Sihang Cai
HVD: Human Vision-Driven Video Representation Learning for Text-Video Retrieval
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:The success of CLIP has driven substantial progress in text-video retrieval. However, current methods often suffer from "blind" feature interaction, where the model struggles to discern key visual information from background noise due to the sparsity of textual queries. To bridge this gap, we draw inspiration from human cognitive behavior and propose the Human Vision-Driven (HVD) model. Our framework establishes a coarse-to-fine alignment mechanism comprising two key components: the Frame Features Selection Module (FFSM) and the Patch Features Compression Module (PFCM). FFSM mimics the human macro-perception ability by selecting key frames to eliminate temporal redundancy. Subsequently, PFCM simulates micro-perception by aggregating patch features into salient visual entities through an advanced attention mechanism, enabling precise entity-level matching. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate that HVD not only captures human-like visual focus but also achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Chat-Driven Text Generation and Interaction for Person Retrieval
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Text-based person search (TBPS) enables the retrieval of person images from large-scale databases using natural language descriptions, offering critical value in surveillance applications. However, a major challenge lies in the labor-intensive process of obtaining high-quality textual annotations, which limits scalability and practical deployment. To address this, we introduce two complementary modules: Multi-Turn Text Generation (MTG) and Multi-Turn Text Interaction (MTI). MTG generates rich pseudo-labels through simulated dialogues with MLLMs, producing fine-grained and diverse visual descriptions without manual supervision. MTI refines user queries at inference time through dynamic, dialogue-based reasoning, enabling the system to interpret and resolve vague, incomplete, or ambiguous descriptions - characteristics often seen in real-world search scenarios. Together, MTG and MTI form a unified and annotation-free framework that significantly improves retrieval accuracy, robustness, and usability. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves competitive or superior results while eliminating the need for manual captions, paving the way for scalable and practical deployment of TBPS systems.
Astrea: A MOE-based Visual Understanding Model with Progressive Alignment
Mar 12, 2025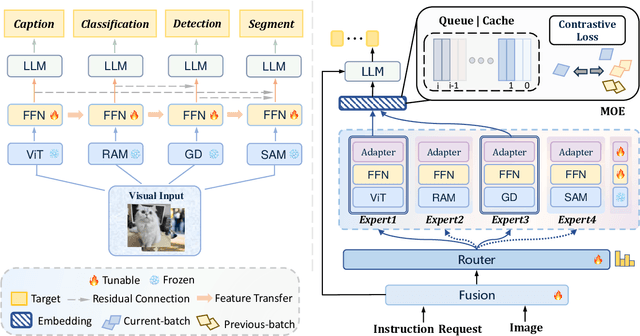
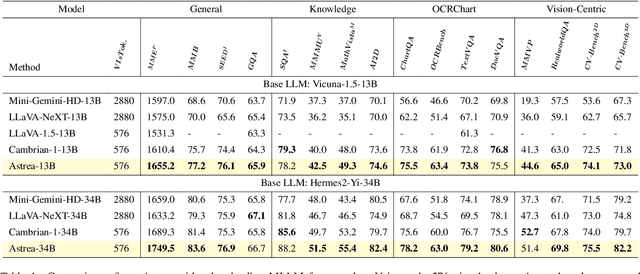
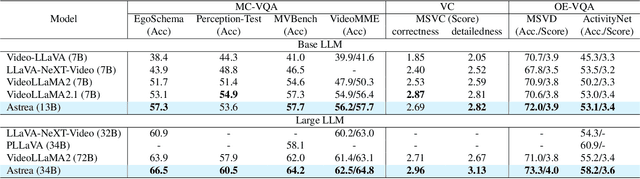
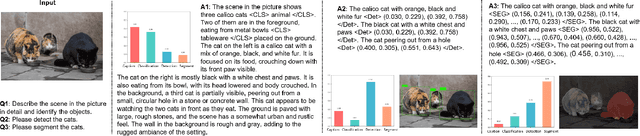
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) based on Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have emerged as a pivotal paradigm in multimodal understanding, offering a powerful framework for integrating visual and linguistic information. However, the increasing complexity and diversity of tasks present significant challenges in coordinating load balancing across heterogeneous visual experts, where optimizing one specialist's performance often compromises others' capabilities. To address task heterogeneity and expert load imbalance, we propose Astrea, a novel multi-expert collaborative VLM architecture based on progressive pre-alignment. Astrea introduces three key innovations: 1) A heterogeneous expert coordination mechanism that integrates four specialized models (detection, segmentation, classification, captioning) into a comprehensive expert matrix covering essential visual comprehension elements; 2) A dynamic knowledge fusion strategy featuring progressive pre-alignment to harmonize experts within the VLM latent space through contrastive learning, complemented by probabilistically activated stochastic residual connections to preserve knowledge continuity; 3) An enhanced optimization framework utilizing momentum contrastive learning for long-range dependency modeling and adaptive weight allocators for real-time expert contribution calibration. Extensive evaluations across 12 benchmark tasks spanning VQA, image captioning, and cross-modal retrieval demonstrate Astrea's superiority over state-of-the-art models, achieving an average performance gain of +4.7\%. This study provides the first empirical demonstration that progressive pre-alignment strategies enable VLMs to overcome task heterogeneity limitations, establishing new methodological foundations for developing general-purpose multimodal agents.
EAGER-LLM: Enhancing Large Language Models as Recommenders through Exogenous Behavior-Semantic Integration
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly leveraged as foundational backbones in the development of advanced recommender systems, offering enhanced capabilities through their extensive knowledge and reasoning. Existing llm-based recommender systems (RSs) often face challenges due to the significant differences between the linguistic semantics of pre-trained LLMs and the collaborative semantics essential for RSs. These systems use pre-trained linguistic semantics but learn collaborative semantics from scratch via the llm-Backbone. However, LLMs are not designed for recommendations, leading to inefficient collaborative learning, weak result correlations, and poor integration of traditional RS features. To address these challenges, we propose EAGER-LLM, a decoder-only llm-based generative recommendation framework that integrates endogenous and exogenous behavioral and semantic information in a non-intrusive manner. Specifically, we propose 1)dual-source knowledge-rich item indices that integrates indexing sequences for exogenous signals, enabling efficient link-wide processing; 2)non-invasive multiscale alignment reconstruction tasks guide the model toward a deeper understanding of both collaborative and semantic signals; 3)an annealing adapter designed to finely balance the model's recommendation performance with its comprehension capabilities. We demonstrate EAGER-LLM's effectiveness through rigorous testing on three public benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge