Shengwei Zhao
MMRAG-RFT: Two-stage Reinforcement Fine-tuning for Explainable Multi-modal Retrieval-augmented Generation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Multi-modal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MMRAG) enables highly credible generation by integrating external multi-modal knowledge, thus demonstrating impressive performance in complex multi-modal scenarios. However, existing MMRAG methods fail to clarify the reasoning logic behind retrieval and response generation, which limits the explainability of the results. To address this gap, we propose to introduce reinforcement learning into multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation, enhancing the reasoning capabilities of multi-modal large language models through a two-stage reinforcement fine-tuning framework to achieve explainable multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation. Specifically, in the first stage, rule-based reinforcement fine-tuning is employed to perform coarse-grained point-wise ranking of multi-modal documents, effectively filtering out those that are significantly irrelevant. In the second stage, reasoning-based reinforcement fine-tuning is utilized to jointly optimize fine-grained list-wise ranking and answer generation, guiding multi-modal large language models to output explainable reasoning logic in the MMRAG process. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on WebQA and MultimodalQA, two benchmark datasets for multi-modal retrieval-augmented generation, and its effectiveness is validated through comprehensive ablation experiments.
Efficient Low-Resolution Face Recognition via Bridge Distillation
Sep 18, 2024Abstract:Face recognition in the wild is now advancing towards light-weight models, fast inference speed and resolution-adapted capability. In this paper, we propose a bridge distillation approach to turn a complex face model pretrained on private high-resolution faces into a light-weight one for low-resolution face recognition. In our approach, such a cross-dataset resolution-adapted knowledge transfer problem is solved via two-step distillation. In the first step, we conduct cross-dataset distillation to transfer the prior knowledge from private high-resolution faces to public high-resolution faces and generate compact and discriminative features. In the second step, the resolution-adapted distillation is conducted to further transfer the prior knowledge to synthetic low-resolution faces via multi-task learning. By learning low-resolution face representations and mimicking the adapted high-resolution knowledge, a light-weight student model can be constructed with high efficiency and promising accuracy in recognizing low-resolution faces. Experimental results show that the student model performs impressively in recognizing low-resolution faces with only 0.21M parameters and 0.057MB memory. Meanwhile, its speed reaches up to 14,705, ~934 and 763 faces per second on GPU, CPU and mobile phone, respectively.
* This paper is published in IEEE TIP 2020
Look One and More: Distilling Hybrid Order Relational Knowledge for Cross-Resolution Image Recognition
Sep 09, 2024



Abstract:In spite of great success in many image recognition tasks achieved by recent deep models, directly applying them to recognize low-resolution images may suffer from low accuracy due to the missing of informative details during resolution degradation. However, these images are still recognizable for subjects who are familiar with the corresponding high-resolution ones. Inspired by that, we propose a teacher-student learning approach to facilitate low-resolution image recognition via hybrid order relational knowledge distillation. The approach refers to three streams: the teacher stream is pretrained to recognize high-resolution images in high accuracy, the student stream is learned to identify low-resolution images by mimicking the teacher's behaviors, and the extra assistant stream is introduced as bridge to help knowledge transfer across the teacher to the student. To extract sufficient knowledge for reducing the loss in accuracy, the learning of student is supervised with multiple losses, which preserves the similarities in various order relational structures. In this way, the capability of recovering missing details of familiar low-resolution images can be effectively enhanced, leading to a better knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on metric learning, low-resolution image classification and low-resolution face recognition tasks show the effectiveness of our approach, while taking reduced models.
Uncertainty-Aware Learning Against Label Noise on Imbalanced Datasets
Jul 12, 2022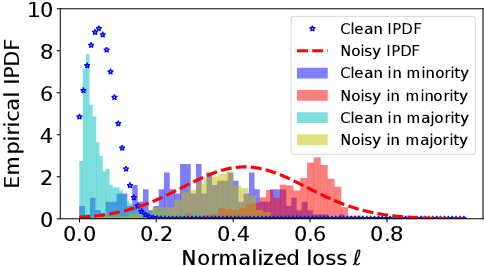
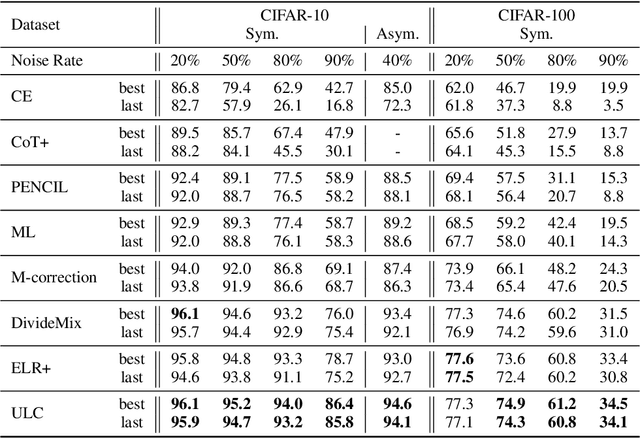
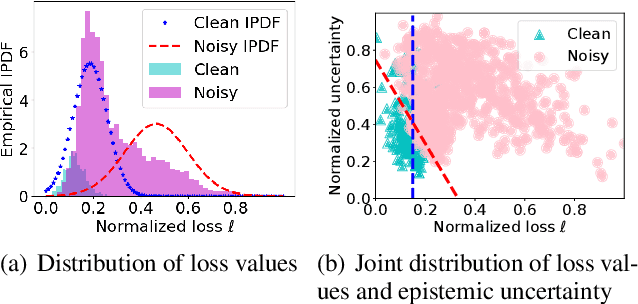
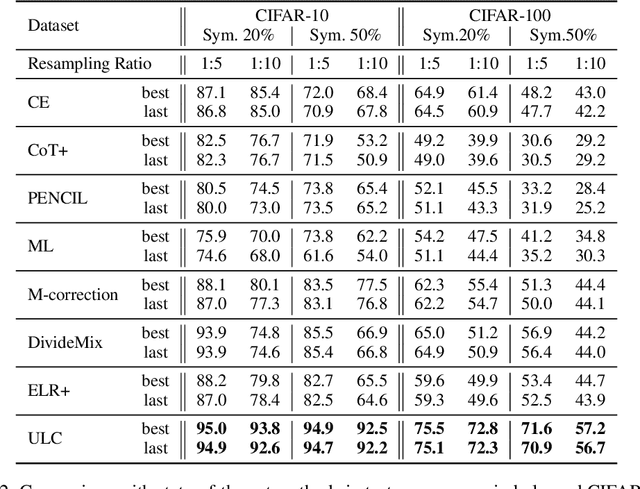
Abstract:Learning against label noise is a vital topic to guarantee a reliable performance for deep neural networks. Recent research usually refers to dynamic noise modeling with model output probabilities and loss values, and then separates clean and noisy samples. These methods have gained notable success. However, unlike cherry-picked data, existing approaches often cannot perform well when facing imbalanced datasets, a common scenario in the real world. We thoroughly investigate this phenomenon and point out two major issues that hinder the performance, i.e., \emph{inter-class loss distribution discrepancy} and \emph{misleading predictions due to uncertainty}. The first issue is that existing methods often perform class-agnostic noise modeling. However, loss distributions show a significant discrepancy among classes under class imbalance, and class-agnostic noise modeling can easily get confused with noisy samples and samples in minority classes. The second issue refers to that models may output misleading predictions due to epistemic uncertainty and aleatoric uncertainty, thus existing methods that rely solely on the output probabilities may fail to distinguish confident samples. Inspired by our observations, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Label Correction framework~(ULC) to handle label noise on imbalanced datasets. First, we perform epistemic uncertainty-aware class-specific noise modeling to identify trustworthy clean samples and refine/discard highly confident true/corrupted labels. Then, we introduce aleatoric uncertainty in the subsequent learning process to prevent noise accumulation in the label noise modeling process. We conduct experiments on several synthetic and real-world datasets. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, especially on imbalanced datasets.
Spatiotemporal Knowledge Distillation for Efficient Estimation of Aerial Video Saliency
Apr 10, 2019



Abstract:The performance of video saliency estimation techniques has achieved significant advances along with the rapid development of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). However, devices like cameras and drones may have limited computational capability and storage space so that the direct deployment of complex deep saliency models becomes infeasible. To address this problem, this paper proposes a dynamic saliency estimation approach for aerial videos via spatiotemporal knowledge distillation. In this approach, five components are involved, including two teachers, two students and the desired spatiotemporal model. The knowledge of spatial and temporal saliency is first separately transferred from the two complex and redundant teachers to their simple and compact students, and the input scenes are also degraded from high-resolution to low-resolution to remove the probable data redundancy so as to greatly speed up the feature extraction process. After that, the desired spatiotemporal model is further trained by distilling and encoding the spatial and temporal saliency knowledge of two students into a unified network. In this manner, the inter-model redundancy can be further removed for the effective estimation of dynamic saliency on aerial videos. Experimental results show that the proposed approach outperforms ten state-of-the-art models in estimating visual saliency on aerial videos, while its speed reaches up to 28,738 FPS on the GPU platform.
Low-resolution Face Recognition in the Wild via Selective Knowledge Distillation
Nov 25, 2018
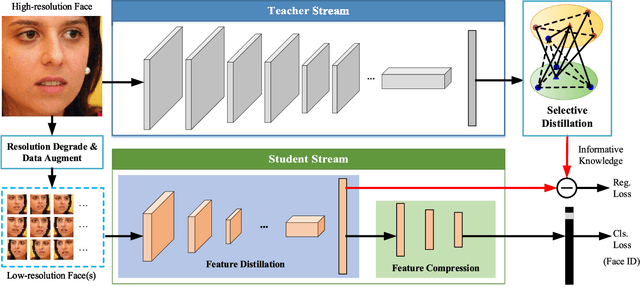
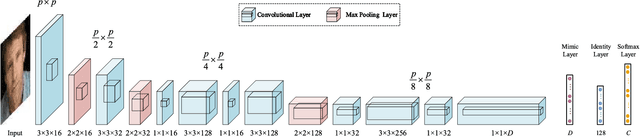
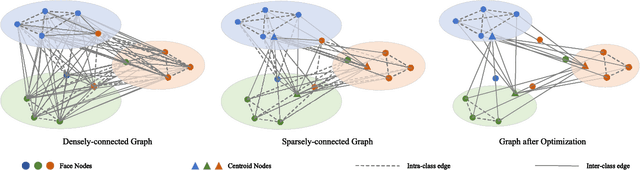
Abstract:Typically, the deployment of face recognition models in the wild needs to identify low-resolution faces with extremely low computational cost. To address this problem, a feasible solution is compressing a complex face model to achieve higher speed and lower memory at the cost of minimal performance drop. Inspired by that, this paper proposes a learning approach to recognize low-resolution faces via selective knowledge distillation. In this approach, a two-stream convolutional neural network (CNN) is first initialized to recognize high-resolution faces and resolution-degraded faces with a teacher stream and a student stream, respectively. The teacher stream is represented by a complex CNN for high-accuracy recognition, and the student stream is represented by a much simpler CNN for low-complexity recognition. To avoid significant performance drop at the student stream, we then selectively distil the most informative facial features from the teacher stream by solving a sparse graph optimization problem, which are then used to regularize the fine-tuning process of the student stream. In this way, the student stream is actually trained by simultaneously handling two tasks with limited computational resources: approximating the most informative facial cues via feature regression, and recovering the missing facial cues via low-resolution face classification. Experimental results show that the student stream performs impressively in recognizing low-resolution faces and costs only 0.15MB memory and runs at 418 faces per second on CPU and 9,433 faces per second on GPU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge