Haoyan Gong
LP-LLM: End-to-End Real-World Degraded License Plate Text Recognition via Large Multimodal Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Real-world License Plate Recognition (LPR) faces significant challenges from severe degradations such as motion blur, low resolution, and complex illumination. The prevailing "restoration-then-recognition" two-stage paradigm suffers from a fundamental flaw: the pixel-level optimization objectives of image restoration models are misaligned with the semantic goals of character recognition, leading to artifact interference and error accumulation. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated powerful general capabilities, they lack explicit structural modeling for license plate character sequences (e.g., fixed length, specific order). To address this, we propose an end-to-end structure-aware multimodal reasoning framework based on Qwen3-VL. The core innovation lies in the Character-Aware Multimodal Reasoning Module (CMRM), which introduces a set of learnable Character Slot Queries. Through a cross-attention mechanism, these queries actively retrieve fine-grained evidence corresponding to character positions from visual features. Subsequently, we inject these character-aware representations back into the visual tokens via residual modulation, enabling the language model to perform autoregressive generation based on explicit structural priors. Furthermore, combined with the LoRA parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategy, the model achieves domain adaptation while retaining the generalization capabilities of the large model. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world severely degraded datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing restoration-recognition combinations and general VLMs, validating the superiority of incorporating structured reasoning into large models for low-quality text recognition tasks.
A Dataset and Model for Realistic License Plate Deblurring
Apr 23, 2024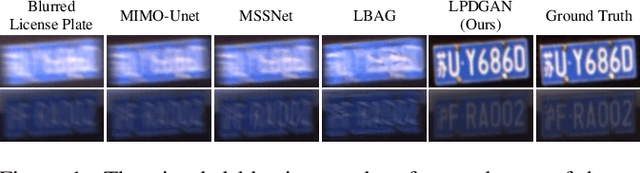
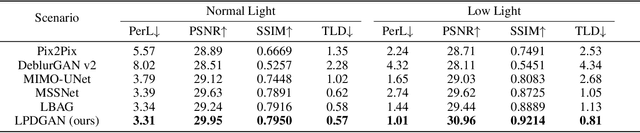
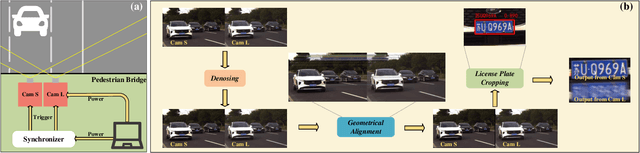
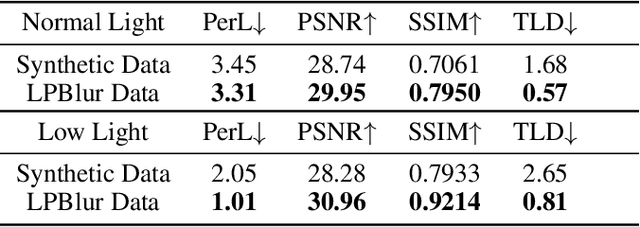
Abstract:Vehicle license plate recognition is a crucial task in intelligent traffic management systems. However, the challenge of achieving accurate recognition persists due to motion blur from fast-moving vehicles. Despite the widespread use of image synthesis approaches in existing deblurring and recognition algorithms, their effectiveness in real-world scenarios remains unproven. To address this, we introduce the first large-scale license plate deblurring dataset named License Plate Blur (LPBlur), captured by a dual-camera system and processed through a post-processing pipeline to avoid misalignment issues. Then, we propose a License Plate Deblurring Generative Adversarial Network (LPDGAN) to tackle the license plate deblurring: 1) a Feature Fusion Module to integrate multi-scale latent codes; 2) a Text Reconstruction Module to restore structure through textual modality; 3) a Partition Discriminator Module to enhance the model's perception of details in each letter. Extensive experiments validate the reliability of the LPBlur dataset for both model training and testing, showcasing that our proposed model outperforms other state-of-the-art motion deblurring methods in realistic license plate deblurring scenarios. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/haoyGONG/LPDGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge