Se Young Chun
DiffBMP: Differentiable Rendering with Bitmap Primitives
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:We introduce DiffBMP, a scalable and efficient differentiable rendering engine for a collection of bitmap images. Our work addresses a limitation that traditional differentiable renderers are constrained to vector graphics, given that most images in the world are bitmaps. Our core contribution is a highly parallelized rendering pipeline, featuring a custom CUDA implementation for calculating gradients. This system can, for example, optimize the position, rotation, scale, color, and opacity of thousands of bitmap primitives all in under 1 min using a consumer GPU. We employ and validate several techniques to facilitate the optimization: soft rasterization via Gaussian blur, structure-aware initialization, noisy canvas, and specialized losses/heuristics for videos or spatially constrained images. We demonstrate DiffBMP is not just an isolated tool, but a practical one designed to integrate into creative workflows. It supports exporting compositions to a native, layered file format, and the entire framework is publicly accessible via an easy-to-hack Python package.
Continual Multiple Instance Learning with Enhanced Localization for Histopathological Whole Slide Image Analysis
Jul 03, 2025
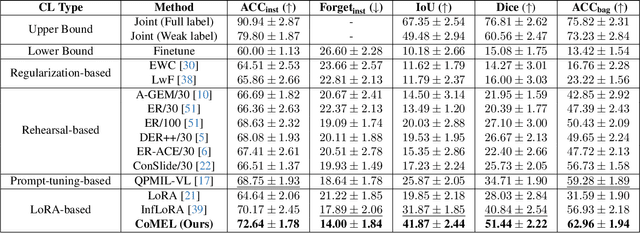
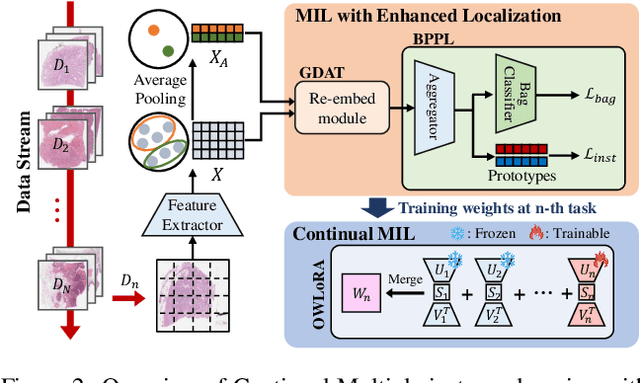
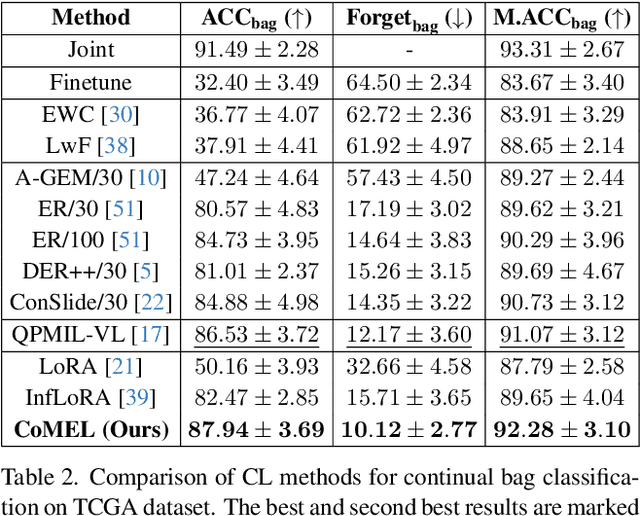
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) significantly reduced annotation costs via bag-level weak labels for large-scale images, such as histopathological whole slide images (WSIs). However, its adaptability to continual tasks with minimal forgetting has been rarely explored, especially on instance classification for localization. Weakly incremental learning for semantic segmentation has been studied for continual localization, but it focused on natural images, leveraging global relationships among hundreds of small patches (e.g., $16 \times 16$) using pre-trained models. This approach seems infeasible for MIL localization due to enormous amounts ($\sim 10^5$) of large patches (e.g., $256 \times 256$) and no available global relationships such as cancer cells. To address these challenges, we propose Continual Multiple Instance Learning with Enhanced Localization (CoMEL), an MIL framework for both localization and adaptability with minimal forgetting. CoMEL consists of (1) Grouped Double Attention Transformer (GDAT) for efficient instance encoding, (2) Bag Prototypes-based Pseudo-Labeling (BPPL) for reliable instance pseudo-labeling, and (3) Orthogonal Weighted Low-Rank Adaptation (OWLoRA) to mitigate forgetting in both bag and instance classification. Extensive experiments on three public WSI datasets demonstrate superior performance of CoMEL, outperforming the prior arts by up to $11.00\%$ in bag-level accuracy and up to $23.4\%$ in localization accuracy under the continual MIL setup.
Self-Cascaded Diffusion Models for Arbitrary-Scale Image Super-Resolution
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Arbitrary-scale image super-resolution aims to upsample images to any desired resolution, offering greater flexibility than traditional fixed-scale super-resolution. Recent approaches in this domain utilize regression-based or generative models, but many of them are a single-stage upsampling process, which may be challenging to learn across a wide, continuous distribution of scaling factors. Progressive upsampling strategies have shown promise in mitigating this issue, yet their integration with diffusion models for flexible upscaling remains underexplored. Here, we present CasArbi, a novel self-cascaded diffusion framework for arbitrary-scale image super-resolution. CasArbi meets the varying scaling demands by breaking them down into smaller sequential factors and progressively enhancing the image resolution at each step with seamless transitions for arbitrary scales. Our novel coordinate-guided residual diffusion model allows for the learning of continuous image representations while enabling efficient diffusion sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CasArbi outperforms prior arts in both perceptual and distortion performance metrics across diverse arbitrary-scale super-resolution benchmarks.
GeoMan: Temporally Consistent Human Geometry Estimation using Image-to-Video Diffusion
May 29, 2025Abstract:Estimating accurate and temporally consistent 3D human geometry from videos is a challenging problem in computer vision. Existing methods, primarily optimized for single images, often suffer from temporal inconsistencies and fail to capture fine-grained dynamic details. To address these limitations, we present GeoMan, a novel architecture designed to produce accurate and temporally consistent depth and normal estimations from monocular human videos. GeoMan addresses two key challenges: the scarcity of high-quality 4D training data and the need for metric depth estimation to accurately model human size. To overcome the first challenge, GeoMan employs an image-based model to estimate depth and normals for the first frame of a video, which then conditions a video diffusion model, reframing video geometry estimation task as an image-to-video generation problem. This design offloads the heavy lifting of geometric estimation to the image model and simplifies the video model's role to focus on intricate details while using priors learned from large-scale video datasets. Consequently, GeoMan improves temporal consistency and generalizability while requiring minimal 4D training data. To address the challenge of accurate human size estimation, we introduce a root-relative depth representation that retains critical human-scale details and is easier to be estimated from monocular inputs, overcoming the limitations of traditional affine-invariant and metric depth representations. GeoMan achieves state-of-the-art performance in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, demonstrating its effectiveness in overcoming longstanding challenges in 3D human geometry estimation from videos.
Convergent Complex Quasi-Newton Proximal Methods for Gradient-Driven Denoisers in Compressed Sensing MRI Reconstruction
May 07, 2025Abstract:In compressed sensing (CS) MRI, model-based methods are pivotal to achieving accurate reconstruction. One of the main challenges in model-based methods is finding an effective prior to describe the statistical distribution of the target image. Plug-and-Play (PnP) and REgularization by Denoising (RED) are two general frameworks that use denoisers as the prior. While PnP/RED methods with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) based denoisers outperform classical hand-crafted priors in CS MRI, their convergence theory relies on assumptions that do not hold for practical CNNs. The recently developed gradient-driven denoisers offer a framework that bridges the gap between practical performance and theoretical guarantees. However, the numerical solvers for the associated minimization problem remain slow for CS MRI reconstruction. This paper proposes a complex quasi-Newton proximal method that achieves faster convergence than existing approaches. To address the complex domain in CS MRI, we propose a modified Hessian estimation method that guarantees Hermitian positive definiteness. Furthermore, we provide a rigorous convergence analysis of the proposed method for nonconvex settings. Numerical experiments on both Cartesian and non-Cartesian sampling trajectories demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach.
Efficient and robust 3D blind harmonization for large domain gaps
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Blind harmonization has emerged as a promising technique for MR image harmonization to achieve scale-invariant representations, requiring only target domain data (i.e., no source domain data necessary). However, existing methods face limitations such as inter-slice heterogeneity in 3D, moderate image quality, and limited performance for a large domain gap. To address these challenges, we introduce BlindHarmonyDiff, a novel blind 3D harmonization framework that leverages an edge-to-image model tailored specifically to harmonization. Our framework employs a 3D rectified flow trained on target domain images to reconstruct the original image from an edge map, then yielding a harmonized image from the edge of a source domain image. We propose multi-stride patch training for efficient 3D training and a refinement module for robust inference by suppressing hallucination. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BlindHarmonyDiff outperforms prior arts by harmonizing diverse source domain images to the target domain, achieving higher correspondence to the target domain characteristics. Downstream task-based quality assessments such as tissue segmentation and age prediction on diverse MR scanners further confirm the effectiveness of our approach and demonstrate the capability of our robust and generalizable blind harmonization.
On Geometrical Properties of Text Token Embeddings for Strong Semantic Binding in Text-to-Image Generation
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Text-to-Image (T2I) models often suffer from text-image misalignment in complex scenes involving multiple objects and attributes. Semantic binding aims to mitigate this issue by accurately associating the generated attributes and objects with their corresponding noun phrases (NPs). Existing methods rely on text or latent optimizations, yet the factors influencing semantic binding remain underexplored. Here we investigate the geometrical properties of text token embeddings and their cross-attention (CA) maps. We empirically and theoretically analyze that the geometrical properties of token embeddings, specifically both angular distances and norms, play a crucial role in CA map differentiation. Then, we propose \textbf{TeeMo}, a training-free text embedding-aware T2I framework with strong semantic binding. TeeMo consists of Causality-Aware Projection-Out (CAPO) for distinct inter-NP CA maps and Adaptive Token Mixing (ATM) with our loss to enhance inter-NP separation while maintaining intra-NP cohesion in CA maps. Extensive experiments confirm TeeMo consistently outperforms prior arts across diverse baselines and datasets.
Efficient Personalization of Quantized Diffusion Model without Backpropagation
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable performance in image synthesis, but they demand extensive computational and memory resources for training, fine-tuning and inference. Although advanced quantization techniques have successfully minimized memory usage for inference, training and fine-tuning these quantized models still require large memory possibly due to dequantization for accurate computation of gradients and/or backpropagation for gradient-based algorithms. However, memory-efficient fine-tuning is particularly desirable for applications such as personalization that often must be run on edge devices like mobile phones with private data. In this work, we address this challenge by quantizing a diffusion model with personalization via Textual Inversion and by leveraging a zeroth-order optimization on personalization tokens without dequantization so that it does not require gradient and activation storage for backpropagation that consumes considerable memory. Since a gradient estimation using zeroth-order optimization is quite noisy for a single or a few images in personalization, we propose to denoise the estimated gradient by projecting it onto a subspace that is constructed with the past history of the tokens, dubbed Subspace Gradient. In addition, we investigated the influence of text embedding in image generation, leading to our proposed time steps sampling, dubbed Partial Uniform Timestep Sampling for sampling with effective diffusion timesteps. Our method achieves comparable performance to prior methods in image and text alignment scores for personalizing Stable Diffusion with only forward passes while reducing training memory demand up to $8.2\times$.
Localized Concept Erasure for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models Using Training-Free Gated Low-Rank Adaptation
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:Fine-tuning based concept erasing has demonstrated promising results in preventing generation of harmful contents from text-to-image diffusion models by removing target concepts while preserving remaining concepts. To maintain the generation capability of diffusion models after concept erasure, it is necessary to remove only the image region containing the target concept when it locally appears in an image, leaving other regions intact. However, prior arts often compromise fidelity of the other image regions in order to erase the localized target concept appearing in a specific area, thereby reducing the overall performance of image generation. To address these limitations, we first introduce a framework called localized concept erasure, which allows for the deletion of only the specific area containing the target concept in the image while preserving the other regions. As a solution for the localized concept erasure, we propose a training-free approach, dubbed Gated Low-rank adaptation for Concept Erasure (GLoCE), that injects a lightweight module into the diffusion model. GLoCE consists of low-rank matrices and a simple gate, determined only by several generation steps for concepts without training. By directly applying GLoCE to image embeddings and designing the gate to activate only for target concepts, GLoCE can selectively remove only the region of the target concepts, even when target and remaining concepts coexist within an image. Extensive experiments demonstrated GLoCE not only improves the image fidelity to text prompts after erasing the localized target concepts, but also outperforms prior arts in efficacy, specificity, and robustness by large margin and can be extended to mass concept erasure.
Skrr: Skip and Re-use Text Encoder Layers for Memory Efficient Text-to-Image Generation
Feb 12, 2025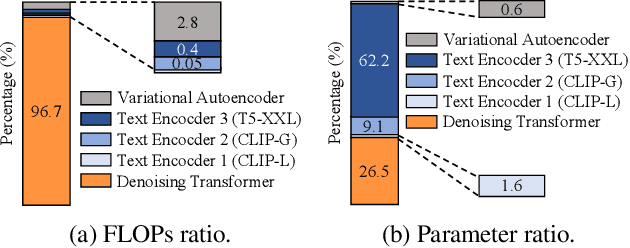
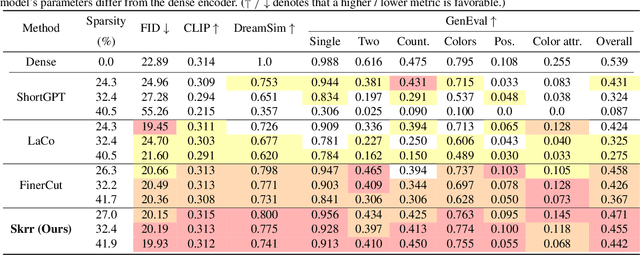
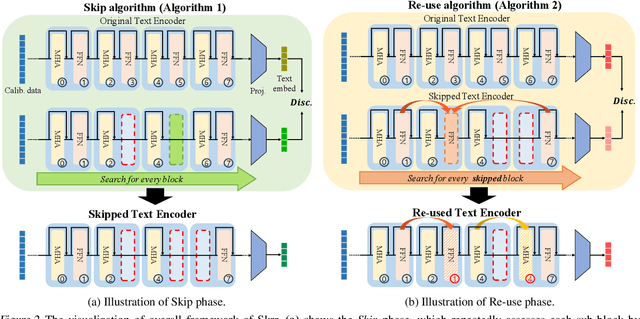
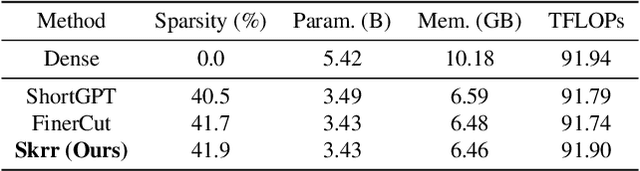
Abstract:Large-scale text encoders in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have demonstrated exceptional performance in generating high-quality images from textual prompts. Unlike denoising modules that rely on multiple iterative steps, text encoders require only a single forward pass to produce text embeddings. However, despite their minimal contribution to total inference time and floating-point operations (FLOPs), text encoders demand significantly higher memory usage, up to eight times more than denoising modules. To address this inefficiency, we propose Skip and Re-use layers (Skrr), a simple yet effective pruning strategy specifically designed for text encoders in T2I diffusion models. Skrr exploits the inherent redundancy in transformer blocks by selectively skipping or reusing certain layers in a manner tailored for T2I tasks, thereby reducing memory consumption without compromising performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Skrr maintains image quality comparable to the original model even under high sparsity levels, outperforming existing blockwise pruning methods. Furthermore, Skrr achieves state-of-the-art memory efficiency while preserving performance across multiple evaluation metrics, including the FID, CLIP, DreamSim, and GenEval scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge