Shanmukha Guttula
CIFE: Code Instruction-Following Evaluation
Dec 19, 2025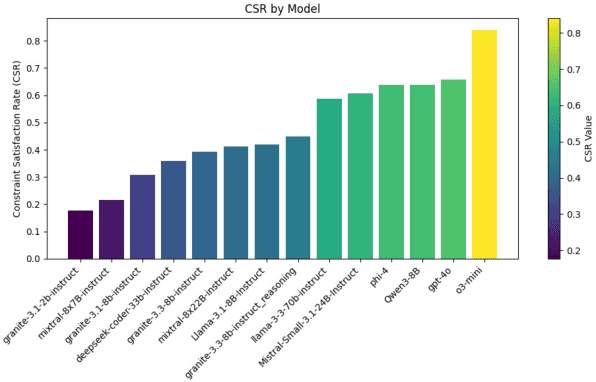
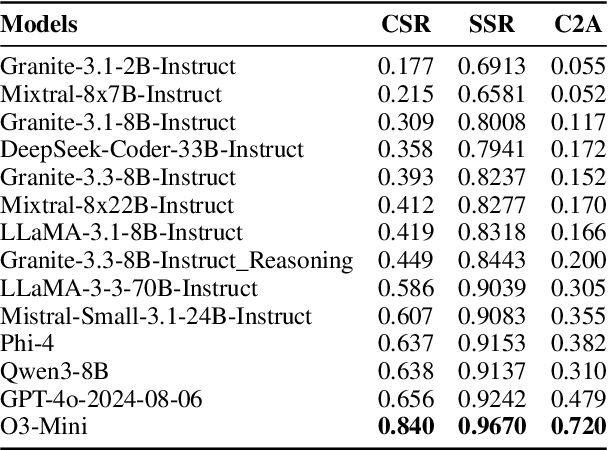
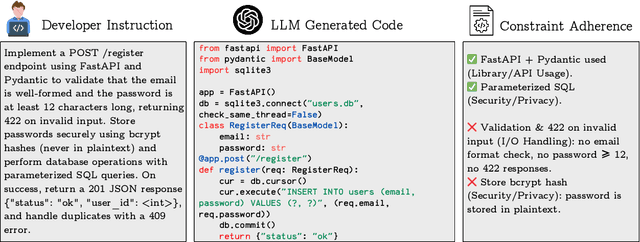

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to real-world code generation, where functional correctness alone is insufficient for reliable deployment, developers also expect adherence to explicit requirements for robustness, formatting, and security. Existing benchmarks primarily assess correctness through test-case execution, offering limited insight into how reliably models follow such constraints. We introduce a benchmark of 1,000 Python tasks, each paired with an average of 7 developer-specified constraints spanning 13 categories. Constraints are curated through a four-stage human-LLM pipeline to ensure they are atomic, relevant, and objective. We evaluate 14 open- and closed-source models using complementary adherence metrics and propose the C2A Score, a composite measure that jointly captures correctness and constraint compliance. Results reveal a substantial gap between partial and strict satisfaction, while strong models achieve over 90% partial adherence, strict adherence remains between 39-66%. These findings highlight that trustworthy code generation requires not only correctness but also consistent adherence to developer intent.
Scaling Granite Code Models to 128K Context
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces long-context Granite code models that support effective context windows of up to 128K tokens. Our solution for scaling context length of Granite 3B/8B code models from 2K/4K to 128K consists of a light-weight continual pretraining by gradually increasing its RoPE base frequency with repository-level file packing and length-upsampled long-context data. Additionally, we also release instruction-tuned models with long-context support which are derived by further finetuning the long context base models on a mix of permissively licensed short and long-context instruction-response pairs. While comparing to the original short-context Granite code models, our long-context models achieve significant improvements on long-context tasks without any noticeable performance degradation on regular code completion benchmarks (e.g., HumanEval). We release all our long-context Granite code models under an Apache 2.0 license for both research and commercial use.
Multi-Intent Detection in User Provided Annotations for Programming by Examples Systems
Jul 08, 2023



Abstract:In mapping enterprise applications, data mapping remains a fundamental part of integration development, but its time consuming. An increasing number of applications lack naming standards, and nested field structures further add complexity for the integration developers. Once the mapping is done, data transformation is the next challenge for the users since each application expects data to be in a certain format. Also, while building integration flow, developers need to understand the format of the source and target data field and come up with transformation program that can change data from source to target format. The problem of automatic generation of a transformation program through program synthesis paradigm from some specifications has been studied since the early days of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Programming by Example (PBE) is one such kind of technique that targets automatic inferencing of a computer program to accomplish a format or string conversion task from user-provided input and output samples. To learn the correct intent, a diverse set of samples from the user is required. However, there is a possibility that the user fails to provide a diverse set of samples. This can lead to multiple intents or ambiguity in the input and output samples. Hence, PBE systems can get confused in generating the correct intent program. In this paper, we propose a deep neural network based ambiguity prediction model, which analyzes the input-output strings and maps them to a different set of properties responsible for multiple intent. Users can analyze these properties and accordingly can provide new samples or modify existing samples which can help in building a better PBE system for mapping enterprise applications.
Data Quality Toolkit: Automatic assessment of data quality and remediation for machine learning datasets
Sep 05, 2021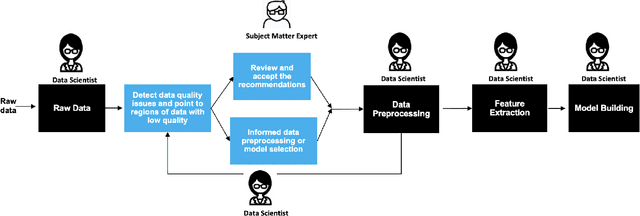
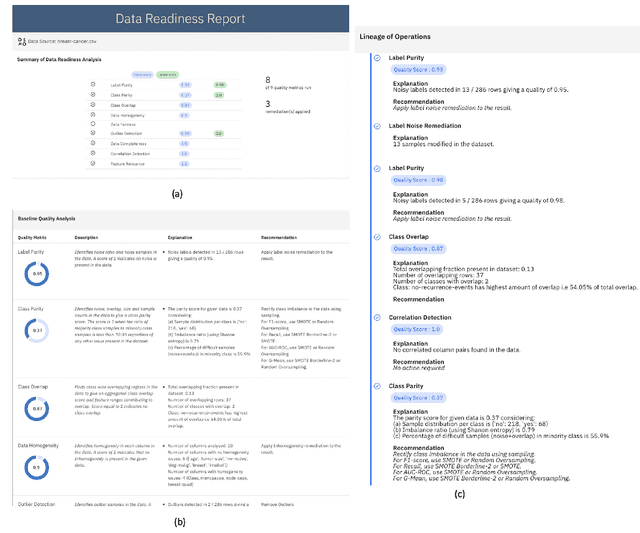
Abstract:The quality of training data has a huge impact on the efficiency, accuracy and complexity of machine learning tasks. Various tools and techniques are available that assess data quality with respect to general cleaning and profiling checks. However these techniques are not applicable to detect data issues in the context of machine learning tasks, like noisy labels, existence of overlapping classes etc. We attempt to re-look at the data quality issues in the context of building a machine learning pipeline and build a tool that can detect, explain and remediate issues in the data, and systematically and automatically capture all the changes applied to the data. We introduce the Data Quality Toolkit for machine learning as a library of some key quality metrics and relevant remediation techniques to analyze and enhance the readiness of structured training datasets for machine learning projects. The toolkit can reduce the turn-around times of data preparation pipelines and streamline the data quality assessment process. Our toolkit is publicly available via IBM API Hub [1] platform, any developer can assess the data quality using the IBM's Data Quality for AI apis [2]. Detailed tutorials are also available on IBM Learning Path [3].
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge