Sridhama Prakhya
Unsupervised Separation of Native and Loanwords for Malayalam and Telugu
Feb 12, 2020
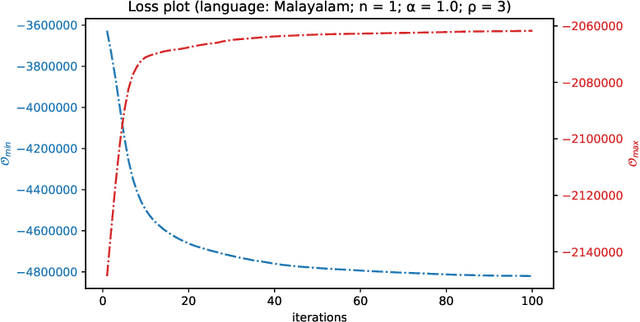
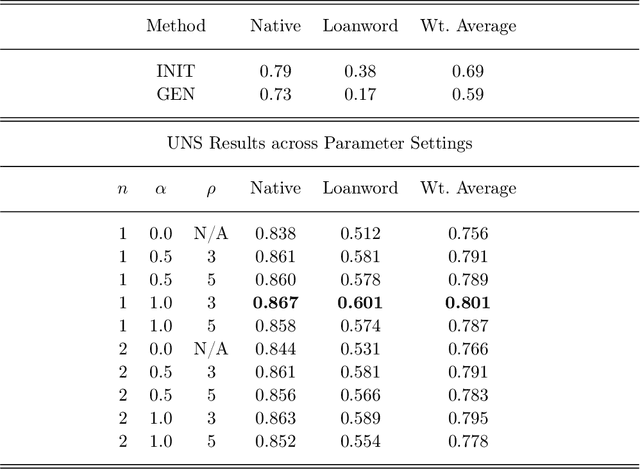
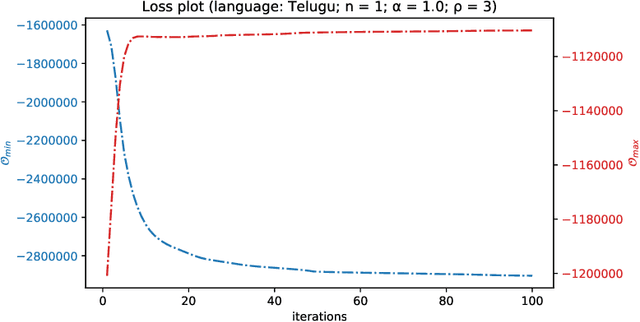
Abstract:Quite often, words from one language are adopted within a different language without translation; these words appear in transliterated form in text written in the latter language. This phenomenon is particularly widespread within Indian languages where many words are loaned from English. In this paper, we address the task of identifying loanwords automatically and in an unsupervised manner, from large datasets of words from agglutinative Dravidian languages. We target two specific languages from the Dravidian family, viz., Malayalam and Telugu. Based on familiarity with the languages, we outline an observation that native words in both these languages tend to be characterized by a much more versatile stem - stem being a shorthand to denote the subword sequence formed by the first few characters of the word - than words that are loaned from other languages. We harness this observation to build an objective function and an iterative optimization formulation to optimize for it, yielding a scoring of each word's nativeness in the process. Through an extensive empirical analysis over real-world datasets from both Malayalam and Telugu, we illustrate the effectiveness of our method in quantifying nativeness effectively over available baselines for the task.
Importance Weighted Adversarial Variational Autoencoders for Spike Inference from Calcium Imaging Data
Jun 07, 2019
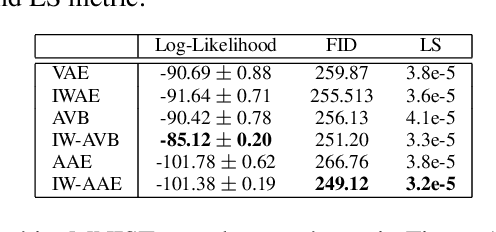
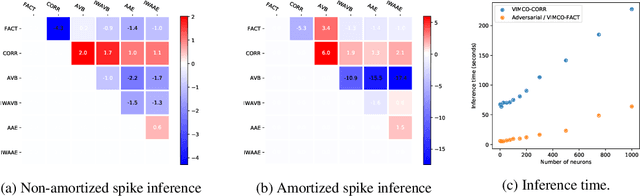
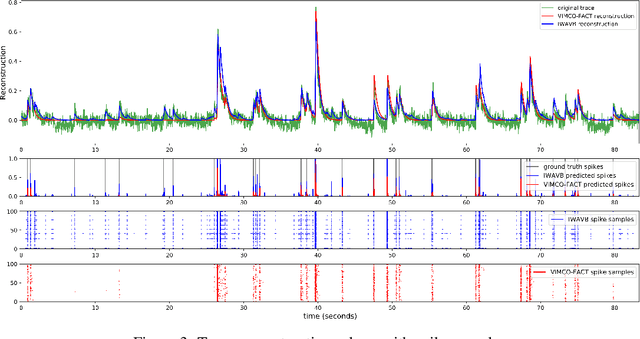
Abstract:The Importance Weighted Auto Encoder (IWAE) objective has been shown to improve the training of generative models over the standard Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) objective. Here, we derive importance weighted extensions to AVB and AAE. These latent variable models use implicitly defined inference networks whose approximate posterior density q_\phi(z|x) cannot be directly evaluated, an essential ingredient for importance weighting. We show improved training and inference in latent variable models with our adversarially trained importance weighting method, and derive new theoretical connections between adversarial generative model training criteria and marginal likelihood based methods. We apply these methods to the important problem of inferring spiking neural activity from calcium imaging data, a challenging posterior inference problem in neuroscience, and show that posterior samples from the adversarial methods outperform factorized posteriors used in VAEs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge