Shai Bagon
Learning to See Inside Opaque Liquid Containers using Speckle Vibrometry
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Computer vision seeks to infer a wide range of information about objects and events. However, vision systems based on conventional imaging are limited to extracting information only from the visible surfaces of scene objects. For instance, a vision system can detect and identify a Coke can in the scene, but it cannot determine whether the can is full or empty. In this paper, we aim to expand the scope of computer vision to include the novel task of inferring the hidden liquid levels of opaque containers by sensing the tiny vibrations on their surfaces. Our method provides a first-of-a-kind way to inspect the fill level of multiple sealed containers remotely, at once, without needing physical manipulation and manual weighing. First, we propose a novel speckle-based vibration sensing system for simultaneously capturing scene vibrations on a 2D grid of points. We use our system to efficiently and remotely capture a dataset of vibration responses for a variety of everyday liquid containers. Then, we develop a transformer-based approach for analyzing the captured vibrations and classifying the container type and its hidden liquid level at the time of measurement. Our architecture is invariant to the vibration source, yielding correct liquid level estimates for controlled and ambient scene sound sources. Moreover, our model generalizes to unseen container instances within known classes (e.g., training on five Coke cans of a six-pack, testing on a sixth) and fluid levels. We demonstrate our method by recovering liquid levels from various everyday containers.
What's in the Image? A Deep-Dive into the Vision of Vision Language Models
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently demonstrated remarkable capabilities in comprehending complex visual content. However, the mechanisms underlying how VLMs process visual information remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we conduct a thorough empirical analysis, focusing on attention modules across layers. We reveal several key insights about how these models process visual data: (i) the internal representation of the query tokens (e.g., representations of "describe the image"), is utilized by VLMs to store global image information; we demonstrate that these models generate surprisingly descriptive responses solely from these tokens, without direct access to image tokens. (ii) Cross-modal information flow is predominantly influenced by the middle layers (approximately 25% of all layers), while early and late layers contribute only marginally.(iii) Fine-grained visual attributes and object details are directly extracted from image tokens in a spatially localized manner, i.e., the generated tokens associated with a specific object or attribute attend strongly to their corresponding regions in the image. We propose novel quantitative evaluation to validate our observations, leveraging real-world complex visual scenes. Finally, we demonstrate the potential of our findings in facilitating efficient visual processing in state-of-the-art VLMs.
DINO-Tracker: Taming DINO for Self-Supervised Point Tracking in a Single Video
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:We present DINO-Tracker -- a new framework for long-term dense tracking in video. The pillar of our approach is combining test-time training on a single video, with the powerful localized semantic features learned by a pre-trained DINO-ViT model. Specifically, our framework simultaneously adopts DINO's features to fit to the motion observations of the test video, while training a tracker that directly leverages the refined features. The entire framework is trained end-to-end using a combination of self-supervised losses, and regularization that allows us to retain and benefit from DINO's semantic prior. Extensive evaluation demonstrates that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on known benchmarks. DINO-tracker significantly outperforms self-supervised methods and is competitive with state-of-the-art supervised trackers, while outperforming them in challenging cases of tracking under long-term occlusions.
Disentangling Structure and Appearance in ViT Feature Space
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:We present a method for semantically transferring the visual appearance of one natural image to another. Specifically, our goal is to generate an image in which objects in a source structure image are "painted" with the visual appearance of their semantically related objects in a target appearance image. To integrate semantic information into our framework, our key idea is to leverage a pre-trained and fixed Vision Transformer (ViT) model. Specifically, we derive novel disentangled representations of structure and appearance extracted from deep ViT features. We then establish an objective function that splices the desired structure and appearance representations, interweaving them together in the space of ViT features. Based on our objective function, we propose two frameworks of semantic appearance transfer -- "Splice", which works by training a generator on a single and arbitrary pair of structure-appearance images, and "SpliceNet", a feed-forward real-time appearance transfer model trained on a dataset of images from a specific domain. Our frameworks do not involve adversarial training, nor do they require any additional input information such as semantic segmentation or correspondences. We demonstrate high-resolution results on a variety of in-the-wild image pairs, under significant variations in the number of objects, pose, and appearance. Code and supplementary material are available in our project page: splice-vit.github.io.
TokenFlow: Consistent Diffusion Features for Consistent Video Editing
Jul 23, 2023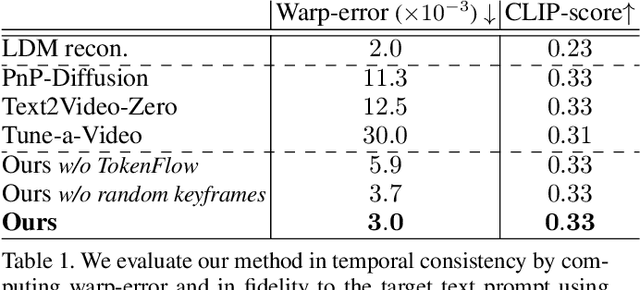
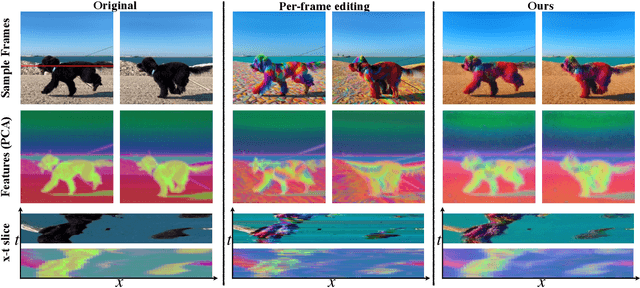

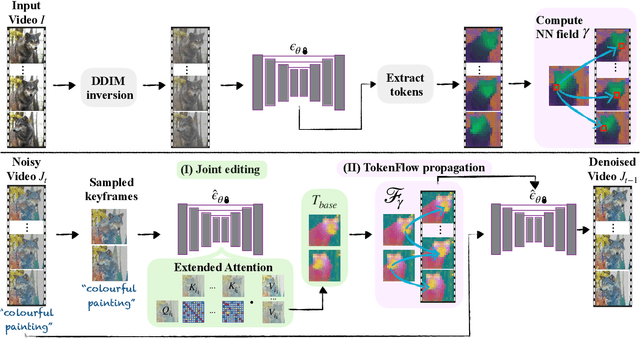
Abstract:The generative AI revolution has recently expanded to videos. Nevertheless, current state-of-the-art video models are still lagging behind image models in terms of visual quality and user control over the generated content. In this work, we present a framework that harnesses the power of a text-to-image diffusion model for the task of text-driven video editing. Specifically, given a source video and a target text-prompt, our method generates a high-quality video that adheres to the target text, while preserving the spatial layout and motion of the input video. Our method is based on a key observation that consistency in the edited video can be obtained by enforcing consistency in the diffusion feature space. We achieve this by explicitly propagating diffusion features based on inter-frame correspondences, readily available in the model. Thus, our framework does not require any training or fine-tuning, and can work in conjunction with any off-the-shelf text-to-image editing method. We demonstrate state-of-the-art editing results on a variety of real-world videos. Webpage: https://diffusion-tokenflow.github.io/
DeepCut: Unsupervised Segmentation using Graph Neural Networks Clustering
Dec 18, 2022



Abstract:Image segmentation is a fundamental task in computer vision. Data annotation for training supervised methods can be labor-intensive, motivating unsupervised methods. Some existing approaches extract deep features from pre-trained networks and build a graph to apply classical clustering methods (e.g., $k$-means and normalized-cuts) as a post-processing stage. These techniques reduce the high-dimensional information encoded in the features to pair-wise scalar affinities. In this work, we replace classical clustering algorithms with a lightweight Graph Neural Network (GNN) trained to achieve the same clustering objective function. However, in contrast to existing approaches, we feed the GNN not only the pair-wise affinities between local image features but also the raw features themselves. Maintaining this connection between the raw feature and the clustering goal allows to perform part semantic segmentation implicitly, without requiring additional post-processing steps. We demonstrate how classical clustering objectives can be formulated as self-supervised loss functions for training our image segmentation GNN. Additionally, we use the Correlation-Clustering (CC) objective to perform clustering without defining the number of clusters ($k$-less clustering). We apply the proposed method for object localization, segmentation, and semantic part segmentation tasks, surpassing state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
Detecting Bone Lesions in X-Ray Under Diverse Acquisition Conditions
Dec 15, 2022Abstract:The diagnosis of primary bone tumors is challenging, as the initial complaints are often non-specific. Early detection of bone cancer is crucial for a favorable prognosis. Incidentally, lesions may be found on radiographs obtained for other reasons. However, these early indications are often missed. In this work, we propose an automatic algorithm to detect bone lesions in conventional radiographs to facilitate early diagnosis. Detecting lesions in such radiographs is challenging: first, the prevalence of bone cancer is very low; any method must show high precision to avoid a prohibitive number of false alarms. Second, radiographs taken in health maintenance organizations (HMOs) or emergency departments (EDs) suffer from inherent diversity due to different X-ray machines, technicians and imaging protocols. This diversity poses a major challenge to any automatic analysis method. We propose to train an off-the-shelf object detection algorithm to detect lesions in radiographs. The novelty of our approach stems from a dedicated preprocessing stage that directly addresses the diversity of the data. The preprocessing consists of self-supervised region-of-interest detection using vision transformer (ViT), and a foreground-based histogram equalization for contrast enhancement to relevant regions only. We evaluate our method via a retrospective study that analyzes bone tumors on radiographs acquired from January 2003 to December 2018 under diverse acquisition protocols. Our method obtains 82.43% sensitivity at 1.5% false-positive rate and surpasses existing preprocessing methods. For lesion detection, our method achieves 82.5% accuracy and an IoU of 0.69. The proposed preprocessing method enables to effectively cope with the inherent diversity of radiographs acquired in HMOs and EDs.
Plug-and-Play Diffusion Features for Text-Driven Image-to-Image Translation
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:Large-scale text-to-image generative models have been a revolutionary breakthrough in the evolution of generative AI, allowing us to synthesize diverse images that convey highly complex visual concepts. However, a pivotal challenge in leveraging such models for real-world content creation tasks is providing users with control over the generated content. In this paper, we present a new framework that takes text-to-image synthesis to the realm of image-to-image translation -- given a guidance image and a target text prompt, our method harnesses the power of a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model to generate a new image that complies with the target text, while preserving the semantic layout of the source image. Specifically, we observe and empirically demonstrate that fine-grained control over the generated structure can be achieved by manipulating spatial features and their self-attention inside the model. This results in a simple and effective approach, where features extracted from the guidance image are directly injected into the generation process of the target image, requiring no training or fine-tuning and applicable for both real or generated guidance images. We demonstrate high-quality results on versatile text-guided image translation tasks, including translating sketches, rough drawings and animations into realistic images, changing of the class and appearance of objects in a given image, and modifications of global qualities such as lighting and color.
Combining Internal and External Constraints for Unrolling Shutter in Videos
Jul 24, 2022
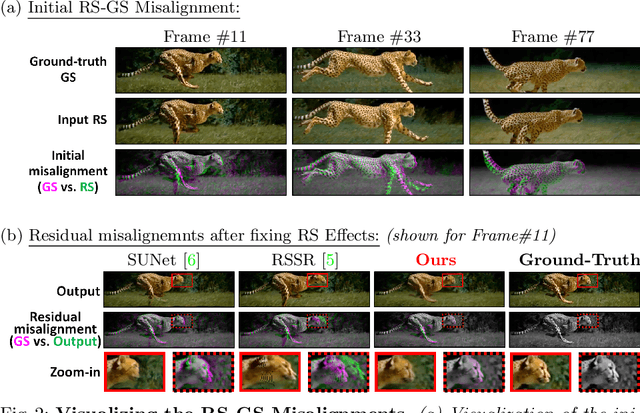
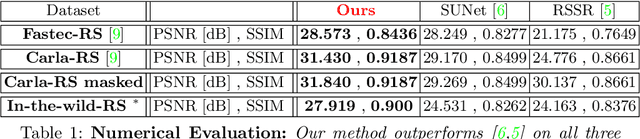

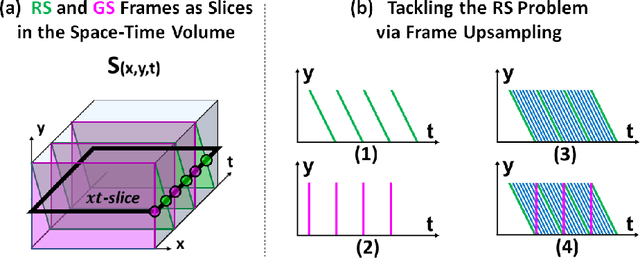
Abstract:Videos obtained by rolling-shutter (RS) cameras result in spatially-distorted frames. These distortions become significant under fast camera/scene motions. Undoing effects of RS is sometimes addressed as a spatial problem, where objects need to be rectified/displaced in order to generate their correct global shutter (GS) frame. However, the cause of the RS effect is inherently temporal, not spatial. In this paper we propose a space-time solution to the RS problem. We observe that despite the severe differences between their xy frames, a RS video and its corresponding GS video tend to share the exact same xt slices -- up to a known sub-frame temporal shift. Moreover, they share the same distribution of small 2D xt-patches, despite the strong temporal aliasing within each video. This allows to constrain the GS output video using video-specific constraints imposed by the RS input video. Our algorithm is composed of 3 main components: (i) Dense temporal upsampling between consecutive RS frames using an off-the-shelf method, (which was trained on regular video sequences), from which we extract GS "proposals". (ii) Learning to correctly merge an ensemble of such GS "proposals" using a dedicated MergeNet. (iii) A video-specific zero-shot optimization which imposes the similarity of xt-patches between the GS output video and the RS input video. Our method obtains state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets, both numerically and visually, despite being trained on a small synthetic RS/GS dataset. Moreover, it generalizes well to new complex RS videos with motion types outside the distribution of the training set (e.g., complex non-rigid motions) -- videos which competing methods trained on much more data cannot handle well. We attribute these generalization capabilities to the combination of external and internal constraints.
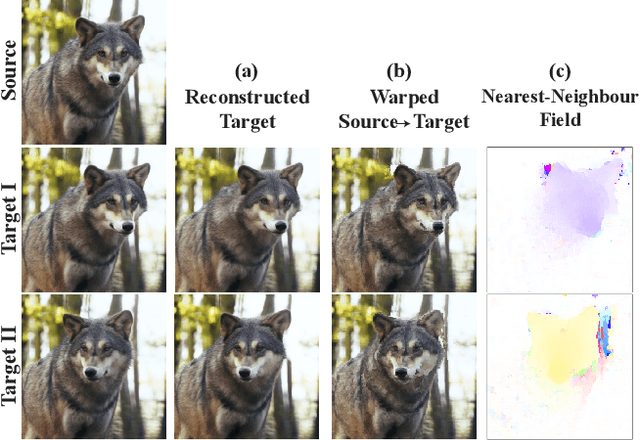
Diverse Video Generation from a Single Video
May 11, 2022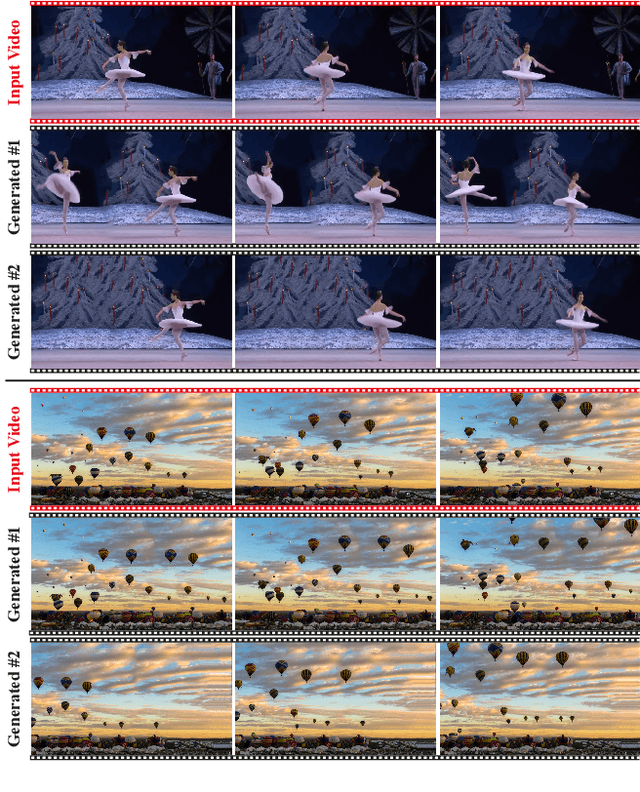
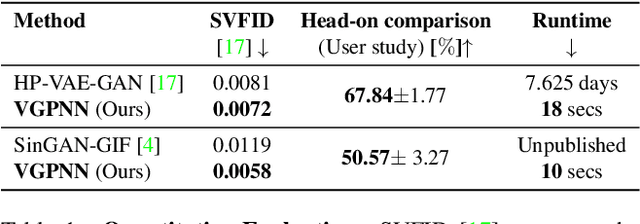
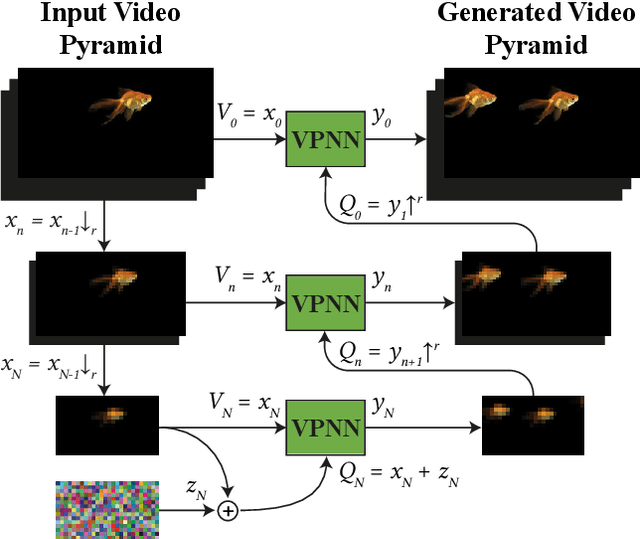
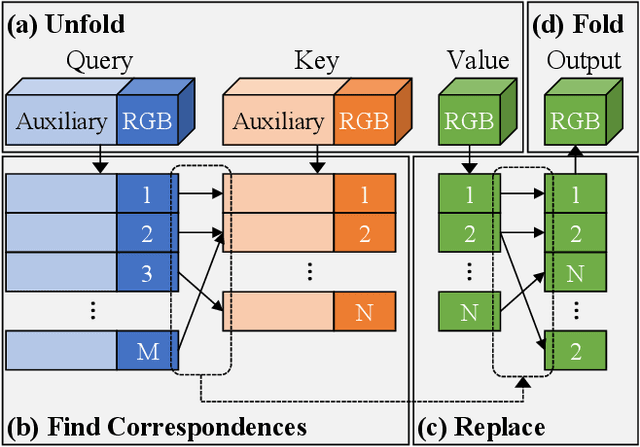
Abstract:GANs are able to perform generation and manipulation tasks, trained on a single video. However, these single video GANs require unreasonable amount of time to train on a single video, rendering them almost impractical. In this paper we question the necessity of a GAN for generation from a single video, and introduce a non-parametric baseline for a variety of generation and manipulation tasks. We revive classical space-time patches-nearest-neighbors approaches and adapt them to a scalable unconditional generative model, without any learning. This simple baseline surprisingly outperforms single-video GANs in visual quality and realism (confirmed by quantitative and qualitative evaluations), and is disproportionately faster (runtime reduced from several days to seconds). Our approach is easily scaled to Full-HD videos. We also use the same framework to demonstrate video analogies and spatio-temporal retargeting. These observations show that classical approaches significantly outperform heavy deep learning machinery for these tasks. This sets a new baseline for single-video generation and manipulation tasks, and no less important -- makes diverse generation from a single video practically possible for the first time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge