Yingsong Huang
Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty with Asymmetric Learning for Diffusion-Generated Image Detection
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:The rapid progress of diffusion models highlights the growing need for detecting generated images. Previous research demonstrates that incorporating diffusion-based measurements, such as reconstruction error, can enhance the generalizability of detectors. However, ignoring the differing impacts of aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty on reconstruction error can undermine detection performance. Aleatoric uncertainty, arising from inherent data noise, creates ambiguity that impedes accurate detection of generated images. As it reflects random variations within the data (e.g., noise in natural textures), it does not help distinguish generated images. In contrast, epistemic uncertainty, which represents the model's lack of knowledge about unfamiliar patterns, supports detection. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty with Asymmetric Learning~(DEUA), for detecting diffusion-generated images. We introduce Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty~(DEU) estimation via the Laplace approximation to assess the proximity of data to the manifold of diffusion-generated samples. Additionally, an asymmetric loss function is introduced to train a balanced classifier with larger margins, further enhancing generalizability. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks validate the state-of-the-art performance of our method.
Uncertainty-Aware Learning Against Label Noise on Imbalanced Datasets
Jul 12, 2022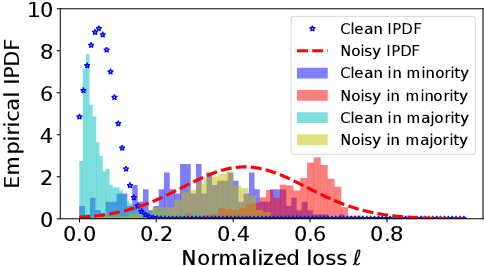
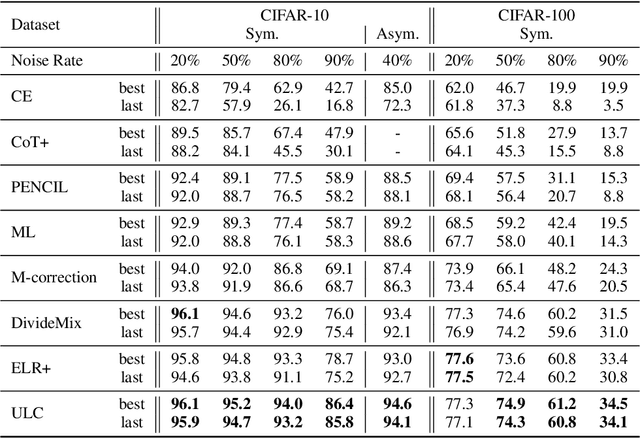
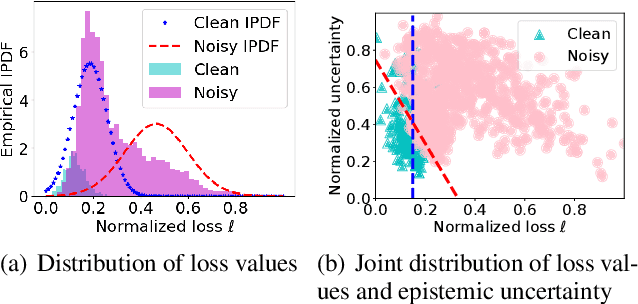
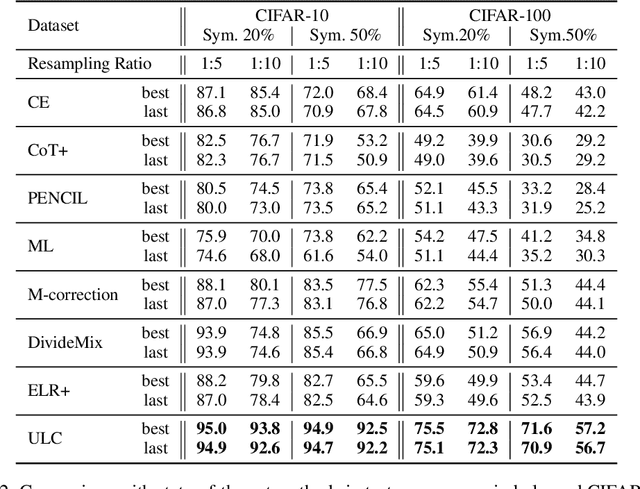
Abstract:Learning against label noise is a vital topic to guarantee a reliable performance for deep neural networks. Recent research usually refers to dynamic noise modeling with model output probabilities and loss values, and then separates clean and noisy samples. These methods have gained notable success. However, unlike cherry-picked data, existing approaches often cannot perform well when facing imbalanced datasets, a common scenario in the real world. We thoroughly investigate this phenomenon and point out two major issues that hinder the performance, i.e., \emph{inter-class loss distribution discrepancy} and \emph{misleading predictions due to uncertainty}. The first issue is that existing methods often perform class-agnostic noise modeling. However, loss distributions show a significant discrepancy among classes under class imbalance, and class-agnostic noise modeling can easily get confused with noisy samples and samples in minority classes. The second issue refers to that models may output misleading predictions due to epistemic uncertainty and aleatoric uncertainty, thus existing methods that rely solely on the output probabilities may fail to distinguish confident samples. Inspired by our observations, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Label Correction framework~(ULC) to handle label noise on imbalanced datasets. First, we perform epistemic uncertainty-aware class-specific noise modeling to identify trustworthy clean samples and refine/discard highly confident true/corrupted labels. Then, we introduce aleatoric uncertainty in the subsequent learning process to prevent noise accumulation in the label noise modeling process. We conduct experiments on several synthetic and real-world datasets. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, especially on imbalanced datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge