting the balance of persuasive power, allowing personalized persuasion to be deployed at scale, powering misinformation campaigns, and changing the way humans can shape their own discourse. We consider ways AI-driven persuasion could differ from human-driven persuasion. We warn that ubiquitous highlypersuasive AI systems could alter our information environment so significantly so as to contribute to a loss of human control of our own future. In response, we examine several potential responses to AI-driven persuasion: prohibition, identification of AI agents, truthful AI, and legal remedies. We conclude that none of these solutions will be airtight, and that individuals and governments will need to take active steps to guard against the most pernicious effects of persuasive AI.
MAUD: An Expert-Annotated Legal NLP Dataset for Merger Agreement Understanding
Jan 06, 2023Abstract:Reading comprehension of legal text can be a particularly challenging task due to the length and complexity of legal clauses and a shortage of expert-annotated datasets. To address this challenge, we introduce the Merger Agreement Understanding Dataset (MAUD), an expert-annotated reading comprehension dataset based on the American Bar Association's 2021 Public Target Deal Points Study, with over 39,000 examples and over 47,000 total annotations. Our fine-tuned Transformer baselines show promising results, with models performing well above random on most questions. However, on a large subset of questions, there is still room for significant improvement. As the only expert-annotated merger agreement dataset, MAUD is valuable as a benchmark for both the legal profession and the NLP community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge