Tao Jun Lin
Geometry-guided Cross-view Diffusion for One-to-many Cross-view Image Synthesis
Dec 04, 2024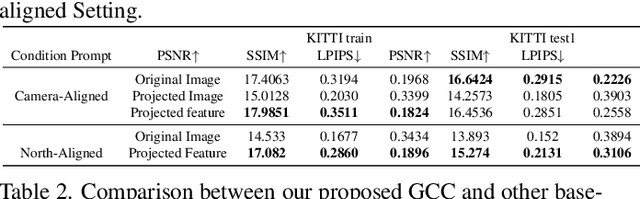
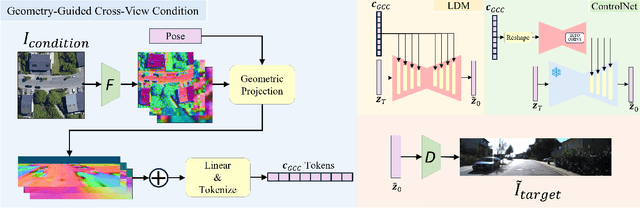
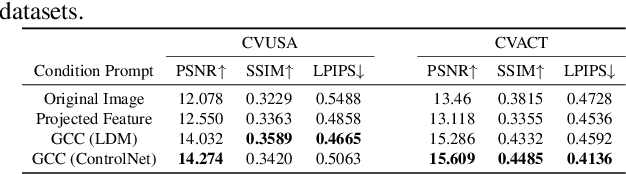
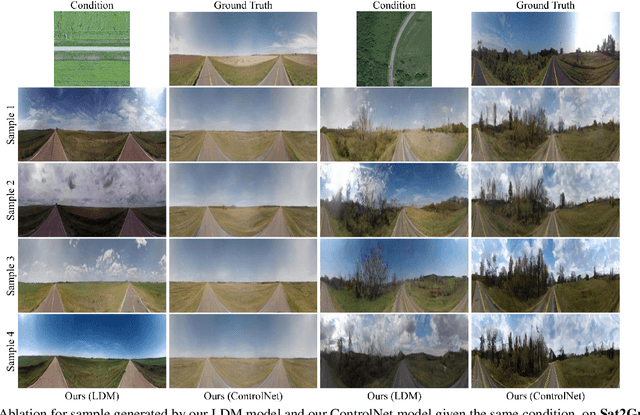
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach for cross-view synthesis aimed at generating plausible ground-level images from corresponding satellite imagery or vice versa. We refer to these tasks as satellite-to-ground (Sat2Grd) and ground-to-satellite (Grd2Sat) synthesis, respectively. Unlike previous works that typically focus on one-to-one generation, producing a single output image from a single input image, our approach acknowledges the inherent one-to-many nature of the problem. This recognition stems from the challenges posed by differences in illumination, weather conditions, and occlusions between the two views. To effectively model this uncertainty, we leverage recent advancements in diffusion models. Specifically, we exploit random Gaussian noise to represent the diverse possibilities learnt from the target view data. We introduce a Geometry-guided Cross-view Condition (GCC) strategy to establish explicit geometric correspondences between satellite and street-view features. This enables us to resolve the geometry ambiguity introduced by camera pose between image pairs, boosting the performance of cross-view image synthesis. Through extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses on three benchmark cross-view datasets, we demonstrate the superiority of our proposed geometry-guided cross-view condition over baseline methods, including recent state-of-the-art approaches in cross-view image synthesis. Our method generates images of higher quality, fidelity, and diversity than other state-of-the-art approaches.
R$^2$-Gaussian: Rectifying Radiative Gaussian Splatting for Tomographic Reconstruction
May 31, 2024Abstract:3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) has shown promising results in image rendering and surface reconstruction. However, its potential in volumetric reconstruction tasks, such as X-ray computed tomography, remains under-explored. This paper introduces R2-Gaussian, the first 3DGS-based framework for sparse-view tomographic reconstruction. By carefully deriving X-ray rasterization functions, we discover a previously unknown integration bias in the standard 3DGS formulation, which hampers accurate volume retrieval. To address this issue, we propose a novel rectification technique via refactoring the projection from 3D to 2D Gaussians. Our new method presents three key innovations: (1) introducing tailored Gaussian kernels, (2) extending rasterization to X-ray imaging, and (3) developing a CUDA-based differentiable voxelizer. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches by 0.93 dB in PSNR and 0.014 in SSIM. Crucially, it delivers high-quality results in 3 minutes, which is 12x faster than NeRF-based methods and on par with traditional algorithms. The superior performance and rapid convergence of our method highlight its practical value.
MAVIS: Multi-Camera Augmented Visual-Inertial SLAM using SE2(3) Based Exact IMU Pre-integration
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel optimization-based Visual-Inertial SLAM system designed for multiple partially overlapped camera systems, named MAVIS. Our framework fully exploits the benefits of wide field-of-view from multi-camera systems, and the metric scale measurements provided by an inertial measurement unit (IMU). We introduce an improved IMU pre-integration formulation based on the exponential function of an automorphism of SE_2(3), which can effectively enhance tracking performance under fast rotational motion and extended integration time. Furthermore, we extend conventional front-end tracking and back-end optimization module designed for monocular or stereo setup towards multi-camera systems, and introduce implementation details that contribute to the performance of our system in challenging scenarios. The practical validity of our approach is supported by our experiments on public datasets. Our MAVIS won the first place in all the vision-IMU tracks (single and multi-session SLAM) on Hilti SLAM Challenge 2023 with 1.7 times the score compared to the second place.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge