Stephan Vogel
Incremental Decoding and Training Methods for Simultaneous Translation in Neural Machine Translation
Jun 10, 2018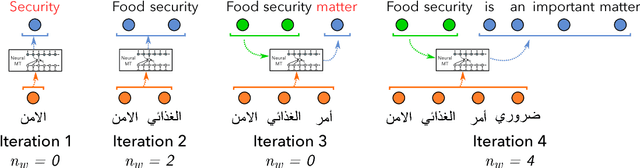
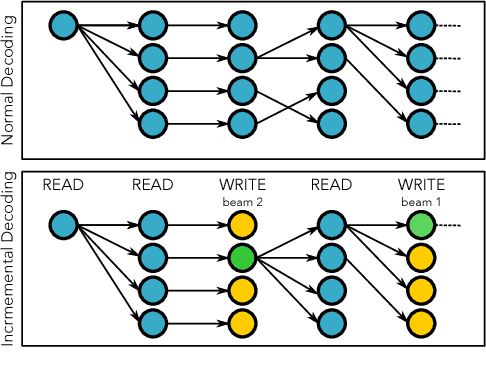
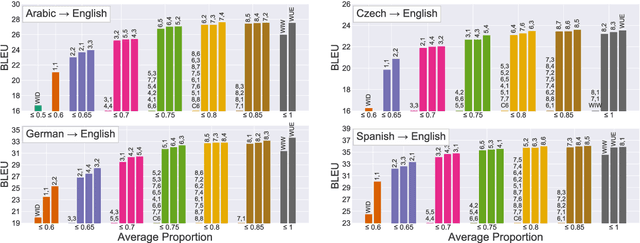
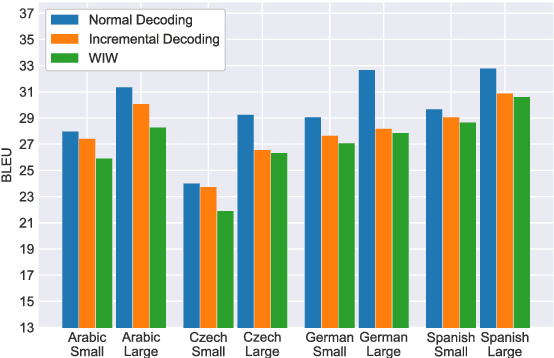
Abstract:We address the problem of simultaneous translation by modifying the Neural MT decoder to operate with dynamically built encoder and attention. We propose a tunable agent which decides the best segmentation strategy for a user-defined BLEU loss and Average Proportion (AP) constraint. Our agent outperforms previously proposed Wait-if-diff and Wait-if-worse agents (Cho and Esipova, 2016) on BLEU with a lower latency. Secondly we proposed data-driven changes to Neural MT training to better match the incremental decoding framework.
Robust Tuning Datasets for Statistical Machine Translation
Oct 01, 2017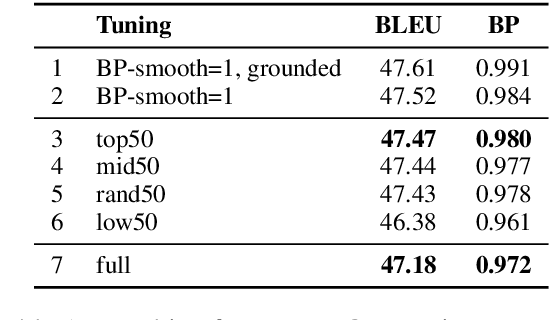
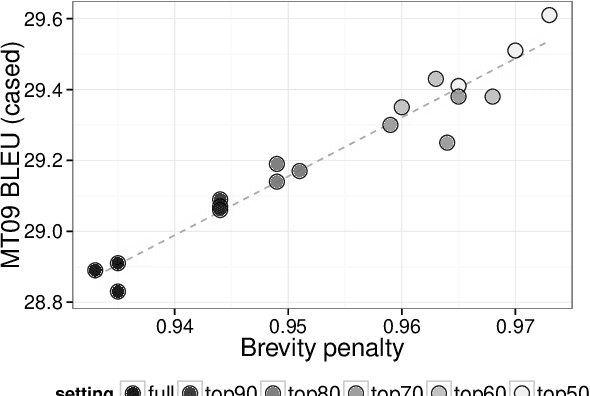
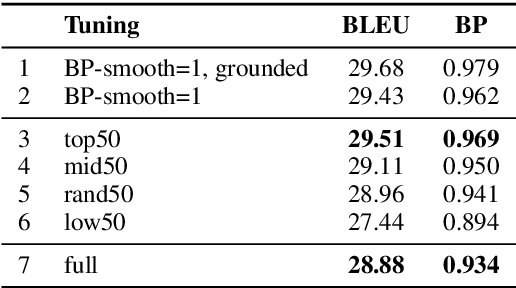
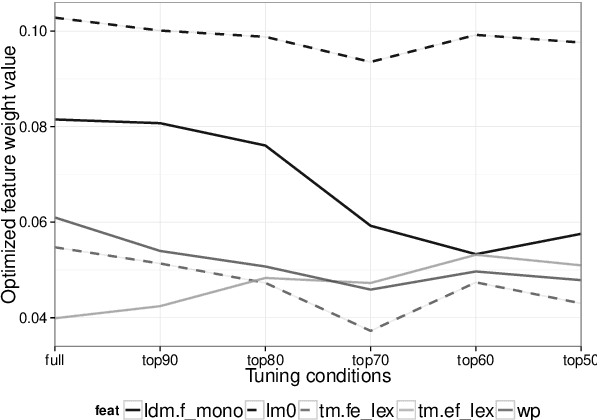
Abstract:We explore the idea of automatically crafting a tuning dataset for Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) that makes the hyper-parameters of the SMT system more robust with respect to some specific deficiencies of the parameter tuning algorithms. This is an under-explored research direction, which can allow better parameter tuning. In this paper, we achieve this goal by selecting a subset of the available sentence pairs, which are more suitable for specific combinations of optimizers, objective functions, and evaluation measures. We demonstrate the potential of the idea with the pairwise ranking optimization (PRO) optimizer, which is known to yield too short translations. We show that the learning problem can be alleviated by tuning on a subset of the development set, selected based on sentence length. In particular, using the longest 50% of the tuning sentences, we achieve two-fold tuning speedup, and improvements in BLEU score that rival those of alternatives, which fix BLEU+1's smoothing instead.
Speech Recognition Challenge in the Wild: Arabic MGB-3
Sep 21, 2017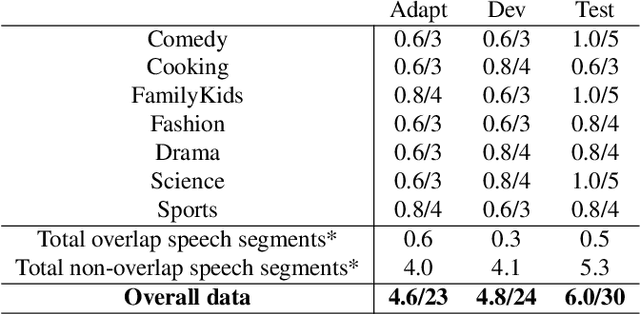
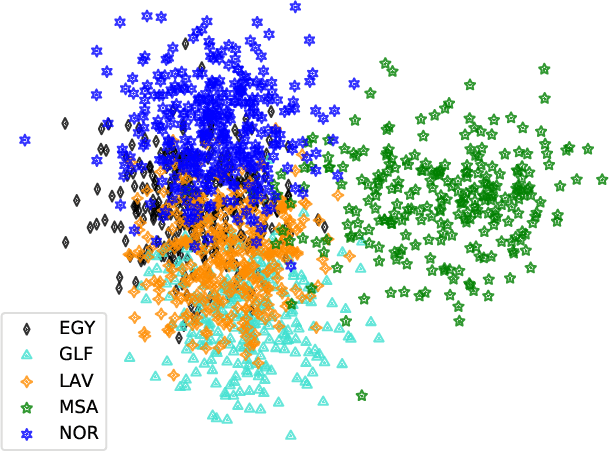

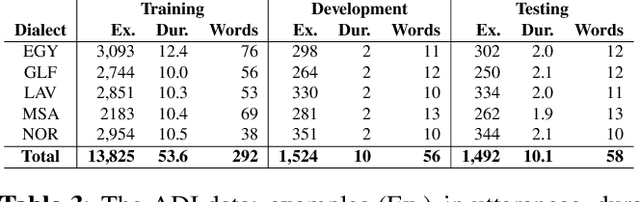
Abstract:This paper describes the Arabic MGB-3 Challenge - Arabic Speech Recognition in the Wild. Unlike last year's Arabic MGB-2 Challenge, for which the recognition task was based on more than 1,200 hours broadcast TV news recordings from Aljazeera Arabic TV programs, MGB-3 emphasises dialectal Arabic using a multi-genre collection of Egyptian YouTube videos. Seven genres were used for the data collection: comedy, cooking, family/kids, fashion, drama, sports, and science (TEDx). A total of 16 hours of videos, split evenly across the different genres, were divided into adaptation, development and evaluation data sets. The Arabic MGB-Challenge comprised two tasks: A) Speech transcription, evaluated on the MGB-3 test set, along with the 10 hour MGB-2 test set to report progress on the MGB-2 evaluation; B) Arabic dialect identification, introduced this year in order to distinguish between four major Arabic dialects - Egyptian, Levantine, North African, Gulf, as well as Modern Standard Arabic. Two hours of audio per dialect were released for development and a further two hours were used for evaluation. For dialect identification, both lexical features and i-vector bottleneck features were shared with participants in addition to the raw audio recordings. Overall, thirteen teams submitted ten systems to the challenge. We outline the approaches adopted in each system, and summarise the evaluation results.
Neural Machine Translation Training in a Multi-Domain Scenario
Sep 03, 2017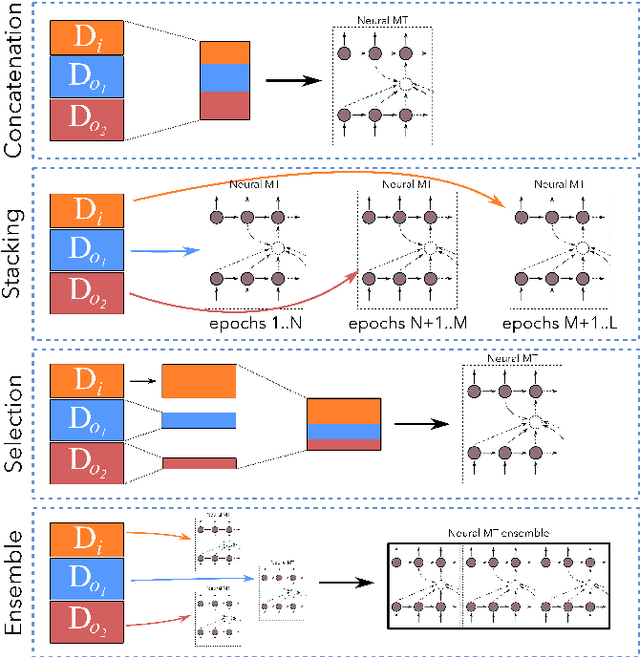

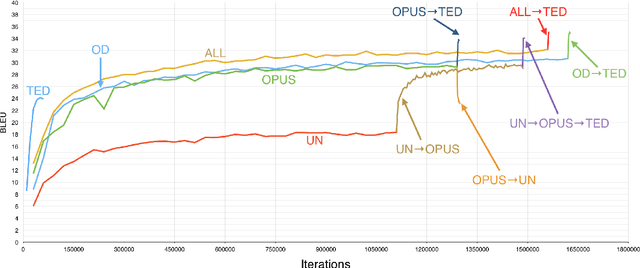
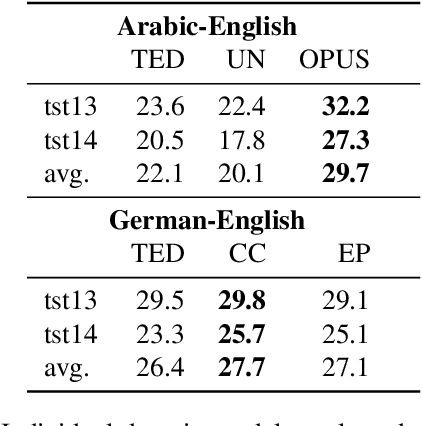
Abstract:In this paper, we explore alternative ways to train a neural machine translation system in a multi-domain scenario. We investigate data concatenation (with fine tuning), model stacking (multi-level fine tuning), data selection and weighted ensemble. We evaluate these methods based on three criteria: i) translation quality, ii) training time, and iii) robustness towards out-of-domain tests. Our findings on Arabic-English and German-English language pairs show that the best translation quality can be achieved by building an initial system on a concatenation of available out-of-domain data and then fine-tuning it on in-domain data. Model stacking works best when training begins with the furthest out-of-domain data and the model is incrementally fine-tuned with the next furthest domain and so on. Data selection did not give the best results, but can be considered as a decent compromise between training time and translation quality. A weighted ensemble of different individual models performed better than data selection. It is beneficial in a scenario when there is no time for fine-tuning.
QCRI Machine Translation Systems for IWSLT 16
Jan 14, 2017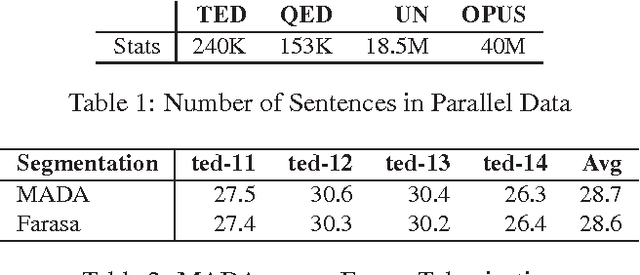
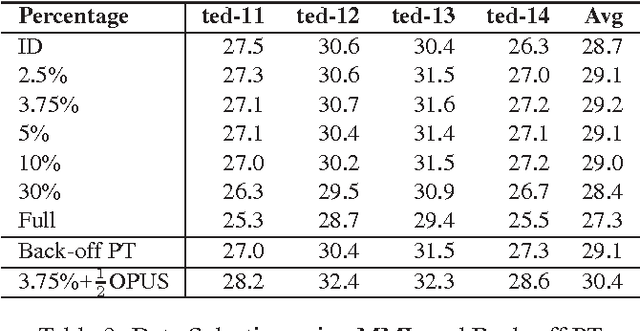
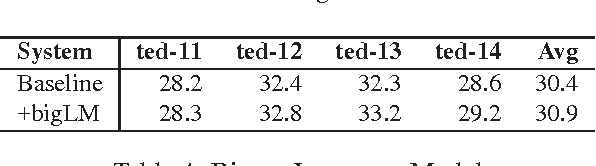
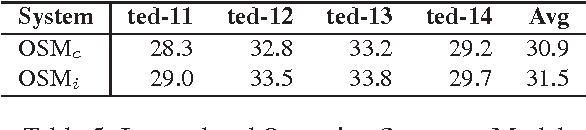
Abstract:This paper describes QCRI's machine translation systems for the IWSLT 2016 evaluation campaign. We participated in the Arabic->English and English->Arabic tracks. We built both Phrase-based and Neural machine translation models, in an effort to probe whether the newly emerged NMT framework surpasses the traditional phrase-based systems in Arabic-English language pairs. We trained a very strong phrase-based system including, a big language model, the Operation Sequence Model, Neural Network Joint Model and Class-based models along with different domain adaptation techniques such as MML filtering, mixture modeling and using fine tuning over NNJM model. However, a Neural MT system, trained by stacking data from different genres through fine-tuning, and applying ensemble over 8 models, beat our very strong phrase-based system by a significant 2 BLEU points margin in Arabic->English direction. We did not obtain similar gains in the other direction but were still able to outperform the phrase-based system. We also applied system combination on phrase-based and NMT outputs.
Enabling Medical Translation for Low-Resource Languages
Oct 09, 2016
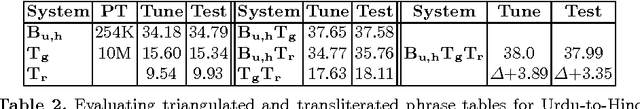


Abstract:We present research towards bridging the language gap between migrant workers in Qatar and medical staff. In particular, we present the first steps towards the development of a real-world Hindi-English machine translation system for doctor-patient communication. As this is a low-resource language pair, especially for speech and for the medical domain, our initial focus has been on gathering suitable training data from various sources. We applied a variety of methods ranging from fully automatic extraction from the Web to manual annotation of test data. Moreover, we developed a method for automatically augmenting the training data with synthetically generated variants, which yielded a very sizable improvement of more than 3 BLEU points absolute.
Egyptian Arabic to English Statistical Machine Translation System for NIST OpenMT'2015
Jun 18, 2016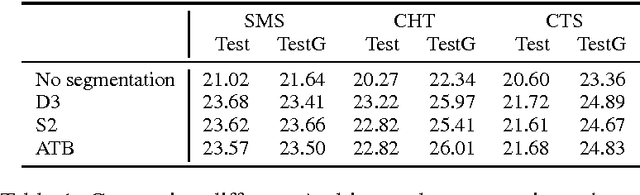
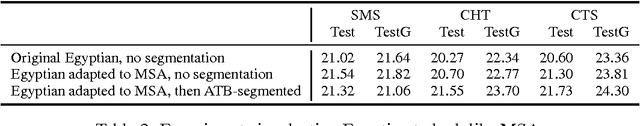

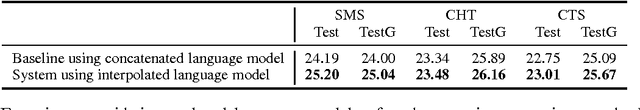
Abstract:The paper describes the Egyptian Arabic-to-English statistical machine translation (SMT) system that the QCRI-Columbia-NYUAD (QCN) group submitted to the NIST OpenMT'2015 competition. The competition focused on informal dialectal Arabic, as used in SMS, chat, and speech. Thus, our efforts focused on processing and standardizing Arabic, e.g., using tools such as 3arrib and MADAMIRA. We further trained a phrase-based SMT system using state-of-the-art features and components such as operation sequence model, class-based language model, sparse features, neural network joint model, genre-based hierarchically-interpolated language model, unsupervised transliteration mining, phrase-table merging, and hypothesis combination. Our system ranked second on all three genres.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge