Shengyin Shen
Behavioral Safety Assessment towards Large-scale Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles
May 22, 2025Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) have significantly advanced in real-world deployment in recent years, yet safety continues to be a critical barrier to widespread adoption. Traditional functional safety approaches, which primarily verify the reliability, robustness, and adequacy of AV hardware and software systems from a vehicle-centric perspective, do not sufficiently address the AV's broader interactions and behavioral impact on the surrounding traffic environment. To overcome this limitation, we propose a paradigm shift toward behavioral safety, a comprehensive approach focused on evaluating AV responses and interactions within the traffic environment. To systematically assess behavioral safety, we introduce a third-party AV safety assessment framework comprising two complementary evaluation components: the Driver Licensing Test and the Driving Intelligence Test. The Driver Licensing Test evaluates the AV's reactive behaviors under controlled scenarios, ensuring basic behavioral competency. In contrast, the Driving Intelligence Test assesses the AV's interactive behaviors within naturalistic traffic conditions, quantifying the frequency of safety-critical events to deliver statistically meaningful safety metrics before large-scale deployment. We validated our proposed framework using Autoware.Universe, an open-source Level 4 AV, tested both in simulated environments and on the physical test track at the University of Michigan's Mcity Testing Facility. The results indicate that Autoware.Universe passed 6 out of 14 scenarios and exhibited a crash rate of 3.01e-3 crashes per mile, approximately 1,000 times higher than the average human driver crash rate. During the tests, we also uncovered several unknown unsafe scenarios for Autoware.Universe. These findings underscore the necessity of behavioral safety evaluations for improving AV safety performance prior to widespread public deployment.
TeraSim: Uncovering Unknown Unsafe Events for Autonomous Vehicles through Generative Simulation
Mar 06, 2025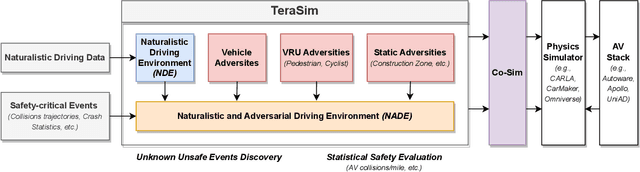
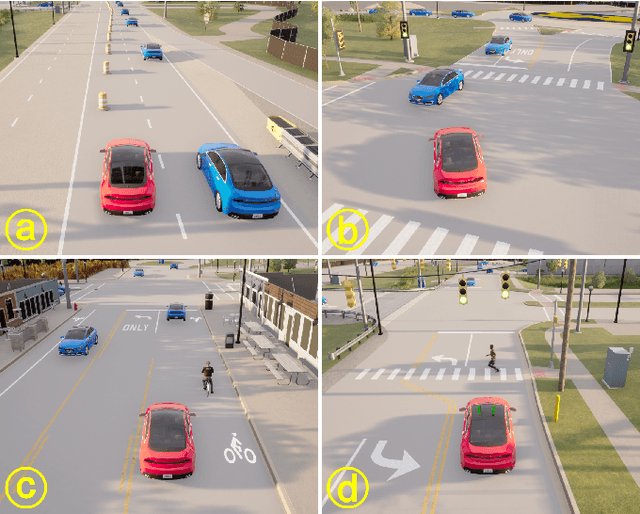
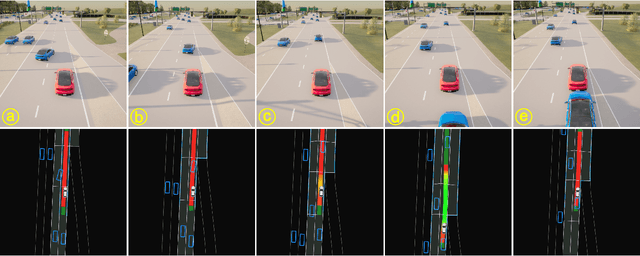
Abstract:Traffic simulation is essential for autonomous vehicle (AV) development, enabling comprehensive safety evaluation across diverse driving conditions. However, traditional rule-based simulators struggle to capture complex human interactions, while data-driven approaches often fail to maintain long-term behavioral realism or generate diverse safety-critical events. To address these challenges, we propose TeraSim, an open-source, high-fidelity traffic simulation platform designed to uncover unknown unsafe events and efficiently estimate AV statistical performance metrics, such as crash rates. TeraSim is designed for seamless integration with third-party physics simulators and standalone AV stacks, to construct a complete AV simulation system. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness in generating diverse safety-critical events involving both static and dynamic agents, identifying hidden deficiencies in AV systems, and enabling statistical performance evaluation. These findings highlight TeraSim's potential as a practical tool for AV safety assessment, benefiting researchers, developers, and policymakers. The code is available at https://github.com/mcity/TeraSim.
Evaluating Roadside Perception for Autonomous Vehicles: Insights from Field Testing
Jan 22, 2024Abstract:Roadside perception systems are increasingly crucial in enhancing traffic safety and facilitating cooperative driving for autonomous vehicles. Despite rapid technological advancements, a major challenge persists for this newly arising field: the absence of standardized evaluation methods and benchmarks for these systems. This limitation hampers the ability to effectively assess and compare the performance of different systems, thus constraining progress in this vital field. This paper introduces a comprehensive evaluation methodology specifically designed to assess the performance of roadside perception systems. Our methodology encompasses measurement techniques, metric selection, and experimental trial design, all grounded in real-world field testing to ensure the practical applicability of our approach. We applied our methodology in Mcity\footnote{\url{https://mcity.umich.edu/}}, a controlled testing environment, to evaluate various off-the-shelf perception systems. This approach allowed for an in-depth comparative analysis of their performance in realistic scenarios, offering key insights into their respective strengths and limitations. The findings of this study are poised to inform the development of industry-standard benchmarks and evaluation methods, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of roadside perception system development and deployment for autonomous vehicles. We anticipate that this paper will stimulate essential discourse on standardizing evaluation methods for roadside perception systems, thus pushing the frontiers of this technology. Furthermore, our results offer both academia and industry a comprehensive understanding of the capabilities of contemporary infrastructure-based perception systems.
MSight: An Edge-Cloud Infrastructure-based Perception System for Connected Automated Vehicles
Oct 08, 2023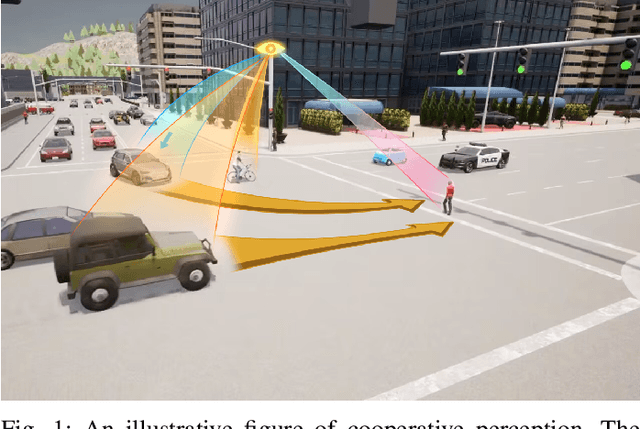
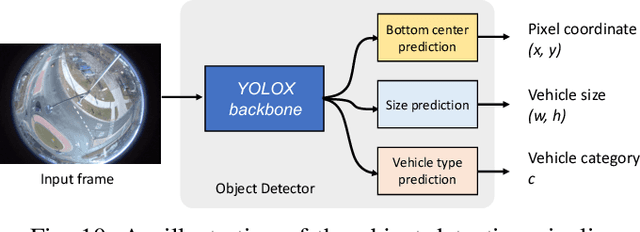
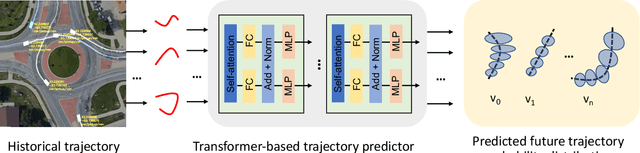
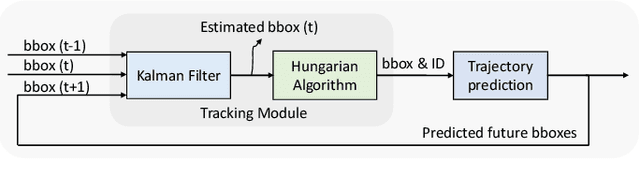
Abstract:As vehicular communication and networking technologies continue to advance, infrastructure-based roadside perception emerges as a pivotal tool for connected automated vehicle (CAV) applications. Due to their elevated positioning, roadside sensors, including cameras and lidars, often enjoy unobstructed views with diminished object occlusion. This provides them a distinct advantage over onboard perception, enabling more robust and accurate detection of road objects. This paper presents MSight, a cutting-edge roadside perception system specifically designed for CAVs. MSight offers real-time vehicle detection, localization, tracking, and short-term trajectory prediction. Evaluations underscore the system's capability to uphold lane-level accuracy with minimal latency, revealing a range of potential applications to enhance CAV safety and efficiency. Presently, MSight operates 24/7 at a two-lane roundabout in the City of Ann Arbor, Michigan.
Robust Roadside Perception for Autonomous Driving: an Annotation-free Strategy with Synthesized Data
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Recently, with the rapid development in vehicle-to-infrastructure communication technologies, the infrastructure-based, roadside perception system for cooperative driving has become a rising field. This paper focuses on one of the most critical challenges - the data-insufficiency problem. The lacking of high-quality labeled roadside sensor data with high diversity leads to low robustness, and low transfer-ability of current roadside perception systems. In this paper, a novel approach is proposed to address this problem by creating synthesized training data using Augmented Reality and Generative Adversarial Network. This method creates synthesized dataset that is capable of training or fine-tuning a roadside perception detector which is robust to different weather and lighting conditions, or to adapt a new deployment location. We validate our approach at two intersections: Mcity intersection and State St/Ellsworth Rd roundabout. Our experiments show that (1) the detector can achieve good performance in all conditions when trained on synthesized data only, and (2) the performance of an existing detector trained with labeled data can be enhanced by synthesized data in harsh conditions.
ROCO: A Roundabout Traffic Conflict Dataset
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:Traffic conflicts have been studied by the transportation research community as a surrogate safety measure for decades. However, due to the rarity of traffic conflicts, collecting large-scale real-world traffic conflict data becomes extremely challenging. In this paper, we introduce and analyze ROCO - a real-world roundabout traffic conflict dataset. The data is collected at a two-lane roundabout at the intersection of State St. and W. Ellsworth Rd. in Ann Arbor, Michigan. We use raw video dataflow captured from four fisheye cameras installed at the roundabout as our input data source. We adopt a learning-based conflict identification algorithm from video to find potential traffic conflicts, and then manually label them for dataset collection and annotation. In total 557 traffic conflicts and 17 traffic crashes are collected from August 2021 to October 2021. We provide trajectory data of the traffic conflict scenes extracted using our roadside perception system. Taxonomy based on traffic conflict severity, reason for the traffic conflict, and its effect on the traffic flow is provided. With the traffic conflict data collected, we discover that failure to yield to circulating vehicles when entering the roundabout is the largest contributing reason for traffic conflicts. ROCO dataset will be made public in the short future.
Real-time Full-stack Traffic Scene Perception for Autonomous Driving with Roadside Cameras
Jun 20, 2022
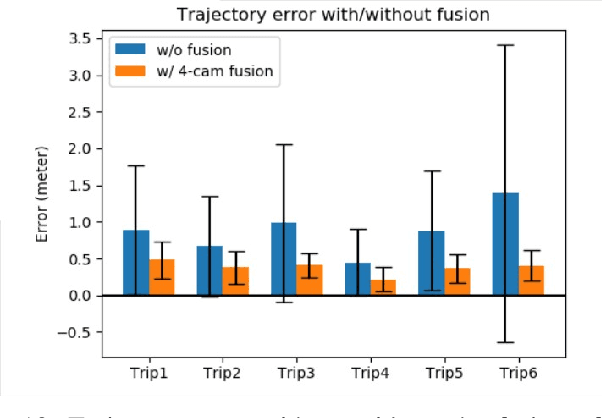
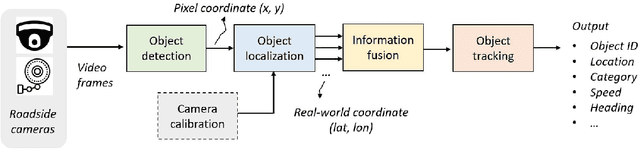
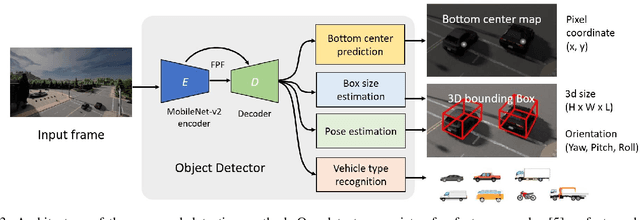
Abstract:We propose a novel and pragmatic framework for traffic scene perception with roadside cameras. The proposed framework covers a full-stack of roadside perception pipeline for infrastructure-assisted autonomous driving, including object detection, object localization, object tracking, and multi-camera information fusion. Unlike previous vision-based perception frameworks rely upon depth offset or 3D annotation at training, we adopt a modular decoupling design and introduce a landmark-based 3D localization method, where the detection and localization can be well decoupled so that the model can be easily trained based on only 2D annotations. The proposed framework applies to either optical or thermal cameras with pinhole or fish-eye lenses. Our framework is deployed at a two-lane roundabout located at Ellsworth Rd. and State St., Ann Arbor, MI, USA, providing 7x24 real-time traffic flow monitoring and high-precision vehicle trajectory extraction. The whole system runs efficiently on a low-power edge computing device with all-component end-to-end delay of less than 20ms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge