Shicheng Liu
Explainable reinforcement learning from human feedback to improve alignment
Dec 15, 2025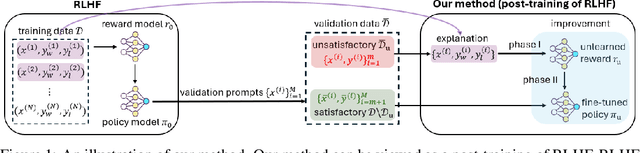
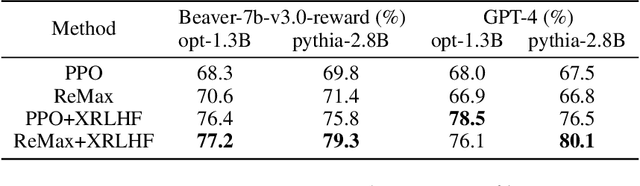
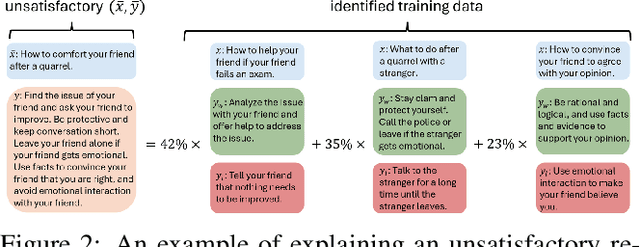
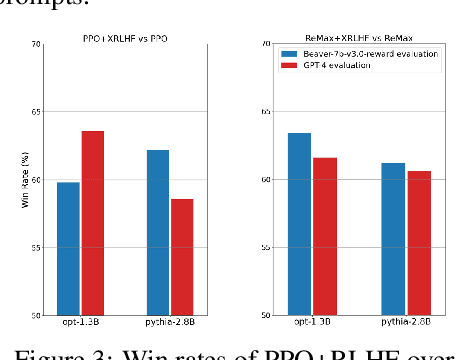
Abstract:A common and effective strategy for humans to improve an unsatisfactory outcome in daily life is to find a cause of this outcome and correct the cause. In this paper, we investigate whether this human improvement strategy can be applied to improving reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) for alignment of language models (LMs). In particular, it is observed in the literature that LMs tuned by RLHF can still output unsatisfactory responses. This paper proposes a method to improve the unsatisfactory responses by correcting their causes. Our method has two parts. The first part proposes a post-hoc explanation method to explain why an unsatisfactory response is generated to a prompt by identifying the training data that lead to this response. We formulate this problem as a constrained combinatorial optimization problem where the objective is to find a set of training data closest to this prompt-response pair in a feature representation space, and the constraint is that the prompt-response pair can be decomposed as a convex combination of this set of training data in the feature space. We propose an efficient iterative data selection algorithm to solve this problem. The second part proposes an unlearning method that improves unsatisfactory responses to some prompts by unlearning the training data that lead to these unsatisfactory responses and, meanwhile, does not significantly degrade satisfactory responses to other prompts. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm can improve RLHF.
SCRIBES: Web-Scale Script-Based Semi-Structured Data Extraction with Reinforcement Learning
Oct 02, 2025
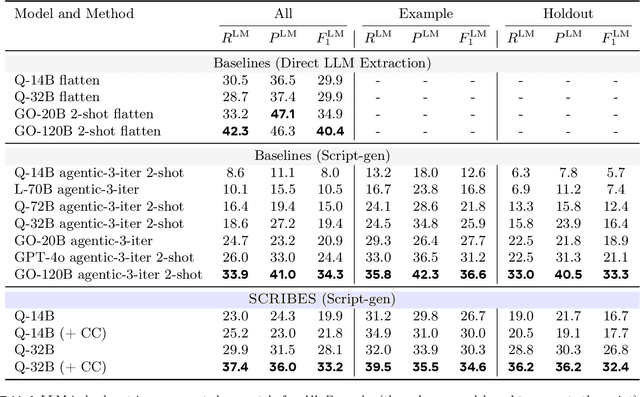

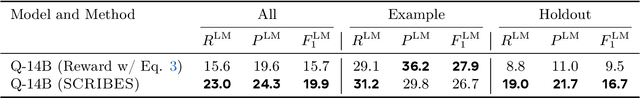
Abstract:Semi-structured content in HTML tables, lists, and infoboxes accounts for a substantial share of factual data on the web, yet the formatting complicates usage, and reliably extracting structured information from them remains challenging. Existing methods either lack generalization or are resource-intensive due to per-page LLM inference. In this paper, we introduce SCRIBES (SCRIpt-Based Semi-Structured Content Extraction at Web-Scale), a novel reinforcement learning framework that leverages layout similarity across webpages within the same site as a reward signal. Instead of processing each page individually, SCRIBES generates reusable extraction scripts that can be applied to groups of structurally similar webpages. Our approach further improves by iteratively training on synthetic annotations from in-the-wild CommonCrawl data. Experiments show that our approach outperforms strong baselines by over 13% in script quality and boosts downstream question answering accuracy by more than 4% for GPT-4o, enabling scalable and resource-efficient web information extraction.
Prompting Large Language Models for Training-Free Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring
May 09, 2025Abstract:Non-intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) aims to disaggregate aggregate household electricity consumption into individual appliance usage, enabling more effective energy management. While deep learning has advanced NILM, it remains limited by its dependence on labeled data, restricted generalization, and lack of interpretability. In this paper, we introduce the first prompt-based NILM framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) with in-context learning. We design and evaluate prompt strategies that integrate appliance features, timestamps and contextual information, as well as representative time-series examples, using the REDD dataset. With optimized prompts, LLMs achieve competitive state detection accuracy, reaching an average F1-score of 0.676 on unseen households, and demonstrate robust generalization without the need for fine-tuning. LLMs also enhance interpretability by providing clear, human-readable explanations for their predictions. Our results show that LLMs can reduce data requirements, improve adaptability, and provide transparent energy disaggregation in NILM applications.
In-Trajectory Inverse Reinforcement Learning: Learn Incrementally From An Ongoing Trajectory
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) aims to learn a reward function and a corresponding policy that best fit the demonstrated trajectories of an expert. However, current IRL works cannot learn incrementally from an ongoing trajectory because they have to wait to collect at least one complete trajectory to learn. To bridge the gap, this paper considers the problem of learning a reward function and a corresponding policy while observing the initial state-action pair of an ongoing trajectory and keeping updating the learned reward and policy when new state-action pairs of the ongoing trajectory are observed. We formulate this problem as an online bi-level optimization problem where the upper level dynamically adjusts the learned reward according to the newly observed state-action pairs with the help of a meta-regularization term, and the lower level learns the corresponding policy. We propose a novel algorithm to solve this problem and guarantee that the algorithm achieves sub-linear local regret $O(\sqrt{T}+\log T+\sqrt{T}\log T)$. If the reward function is linear, we prove that the proposed algorithm achieves sub-linear regret $O(\log T)$. Experiments are used to validate the proposed algorithm.
A Survey of Inverse Constrained Reinforcement Learning: Definitions, Progress and Challenges
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Inverse Constrained Reinforcement Learning (ICRL) is the task of inferring the implicit constraints followed by expert agents from their demonstration data. As an emerging research topic, ICRL has received considerable attention in recent years. This article presents a categorical survey of the latest advances in ICRL. It serves as a comprehensive reference for machine learning researchers and practitioners, as well as starters seeking to comprehend the definitions, advancements, and important challenges in ICRL. We begin by formally defining the problem and outlining the algorithmic framework that facilitates constraint inference across various scenarios. These include deterministic or stochastic environments, environments with limited demonstrations, and multiple agents. For each context, we illustrate the critical challenges and introduce a series of fundamental methods to tackle these issues. This survey encompasses discrete, virtual, and realistic environments for evaluating ICRL agents. We also delve into the most pertinent applications of ICRL, such as autonomous driving, robot control, and sports analytics. To stimulate continuing research, we conclude the survey with a discussion of key unresolved questions in ICRL that can effectively foster a bridge between theoretical understanding and practical industrial applications.
SPINACH: SPARQL-Based Information Navigation for Challenging Real-World Questions
Jul 16, 2024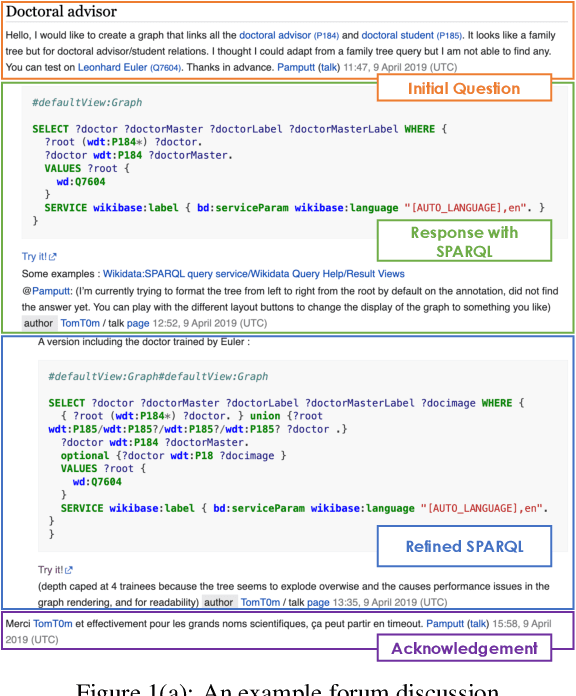

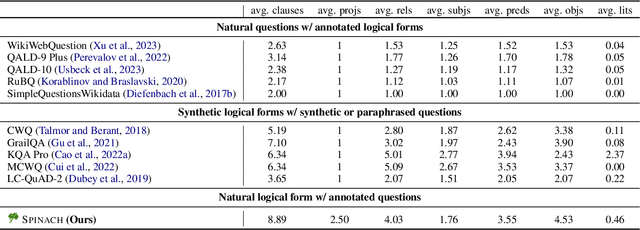
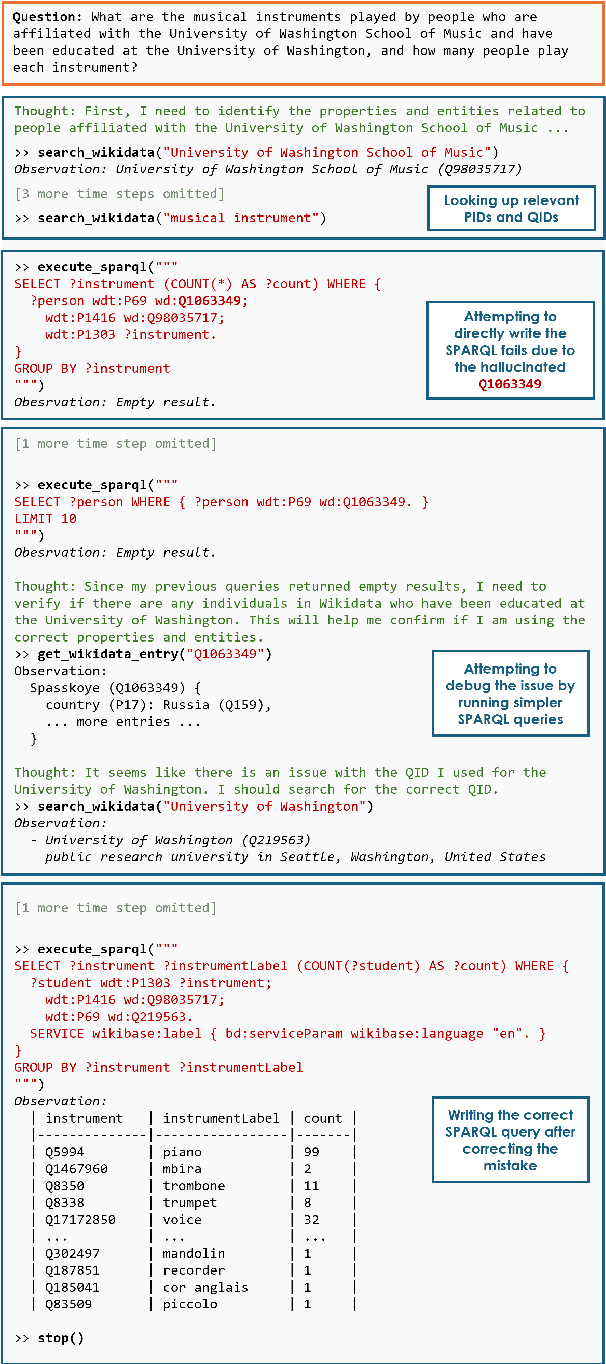
Abstract:Recent work integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to significant improvements in the Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) task. However, we posit that existing KBQA datasets that either have simple questions, use synthetically generated logical forms, or are based on small knowledge base (KB) schemas, do not capture the true complexity of KBQA tasks. To address this, we introduce the SPINACH dataset, an expert-annotated KBQA dataset collected from forum discussions on Wikidata's "Request a Query" forum with 320 decontextualized question-SPARQL pairs. Much more complex than existing datasets, SPINACH calls for strong KBQA systems that do not rely on training data to learn the KB schema, but can dynamically explore large and often incomplete schemas and reason about them. Along with the dataset, we introduce the SPINACH agent, a new KBQA approach that mimics how a human expert would write SPARQLs for such challenging questions. Experiments on existing datasets show SPINACH's capability in KBQA, achieving a new state of the art on the QALD-7, QALD-9 Plus and QALD-10 datasets by 30.1%, 27.0%, and 10.0% in F1, respectively, and coming within 1.6% of the fine-tuned LLaMA SOTA model on WikiWebQuestions. On our new SPINACH dataset, SPINACH agent outperforms all baselines, including the best GPT-4-based KBQA agent, by 38.1% in F1.
LLM-Based Open-Domain Integrated Task and Knowledge Assistants with Programmable Policies
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Programming LLM-based knowledge and task assistants that faithfully conform to developer-provided policies is challenging. These agents must retrieve and provide consistent, accurate, and relevant information to address user's queries and needs. Yet such agents generate unfounded responses ("hallucinate"). Traditional dialogue trees can only handle a limited number of conversation flows, making them inherently brittle. To this end, we present KITA - a programmable framework for creating task-oriented conversational agents that are designed to handle complex user interactions. Unlike LLMs, KITA provides reliable grounded responses, with controllable agent policies through its expressive specification, KITA Worksheet. In contrast to dialog trees, it is resilient to diverse user queries, helpful with knowledge sources, and offers ease of programming policies through its declarative paradigm. Through a real-user study involving 62 participants, we show that KITA beats the GPT-4 with function calling baseline by 26.1, 22.5, and 52.4 points on execution accuracy, dialogue act accuracy, and goal completion rate, respectively. We also release 22 real-user conversations with KITA manually corrected to ensure accuracy.
SPAGHETTI: Open-Domain Question Answering from Heterogeneous Data Sources with Retrieval and Semantic Parsing
Jun 01, 2024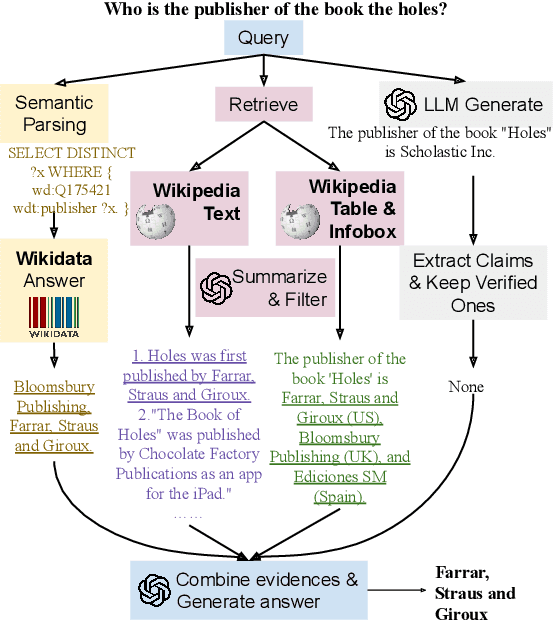
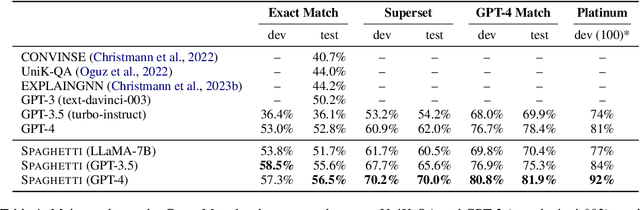
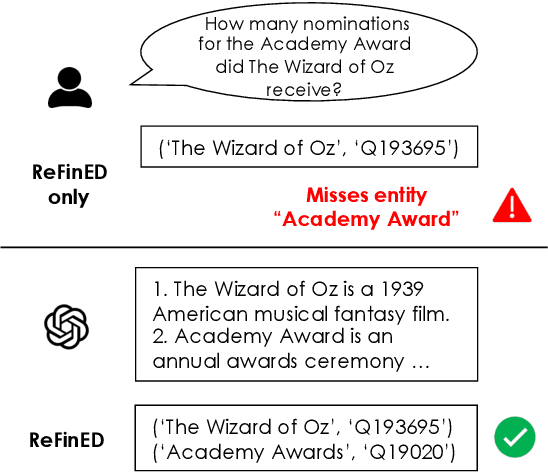

Abstract:We introduce SPAGHETTI: Semantic Parsing Augmented Generation for Hybrid English information from Text Tables and Infoboxes, a hybrid question-answering (QA) pipeline that utilizes information from heterogeneous knowledge sources, including knowledge base, text, tables, and infoboxes. Our LLM-augmented approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Compmix dataset, the most comprehensive heterogeneous open-domain QA dataset, with 56.5% exact match (EM) rate. More importantly, manual analysis on a sample of the dataset suggests that SPAGHETTI is more than 90% accurate, indicating that EM is no longer suitable for assessing the capabilities of QA systems today.
SUQL: Conversational Search over Structured and Unstructured Data with Large Language Models
Nov 16, 2023



Abstract:Many knowledge sources consist of both structured information such as relational databases as well as unstructured free text. Building a conversational interface to such data sources is challenging. This paper introduces SUQL, Structured and Unstructured Query Language, the first formal executable representation that naturally covers compositions of structured and unstructured data queries. Specifically, it augments SQL with several free-text primitives to form a precise, succinct, and expressive representation. This paper also presents a conversational search agent based on large language models, including a few-shot contextual semantic parser for SUQL. To validate our approach, we introduce a dataset consisting of crowdsourced questions and conversations about real restaurants. Over 51% of the questions in the dataset require both structured and unstructured data, suggesting that it is a common phenomenon. We show that our few-shot conversational agent based on SUQL finds an entity satisfying all user requirements 89.3% of the time, compared to just 65.0% for a strong and commonly used baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge