Shaojie Zhang
GAIA: A Data Flywheel System for Training GUI Test-Time Scaling Critic Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:While Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly advanced GUI agents' capabilities in parsing textual instructions, interpreting screen content, and executing tasks, a critical challenge persists: the irreversibility of agent operations, where a single erroneous action can trigger catastrophic deviations. To address this, we propose the GUI Action Critic's Data Flywheel System (GAIA), a training framework that enables the models to have iterative critic capabilities, which are used to improve the Test-Time Scaling (TTS) of basic GUI agents' performance. Specifically, we train an Intuitive Critic Model (ICM) using positive and negative action examples from a base agent first. This critic evaluates the immediate correctness of the agent's intended actions, thereby selecting operations with higher success probability. Then, the initial critic guides agent actions to collect refined positive/negative samples, initiating the self-improving cycle. The augmented data then trains a second-round critic with enhanced discernment capability. We conduct experiments on various datasets and demonstrate that the proposed ICM can improve the test-time performance of various closed-source and open-source models, and the performance can be gradually improved as the data is recycled. The code and dataset will be publicly released.
HyperClick: Advancing Reliable GUI Grounding via Uncertainty Calibration
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Autonomous Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents rely on accurate GUI grounding, which maps language instructions to on-screen coordinates, to execute user commands. However, current models, whether trained via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) or reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), lack self-awareness of their capability boundaries, leading to overconfidence and unreliable predictions. We first systematically evaluate probabilistic and verbalized confidence in general and GUI-specific models, revealing a misalignment between confidence and actual accuracy, which is particularly critical in dynamic GUI automation tasks, where single errors can cause task failure. To address this, we propose HyperClick, a novel framework that enhances reliable GUI grounding through uncertainty calibration. HyperClick introduces a dual reward mechanism, combining a binary reward for correct actions with a truncated Gaussian-based spatial confidence modeling, calibrated using the Brier score. This approach jointly optimizes grounding accuracy and confidence reliability, fostering introspective self-criticism. Extensive experiments on seven challenge benchmarks show that HyperClick achieves state-of-the-art performance while providing well-calibrated confidence. By enabling explicit confidence calibration and introspective self-criticism, HyperClick reduces overconfidence and supports more reliable GUI automation.
Angular Constraint Embedding via SpherePair Loss for Constrained Clustering
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Constrained clustering integrates domain knowledge through pairwise constraints. However, existing deep constrained clustering (DCC) methods are either limited by anchors inherent in end-to-end modeling or struggle with learning discriminative Euclidean embedding, restricting their scalability and real-world applicability. To avoid their respective pitfalls, we propose a novel angular constraint embedding approach for DCC, termed SpherePair. Using the SpherePair loss with a geometric formulation, our method faithfully encodes pairwise constraints and leads to embeddings that are clustering-friendly in angular space, effectively separating representation learning from clustering. SpherePair preserves pairwise relations without conflict, removes the need to specify the exact number of clusters, generalizes to unseen data, enables rapid inference of the number of clusters, and is supported by rigorous theoretical guarantees. Comparative evaluations with state-of-the-art DCC methods on diverse benchmarks, along with empirical validation of theoretical insights, confirm its superior performance, scalability, and overall real-world effectiveness. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/spherepaircc/SpherePairCC/tree/main}{our repository}.
HRTFformer: A Spatially-Aware Transformer for Personalized HRTF Upsampling in Immersive Audio Rendering
Oct 02, 2025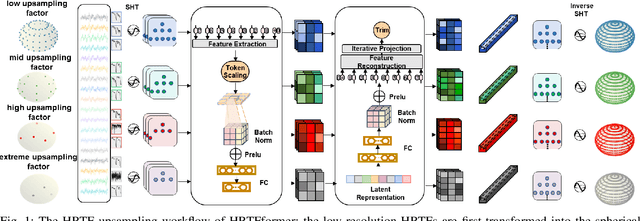
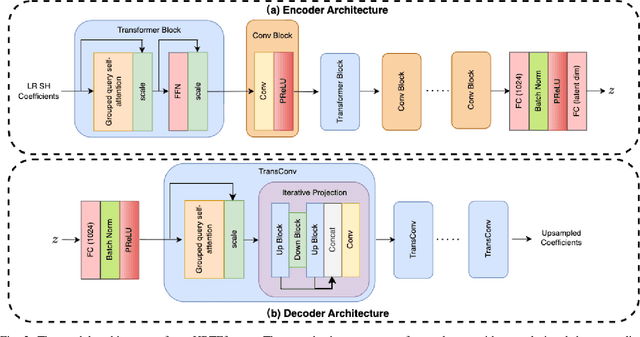
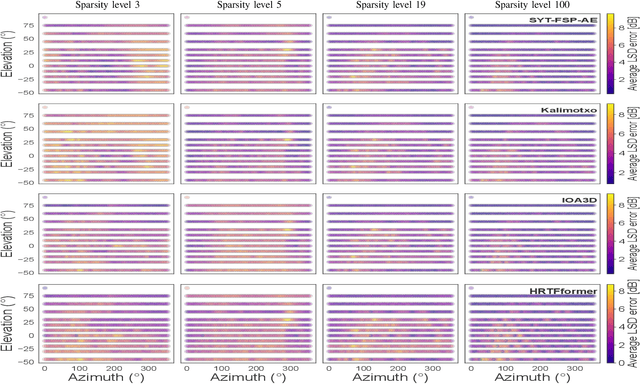
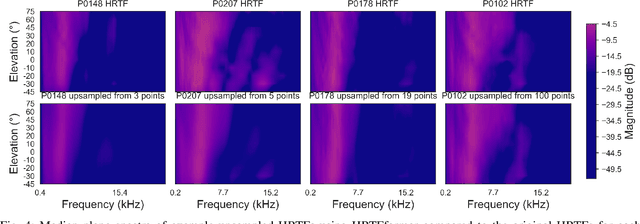
Abstract:Personalized Head-Related Transfer Functions (HRTFs) are starting to be introduced in many commercial immersive audio applications and are crucial for realistic spatial audio rendering. However, one of the main hesitations regarding their introduction is that creating personalized HRTFs is impractical at scale due to the complexities of the HRTF measurement process. To mitigate this drawback, HRTF spatial upsampling has been proposed with the aim of reducing measurements required. While prior work has seen success with different machine learning (ML) approaches, these models often struggle with long-range spatial consistency and generalization at high upsampling factors. In this paper, we propose a novel transformer-based architecture for HRTF upsampling, leveraging the attention mechanism to better capture spatial correlations across the HRTF sphere. Working in the spherical harmonic (SH) domain, our model learns to reconstruct high-resolution HRTFs from sparse input measurements with significantly improved accuracy. To enhance spatial coherence, we introduce a neighbor dissimilarity loss that promotes magnitude smoothness, yielding more realistic upsampling. We evaluate our method using both perceptual localization models and objective spectral distortion metrics. Experiments show that our model surpasses leading methods by a substantial margin in generating realistic, high-fidelity HRTFs.
BTL-UI: Blink-Think-Link Reasoning Model for GUI Agent
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:In the field of AI-driven human-GUI interaction automation, while rapid advances in multimodal large language models and reinforcement fine-tuning techniques have yielded remarkable progress, a fundamental challenge persists: their interaction logic significantly deviates from natural human-GUI communication patterns. To fill this gap, we propose "Blink-Think-Link" (BTL), a brain-inspired framework for human-GUI interaction that mimics the human cognitive process between users and graphical interfaces. The system decomposes interactions into three biologically plausible phases: (1) Blink - rapid detection and attention to relevant screen areas, analogous to saccadic eye movements; (2) Think - higher-level reasoning and decision-making, mirroring cognitive planning; and (3) Link - generation of executable commands for precise motor control, emulating human action selection mechanisms. Additionally, we introduce two key technical innovations for the BTL framework: (1) Blink Data Generation - an automated annotation pipeline specifically optimized for blink data, and (2) BTL Reward -- the first rule-based reward mechanism that enables reinforcement learning driven by both process and outcome. Building upon this framework, we develop a GUI agent model named BTL-UI, which demonstrates consistent state-of-the-art performance across both static GUI understanding and dynamic interaction tasks in comprehensive benchmarks. These results provide conclusive empirical validation of the framework's efficacy in developing advanced GUI Agents.
A Robust Error-Resistant View Selection Method for 3D Reconstruction
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:To address the issue of increased triangulation uncertainty caused by selecting views with small camera baselines in Structure from Motion (SFM) view selection, this paper proposes a robust error-resistant view selection method. The method utilizes a triangulation-based computation to obtain an error-resistant model, which is then used to construct an error-resistant matrix. The sorting results of each row in the error-resistant matrix determine the candidate view set for each view. By traversing the candidate view sets of all views and completing the missing views based on the error-resistant matrix, the integrity of 3D reconstruction is ensured. Experimental comparisons between this method and the exhaustive method with the highest accuracy in the COLMAP program are conducted in terms of average reprojection error and absolute trajectory error in the reconstruction results. The proposed method demonstrates an average reduction of 29.40% in reprojection error accuracy and 5.07% in absolute trajectory error on the TUM dataset and DTU dataset.
An Image Enhancement Method for Improving Small Intestinal Villi Clarity
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents, for the first time, an image enhancement methodology designed to enhance the clarity of small intestinal villi in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy (WCE) images. This method first separates the low-frequency and high-frequency components of small intestinal villi images using guided filtering. Subsequently, an adaptive light gain factor is generated based on the low-frequency component, and an adaptive gradient gain factor is derived from the convolution results of the Laplacian operator in different regions of small intestinal villi images. The obtained light gain factor and gradient gain factor are then combined to enhance the high-frequency components. Finally, the enhanced high-frequency component is fused with the original image to achieve adaptive sharpening of the edges of WCE small intestinal villi images. The experiments affirm that, compared to established WCE image enhancement methods, our approach not only accentuates the edge details of WCE small intestine villi images but also skillfully suppresses noise amplification, thereby preventing the occurrence of edge overshooting.
A Highlight Removal Method for Capsule Endoscopy Images
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:The images captured by Wireless Capsule Endoscopy (WCE) always exhibit specular reflections, and removing highlights while preserving the color and texture in the region remains a challenge. To address this issue, this paper proposes a highlight removal method for capsule endoscopy images. Firstly, the confidence and feature terms of the highlight region's edges are computed, where confidence is obtained by the ratio of known pixels in the RGB space's R channel to the B channel within a window centered on the highlight region's edge pixel, and feature terms are acquired by multiplying the gradient vector of the highlight region's edge pixel with the iso-intensity line. Subsequently, the confidence and feature terms are assigned different weights and summed to obtain the priority of all highlight region's edge pixels, and the pixel with the highest priority is identified. Then, the variance of the highlight region's edge pixels is used to adjust the size of the sample block window, and the best-matching block is searched in the known region based on the RGB color similarity and distance between the sample block and the window centered on the pixel with the highest priority. Finally, the pixels in the best-matching block are copied to the highest priority highlight removal region to achieve the goal of removing the highlight region. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively removes highlights from WCE images, with a lower coefficient of variation in the highlight removal region compared to the Crinimisi algorithm and DeepGin method. Additionally, the color and texture in the highlight removal region are similar to those in the surrounding areas, and the texture is continuous.
An Error-Matching Exclusion Method for Accelerating Visual SLAM
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:In Visual SLAM, achieving accurate feature matching consumes a significant amount of time, severely impacting the real-time performance of the system. This paper proposes an accelerated method for Visual SLAM by integrating GMS (Grid-based Motion Statistics) with RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus) for the removal of mismatched features. The approach first utilizes the GMS algorithm to estimate the quantity of matched pairs within the neighborhood and ranks the matches based on their confidence. Subsequently, the Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) algorithm is employed to further eliminate mismatched features. To address the time-consuming issue of randomly selecting all matched pairs, this method transforms it into the problem of prioritizing sample selection from high-confidence matches. This enables the iterative solution of the optimal model. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a comparable accuracy to the original GMS-RANSAC while reducing the average runtime by 24.13% on the KITTI, TUM desk, and TUM doll datasets.
Region Feature Descriptor Adapted to High Affine Transformations
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:To address the issue of feature descriptors being ineffective in representing grayscale feature information when images undergo high affine transformations, leading to a rapid decline in feature matching accuracy, this paper proposes a region feature descriptor based on simulating affine transformations using classification. The proposed method initially categorizes images with different affine degrees to simulate affine transformations and generate a new set of images. Subsequently, it calculates neighborhood information for feature points on this new image set. Finally, the descriptor is generated by combining the grayscale histogram of the maximum stable extremal region to which the feature point belongs and the normalized position relative to the grayscale centroid of the feature point's region. Experimental results, comparing feature matching metrics under affine transformation scenarios, demonstrate that the proposed descriptor exhibits higher precision and robustness compared to existing classical descriptors. Additionally, it shows robustness when integrated with other descriptors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge