Dong Un Kang
Self-Cascaded Diffusion Models for Arbitrary-Scale Image Super-Resolution
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Arbitrary-scale image super-resolution aims to upsample images to any desired resolution, offering greater flexibility than traditional fixed-scale super-resolution. Recent approaches in this domain utilize regression-based or generative models, but many of them are a single-stage upsampling process, which may be challenging to learn across a wide, continuous distribution of scaling factors. Progressive upsampling strategies have shown promise in mitigating this issue, yet their integration with diffusion models for flexible upscaling remains underexplored. Here, we present CasArbi, a novel self-cascaded diffusion framework for arbitrary-scale image super-resolution. CasArbi meets the varying scaling demands by breaking them down into smaller sequential factors and progressively enhancing the image resolution at each step with seamless transitions for arbitrary scales. Our novel coordinate-guided residual diffusion model allows for the learning of continuous image representations while enabling efficient diffusion sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our CasArbi outperforms prior arts in both perceptual and distortion performance metrics across diverse arbitrary-scale super-resolution benchmarks.
Short-term Object Interaction Anticipation with Disentangled Object Detection @ Ego4D Short Term Object Interaction Anticipation Challenge
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Short-term object interaction anticipation is an important task in egocentric video analysis, including precise predictions of future interactions and their timings as well as the categories and positions of the involved active objects. To alleviate the complexity of this task, our proposed method, SOIA-DOD, effectively decompose it into 1) detecting active object and 2) classifying interaction and predicting their timing. Our method first detects all potential active objects in the last frame of egocentric video by fine-tuning a pre-trained YOLOv9. Then, we combine these potential active objects as query with transformer encoder, thereby identifying the most promising next active object and predicting its future interaction and time-to-contact. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art models on the challenge test set, achieving the best performance in predicting next active objects and their interactions. Finally, our proposed ranked the third overall top-5 mAP when including time-to-contact predictions. The source code is available at https://github.com/KeenyJin/SOIA-DOD.
BeyondScene: Higher-Resolution Human-Centric Scene Generation With Pretrained Diffusion
Apr 06, 2024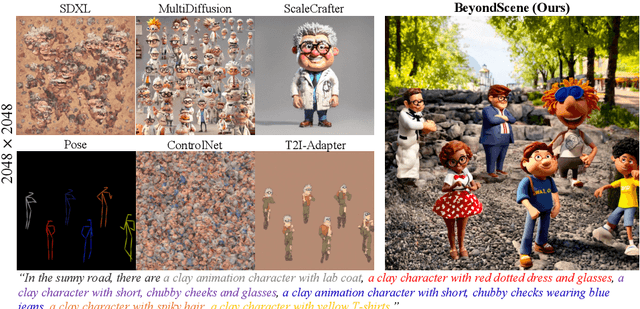
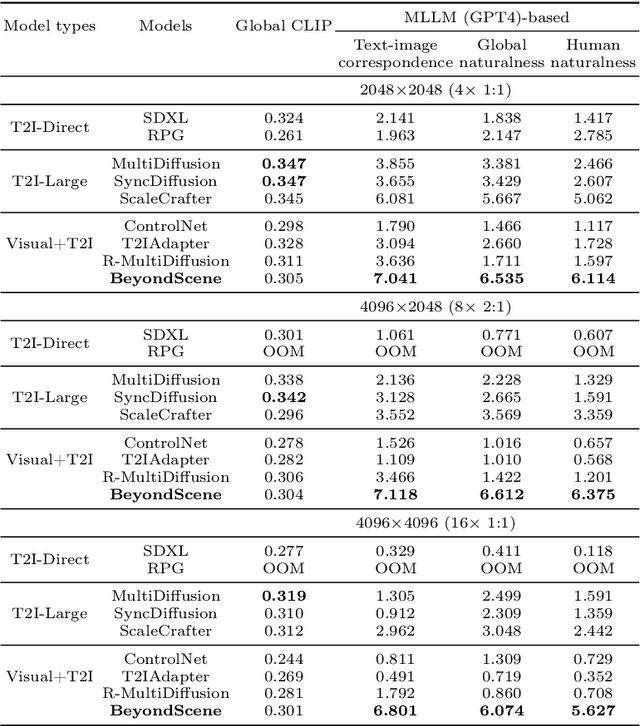

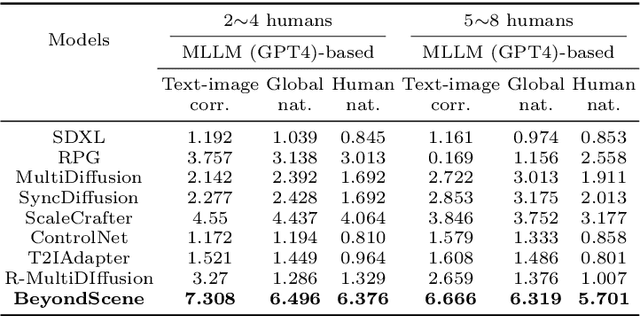
Abstract:Generating higher-resolution human-centric scenes with details and controls remains a challenge for existing text-to-image diffusion models. This challenge stems from limited training image size, text encoder capacity (limited tokens), and the inherent difficulty of generating complex scenes involving multiple humans. While current methods attempted to address training size limit only, they often yielded human-centric scenes with severe artifacts. We propose BeyondScene, a novel framework that overcomes prior limitations, generating exquisite higher-resolution (over 8K) human-centric scenes with exceptional text-image correspondence and naturalness using existing pretrained diffusion models. BeyondScene employs a staged and hierarchical approach to initially generate a detailed base image focusing on crucial elements in instance creation for multiple humans and detailed descriptions beyond token limit of diffusion model, and then to seamlessly convert the base image to a higher-resolution output, exceeding training image size and incorporating details aware of text and instances via our novel instance-aware hierarchical enlargement process that consists of our proposed high-frequency injected forward diffusion and adaptive joint diffusion. BeyondScene surpasses existing methods in terms of correspondence with detailed text descriptions and naturalness, paving the way for advanced applications in higher-resolution human-centric scene creation beyond the capacity of pretrained diffusion models without costly retraining. Project page: https://janeyeon.github.io/beyond-scene.
Detailed Human-Centric Text Description-Driven Large Scene Synthesis
Nov 30, 2023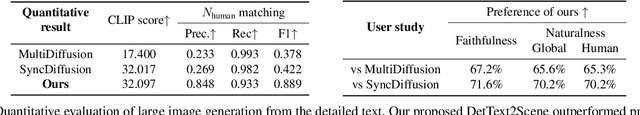
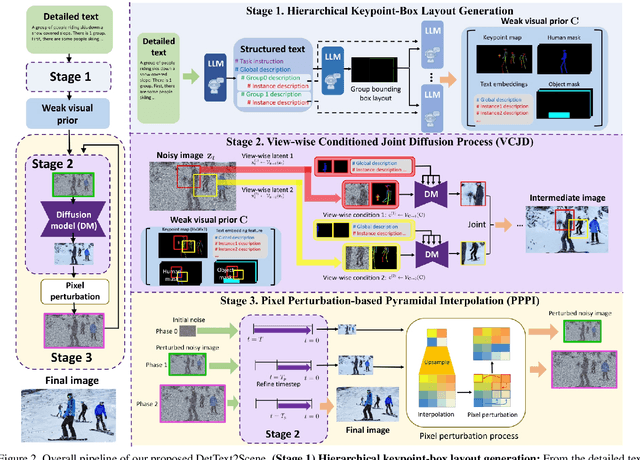


Abstract:Text-driven large scene image synthesis has made significant progress with diffusion models, but controlling it is challenging. While using additional spatial controls with corresponding texts has improved the controllability of large scene synthesis, it is still challenging to faithfully reflect detailed text descriptions without user-provided controls. Here, we propose DetText2Scene, a novel text-driven large-scale image synthesis with high faithfulness, controllability, and naturalness in a global context for the detailed human-centric text description. Our DetText2Scene consists of 1) hierarchical keypoint-box layout generation from the detailed description by leveraging large language model (LLM), 2) view-wise conditioned joint diffusion process to synthesize a large scene from the given detailed text with LLM-generated grounded keypoint-box layout and 3) pixel perturbation-based pyramidal interpolation to progressively refine the large scene for global coherence. Our DetText2Scene significantly outperforms prior arts in text-to-large scene synthesis qualitatively and quantitatively, demonstrating strong faithfulness with detailed descriptions, superior controllability, and excellent naturalness in a global context.
Adaptive GLCM sampling for transformer-based COVID-19 detection on CT
Jul 04, 2022

Abstract:The world has suffered from COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) for the last two years, causing much damage and change in people's daily lives. Thus, automated detection of COVID-19 utilizing deep learning on chest computed tomography (CT) scans became promising, which helps correct diagnosis efficiently. Recently, transformer-based COVID-19 detection method on CT is proposed to utilize 3D information in CT volume. However, its sampling method for selecting slices is not optimal. To leverage rich 3D information in CT volume, we propose a transformer-based COVID-19 detection using a novel data curation and adaptive sampling method using gray level co-occurrence matrices (GLCM). To train the model which consists of CNN layer, followed by transformer architecture, we first executed data curation based on lung segmentation and utilized the entropy of GLCM value of every slice in CT volumes to select important slices for the prediction. The experimental results show that the proposed method improve the detection performance with large margin without much difficult modification to the model.
Blur More To Deblur Better: Multi-Blur2Deblur For Efficient Video Deblurring
Dec 23, 2020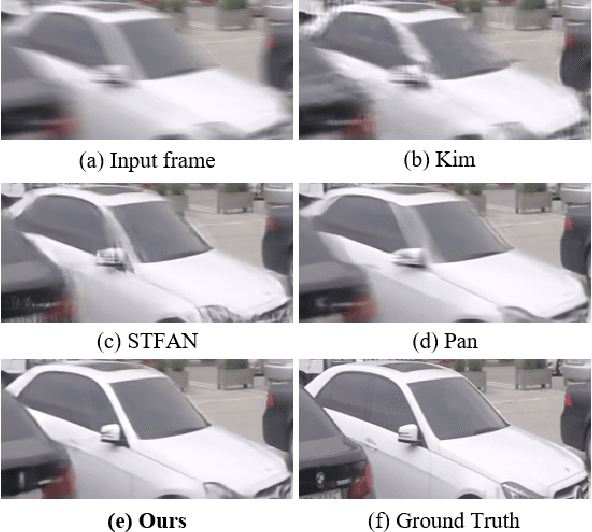
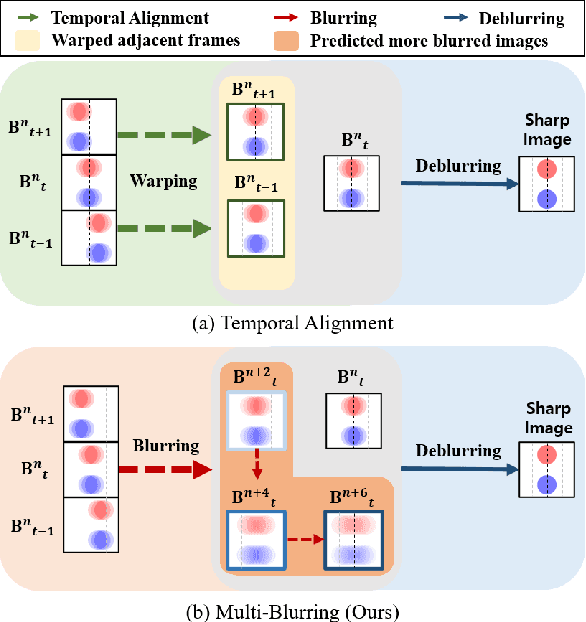
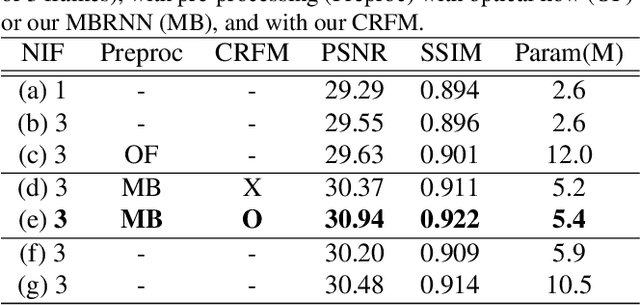
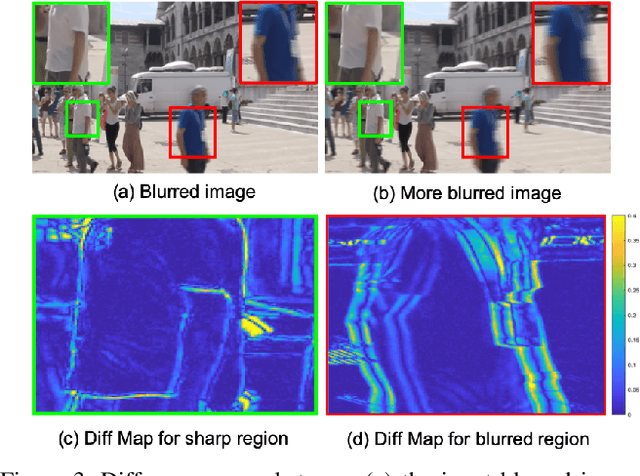
Abstract:One of the key components for video deblurring is how to exploit neighboring frames. Recent state-of-the-art methods either used aligned adjacent frames to the center frame or propagated the information on past frames to the current frame recurrently. Here we propose multi-blur-to-deblur (MB2D), a novel concept to exploit neighboring frames for efficient video deblurring. Firstly, inspired by unsharp masking, we argue that using more blurred images with long exposures as additional inputs significantly improves performance. Secondly, we propose multi-blurring recurrent neural network (MBRNN) that can synthesize more blurred images from neighboring frames, yielding substantially improved performance with existing video deblurring methods. Lastly, we propose multi-scale deblurring with connecting recurrent feature map from MBRNN (MSDR) to achieve state-of-the-art performance on the popular GoPro and Su datasets in fast and memory efficient ways.
Multi-Temporal Recurrent Neural Networks For Progressive Non-Uniform Single Image Deblurring With Incremental Temporal Training
Nov 18, 2019



Abstract:Multi-scale (MS) approaches have been widely investigated for blind single image / video deblurring that sequentially recovers deblurred images in low spatial scale first and then in high spatial scale later with the output of lower scales. MS approaches have been effective especially for severe blurs induced by large motions in high spatial scale since those can be seen as small blurs in low spatial scale. In this work, we investigate alternative approach to MS, called multi-temporal (MT) approach, for non-uniform single image deblurring. We propose incremental temporal training with constructed MT level dataset from time-resolved dataset, develop novel MT-RNNs with recurrent feature maps, and investigate progressive single image deblurring over iterations. Our proposed MT methods outperform state-of-the-art MS methods on the GoPro dataset in PSNR with the smallest number of parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge