Seungwoo Lee
FastAV: Efficient Token Pruning for Audio-Visual Large Language Model Inference
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:In this work, we present FastAV, the first token pruning framework tailored for audio-visual large language models (AV-LLMs). While token pruning has been actively explored in standard large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (LVLMs), its application to AV-LLMs has received little attention, even though multimodal integration substantially increases their token demands. To address this gap, we introduce a pruning strategy that utilizes attention weights to identify tokens emphasized at different stages and estimates their importance. Building on this analysis, FastAV applies a two-stage pruning strategy: (1) global pruning in intermediate layers to remove broadly less influential tokens, and (2) fine pruning in later layers considering the impact on next token generation. Notably, our method does not rely on full attention maps, which makes it fully compatible with efficient attention mechanisms such as FlashAttention. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FastAV reduces FLOPs by more than 40% on two representative AV-LLMs, while preserving or even improving model performance.
FEATHer: Fourier-Efficient Adaptive Temporal Hierarchy Forecaster for Time-Series Forecasting
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Time-series forecasting is fundamental in industrial domains like manufacturing and smart factories. As systems evolve toward automation, models must operate on edge devices (e.g., PLCs, microcontrollers) with strict constraints on latency and memory, limiting parameters to a few thousand. Conventional deep architectures are often impractical here. We propose the Fourier-Efficient Adaptive Temporal Hierarchy Forecaster (FEATHer) for accurate long-term forecasting under severe limits. FEATHer introduces: (i) ultra-lightweight multiscale decomposition into frequency pathways; (ii) a shared Dense Temporal Kernel using projection-depthwise convolution-projection without recurrence or attention; (iii) frequency-aware branch gating that adaptively fuses representations based on spectral characteristics; and (iv) a Sparse Period Kernel reconstructing outputs via period-wise downsampling to capture seasonality. FEATHer maintains a compact architecture (as few as 400 parameters) while outperforming baselines. Across eight benchmarks, it achieves the best ranking, recording 60 first-place results with an average rank of 2.05. These results demonstrate that reliable long-range forecasting is achievable on constrained edge hardware, offering a practical direction for industrial real-time inference.
PoseSyn: Synthesizing Diverse 3D Pose Data from In-the-Wild 2D Data
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Despite considerable efforts to enhance the generalization of 3D pose estimators without costly 3D annotations, existing data augmentation methods struggle in real world scenarios with diverse human appearances and complex poses. We propose PoseSyn, a novel data synthesis framework that transforms abundant in the wild 2D pose dataset into diverse 3D pose image pairs. PoseSyn comprises two key components: Error Extraction Module (EEM), which identifies challenging poses from the 2D pose datasets, and Motion Synthesis Module (MSM), which synthesizes motion sequences around the challenging poses. Then, by generating realistic 3D training data via a human animation model aligned with challenging poses and appearances PoseSyn boosts the accuracy of various 3D pose estimators by up to 14% across real world benchmarks including various backgrounds and occlusions, challenging poses, and multi view scenarios. Extensive experiments further confirm that PoseSyn is a scalable and effective approach for improving generalization without relying on expensive 3D annotations, regardless of the pose estimator's model size or design.
COIN: Confidence Score-Guided Distillation for Annotation-Free Cell Segmentation
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:Cell instance segmentation (CIS) is crucial for identifying individual cell morphologies in histopathological images, providing valuable insights for biological and medical research. While unsupervised CIS (UCIS) models aim to reduce the heavy reliance on labor-intensive image annotations, they fail to accurately capture cell boundaries, causing missed detections and poor performance. Recognizing the absence of error-free instances as a key limitation, we present COIN (COnfidence score-guided INstance distillation), a novel annotation-free framework with three key steps: (1) Increasing the sensitivity for the presence of error-free instances via unsupervised semantic segmentation with optimal transport, leveraging its ability to discriminate spatially minor instances, (2) Instance-level confidence scoring to measure the consistency between model prediction and refined mask and identify highly confident instances, offering an alternative to ground truth annotations, and (3) Progressive expansion of confidence with recursive self-distillation. Extensive experiments across six datasets show COIN outperforming existing UCIS methods, even surpassing semi- and weakly-supervised approaches across all metrics on the MoNuSeg and TNBC datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/shjo-april/COIN.
HourglassNeRF: Casting an Hourglass as a Bundle of Rays for Few-shot Neural Rendering
Mar 16, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in the Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) have bolstered its capabilities for novel view synthesis, yet its reliance on dense multi-view training images poses a practical challenge. Addressing this, we propose HourglassNeRF, an effective regularization-based approach with a novel hourglass casting strategy. Our proposed hourglass is conceptualized as a bundle of additional rays within the area between the original input ray and its corresponding reflection ray, by featurizing the conical frustum via Integrated Positional Encoding (IPE). This design expands the coverage of unseen views and enables an adaptive high-frequency regularization based on target pixel photo-consistency. Furthermore, we propose luminance consistency regularization based on the Lambertian assumption, which is known to be effective for training a set of augmented rays under the few-shot setting. Leveraging the inherent property of a Lambertian surface, which retains consistent luminance irrespective of the viewing angle, we assume our proposed hourglass as a collection of flipped diffuse reflection rays and enhance the luminance consistency between the original input ray and its corresponding hourglass, resulting in more physically grounded training framework and performance improvement. Our HourglassNeRF outperforms its baseline and achieves competitive results on multiple benchmarks with sharply rendered fine details. The code will be available.
AADiff: Audio-Aligned Video Synthesis with Text-to-Image Diffusion
May 06, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have showcased promising results in the text-to-video (T2V) synthesis task. However, as these T2V models solely employ text as the guidance, they tend to struggle in modeling detailed temporal dynamics. In this paper, we introduce a novel T2V framework that additionally employ audio signals to control the temporal dynamics, empowering an off-the-shelf T2I diffusion to generate audio-aligned videos. We propose audio-based regional editing and signal smoothing to strike a good balance between the two contradicting desiderata of video synthesis, i.e., temporal flexibility and coherence. We empirically demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through experiments, and further present practical applications for contents creation.
AHP: Learning to Negative Sample for Hyperedge Prediction
Apr 15, 2022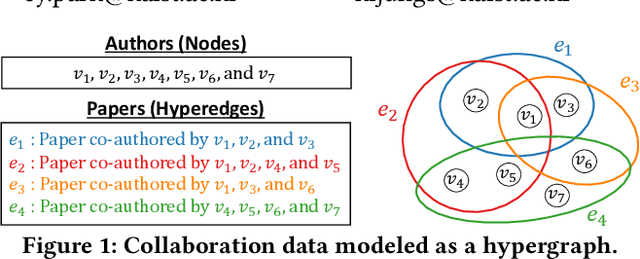
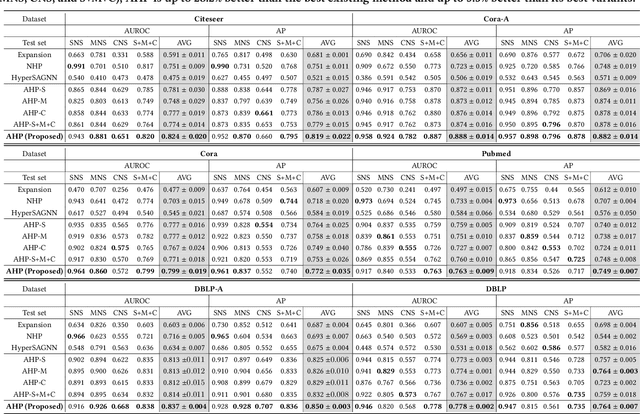
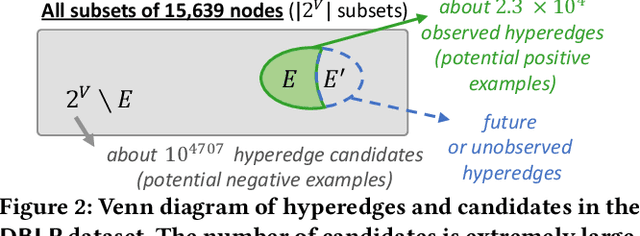
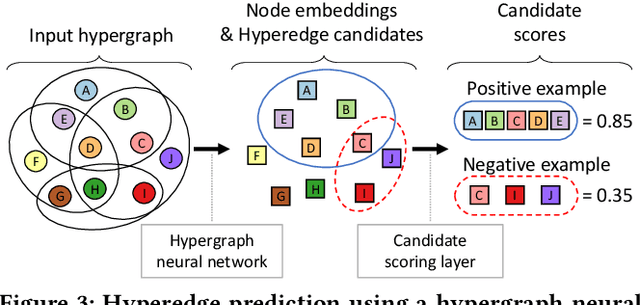
Abstract:Hypergraphs (i.e., sets of hyperedges) naturally represent group relations (e.g., researchers co-authoring a paper and ingredients used together in a recipe), each of which corresponds to a hyperedge (i.e., a subset of nodes). Predicting future or missing hyperedges bears significant implications for many applications (e.g., collaboration and recipe recommendation). What makes hyperedge prediction particularly challenging is the vast number of non-hyperedge subsets, which grows exponentially with the number of nodes. Since it is prohibitive to use all of them as negative examples for model training, it is inevitable to sample a very small portion of them, and to this end, heuristic sampling schemes have been employed. However, trained models suffer from poor generalization capability for examples of different natures. In this paper, we propose AHP, an adversarial training-based hyperedge-prediction method. It learns to sample negative examples without relying on any heuristic schemes. Using six real hypergraphs, we show that AHP generalizes better to negative examples of various natures. It yields up to 28.2% higher AUROC than the best existing methods and often even outperforms its variants with sampling schemes tailored to test sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge