Srinivas Turaga
Importance Weighted Adversarial Variational Autoencoders for Spike Inference from Calcium Imaging Data
Jun 07, 2019
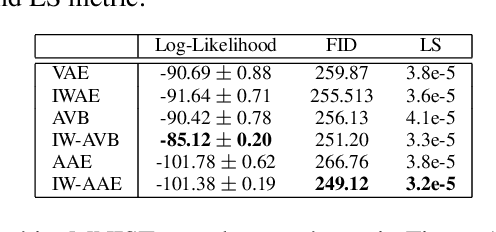
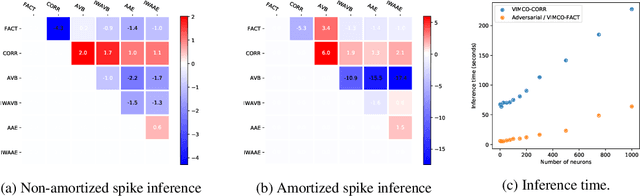
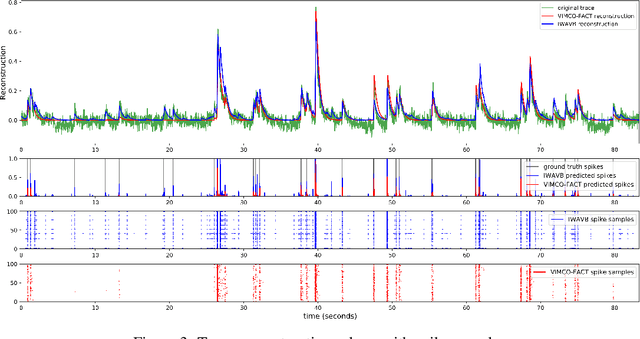
Abstract:The Importance Weighted Auto Encoder (IWAE) objective has been shown to improve the training of generative models over the standard Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) objective. Here, we derive importance weighted extensions to AVB and AAE. These latent variable models use implicitly defined inference networks whose approximate posterior density q_\phi(z|x) cannot be directly evaluated, an essential ingredient for importance weighting. We show improved training and inference in latent variable models with our adversarially trained importance weighting method, and derive new theoretical connections between adversarial generative model training criteria and marginal likelihood based methods. We apply these methods to the important problem of inferring spiking neural activity from calcium imaging data, a challenging posterior inference problem in neuroscience, and show that posterior samples from the adversarial methods outperform factorized posteriors used in VAEs.
Synaptic partner prediction from point annotations in insect brains
Jul 16, 2018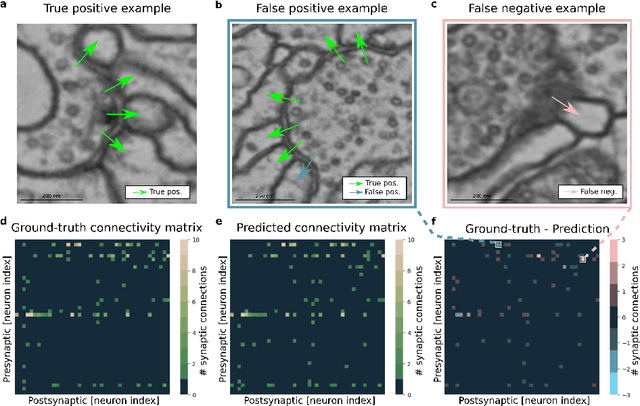
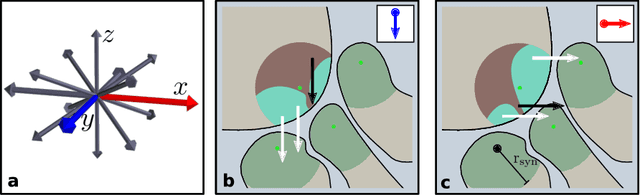
Abstract:High-throughput electron microscopy allows recording of lar- ge stacks of neural tissue with sufficient resolution to extract the wiring diagram of the underlying neural network. Current efforts to automate this process focus mainly on the segmentation of neurons. However, in order to recover a wiring diagram, synaptic partners need to be identi- fied as well. This is especially challenging in insect brains like Drosophila melanogaster, where one presynaptic site is associated with multiple post- synaptic elements. Here we propose a 3D U-Net architecture to directly identify pairs of voxels that are pre- and postsynaptic to each other. To that end, we formulate the problem of synaptic partner identification as a classification problem on long-range edges between voxels to encode both the presence of a synaptic pair and its direction. This formulation allows us to directly learn from synaptic point annotations instead of more ex- pensive voxel-based synaptic cleft or vesicle annotations. We evaluate our method on the MICCAI 2016 CREMI challenge and improve over the current state of the art, producing 3% fewer errors than the next best method.
Discovering Neuronal Cell Types and Their Gene Expression Profiles Using a Spatial Point Process Mixture Model
Jun 11, 2016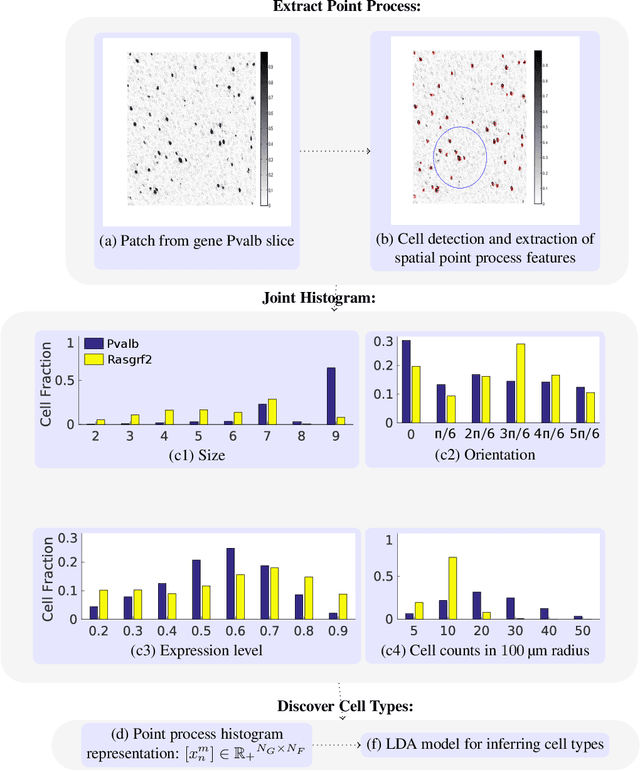
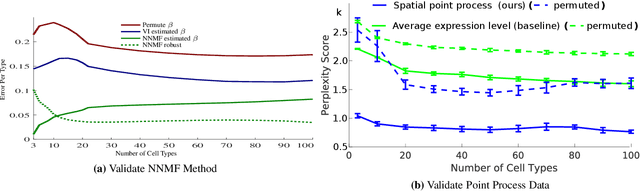
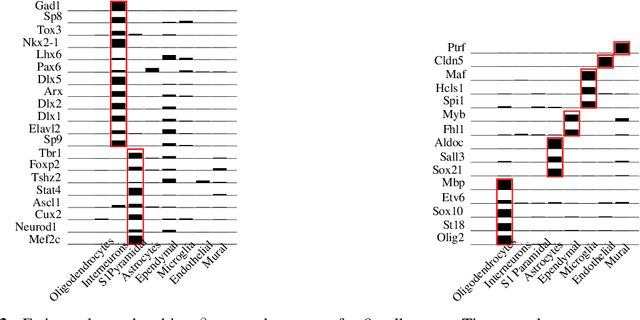
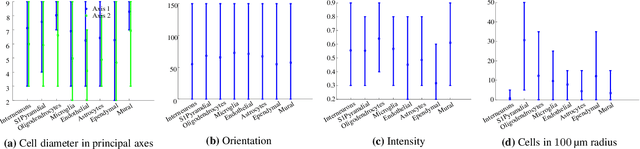
Abstract:Cataloging the neuronal cell types that comprise circuitry of individual brain regions is a major goal of modern neuroscience and the BRAIN initiative. Single-cell RNA sequencing can now be used to measure the gene expression profiles of individual neurons and to categorize neurons based on their gene expression profiles. While the single-cell techniques are extremely powerful and hold great promise, they are currently still labor intensive, have a high cost per cell, and, most importantly, do not provide information on spatial distribution of cell types in specific regions of the brain. We propose a complementary approach that uses computational methods to infer the cell types and their gene expression profiles through analysis of brain-wide single-cell resolution in situ hybridization (ISH) imagery contained in the Allen Brain Atlas (ABA). We measure the spatial distribution of neurons labeled in the ISH image for each gene and model it as a spatial point process mixture, whose mixture weights are given by the cell types which express that gene. By fitting a point process mixture model jointly to the ISH images, we infer both the spatial point process distribution for each cell type and their gene expression profile. We validate our predictions of cell type-specific gene expression profiles using single cell RNA sequencing data, recently published for the mouse somatosensory cortex. Jointly with the gene expression profiles, cell features such as cell size, orientation, intensity and local density level are inferred per cell type.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge