Siqi Huang
Laytrol: Preserving Pretrained Knowledge in Layout Control for Multimodal Diffusion Transformers
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:With the development of diffusion models, enhancing spatial controllability in text-to-image generation has become a vital challenge. As a representative task for addressing this challenge, layout-to-image generation aims to generate images that are spatially consistent with the given layout condition. Existing layout-to-image methods typically introduce the layout condition by integrating adapter modules into the base generative model. However, the generated images often exhibit low visual quality and stylistic inconsistency with the base model, indicating a loss of pretrained knowledge. To alleviate this issue, we construct the Layout Synthesis (LaySyn) dataset, which leverages images synthesized by the base model itself to mitigate the distribution shift from the pretraining data. Moreover, we propose the Layout Control (Laytrol) Network, in which parameters are inherited from MM-DiT to preserve the pretrained knowledge of the base model. To effectively activate the copied parameters and avoid disturbance from unstable control conditions, we adopt a dedicated initialization scheme for Laytrol. In this scheme, the layout encoder is initialized as a pure text encoder to ensure that its output tokens remain within the data domain of MM-DiT. Meanwhile, the outputs of the layout control network are initialized to zero. In addition, we apply Object-level Rotary Position Embedding to the layout tokens to provide coarse positional information. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
CoLM: Collaborative Large Models via A Client-Server Paradigm
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Large models have achieved remarkable performance across a range of reasoning and understanding tasks. Prior work often utilizes model ensembles or multi-agent systems to collaboratively generate responses, effectively operating in a server-to-server paradigm. However, such approaches do not align well with practical deployment settings, where a limited number of server-side models are shared by many clients under modern internet architectures. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{CoLM} (\textbf{Co}llaboration in \textbf{L}arge-\textbf{M}odels), a novel framework for collaborative reasoning that redefines cooperation among large models from a client-server perspective. Unlike traditional ensemble methods that rely on simultaneous inference from multiple models to produce a single output, CoLM allows the outputs of multiple models to be aggregated or shared, enabling each client model to independently refine and update its own generation based on these high-quality outputs. This design enables collaborative benefits by fully leveraging both client-side and shared server-side models. We further extend CoLM to vision-language models (VLMs), demonstrating its applicability beyond language tasks. Experimental results across multiple benchmarks show that CoLM consistently improves model performance on previously failed queries, highlighting the effectiveness of collaborative guidance in enhancing single-model capabilities.
AI Flow: Perspectives, Scenarios, and Approaches
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Pioneered by the foundational information theory by Claude Shannon and the visionary framework of machine intelligence by Alan Turing, the convergent evolution of information and communication technologies (IT/CT) has created an unbroken wave of connectivity and computation. This synergy has sparked a technological revolution, now reaching its peak with large artificial intelligence (AI) models that are reshaping industries and redefining human-machine collaboration. However, the realization of ubiquitous intelligence faces considerable challenges due to substantial resource consumption in large models and high communication bandwidth demands. To address these challenges, AI Flow has been introduced as a multidisciplinary framework that integrates cutting-edge IT and CT advancements, with a particular emphasis on the following three key points. First, device-edge-cloud framework serves as the foundation, which integrates end devices, edge servers, and cloud clusters to optimize scalability and efficiency for low-latency model inference. Second, we introduce the concept of familial models, which refers to a series of different-sized models with aligned hidden features, enabling effective collaboration and the flexibility to adapt to varying resource constraints and dynamic scenarios. Third, connectivity- and interaction-based intelligence emergence is a novel paradigm of AI Flow. By leveraging communication networks to enhance connectivity, the collaboration among AI models across heterogeneous nodes achieves emergent intelligence that surpasses the capability of any single model. The innovations of AI Flow provide enhanced intelligence, timely responsiveness, and ubiquitous accessibility to AI services, paving the way for the tighter fusion of AI techniques and communication systems.
Learn Beneficial Noise as Graph Augmentation
May 25, 2025Abstract:Although graph contrastive learning (GCL) has been widely investigated, it is still a challenge to generate effective and stable graph augmentations. Existing methods often apply heuristic augmentation like random edge dropping, which may disrupt important graph structures and result in unstable GCL performance. In this paper, we propose Positive-incentive Noise driven Graph Data Augmentation (PiNGDA), where positive-incentive noise (pi-noise) scientifically analyzes the beneficial effect of noise under the information theory. To bridge the standard GCL and pi-noise framework, we design a Gaussian auxiliary variable to convert the loss function to information entropy. We prove that the standard GCL with pre-defined augmentations is equivalent to estimate the beneficial noise via the point estimation. Following our analysis, PiNGDA is derived from learning the beneficial noise on both topology and attributes through a trainable noise generator for graph augmentations, instead of the simple estimation. Since the generator learns how to produce beneficial perturbations on graph topology and node attributes, PiNGDA is more reliable compared with the existing methods. Extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness and stability of PiNGDA.
Why Does Dropping Edges Usually Outperform Adding Edges in Graph Contrastive Learning?
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Graph contrastive learning (GCL) has been widely used as an effective self-supervised learning method for graph representation learning. However, how to apply adequate and stable graph augmentation to generating proper views for contrastive learning remains an essential problem. Dropping edges is a primary augmentation in GCL while adding edges is not a common method due to its unstable performance. To our best knowledge, there is no theoretical analysis to study why dropping edges usually outperforms adding edges. To answer this question, we introduce a new metric, namely Error Passing Rate (EPR), to quantify how a graph fits the network. Inspired by the theoretical conclusions, we propose a novel GCL algorithm, Error-PAssing-based Graph Contrastive Learning (EPAGCL), which uses both edge adding and edge dropping as its augmentation. To be specific, we generate views by adding and dropping edges according to the weights derived from EPR. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets are conducted to validate the correctness of our theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of our proposed algorithm.
A Dataset and Model for Realistic License Plate Deblurring
Apr 23, 2024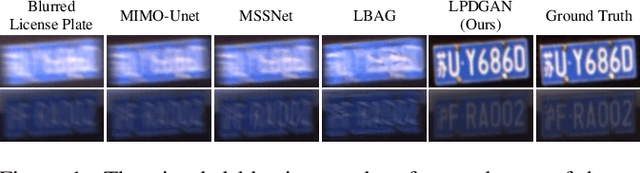
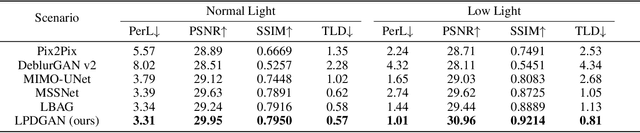
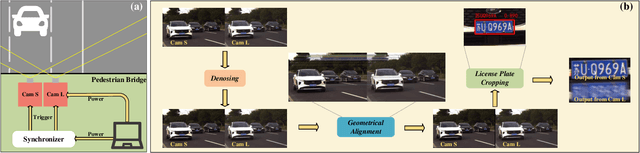
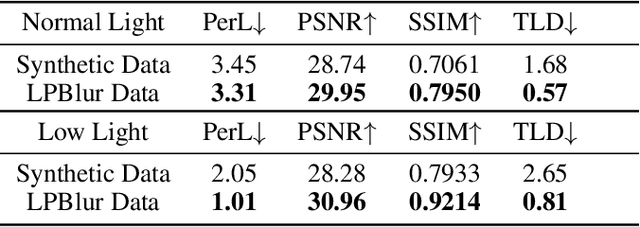
Abstract:Vehicle license plate recognition is a crucial task in intelligent traffic management systems. However, the challenge of achieving accurate recognition persists due to motion blur from fast-moving vehicles. Despite the widespread use of image synthesis approaches in existing deblurring and recognition algorithms, their effectiveness in real-world scenarios remains unproven. To address this, we introduce the first large-scale license plate deblurring dataset named License Plate Blur (LPBlur), captured by a dual-camera system and processed through a post-processing pipeline to avoid misalignment issues. Then, we propose a License Plate Deblurring Generative Adversarial Network (LPDGAN) to tackle the license plate deblurring: 1) a Feature Fusion Module to integrate multi-scale latent codes; 2) a Text Reconstruction Module to restore structure through textual modality; 3) a Partition Discriminator Module to enhance the model's perception of details in each letter. Extensive experiments validate the reliability of the LPBlur dataset for both model training and testing, showcasing that our proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art motion deblurring methods in realistic license plate deblurring scenarios. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/haoyGONG/LPDGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge