Ryan S. Baker
The Quick Red Fox gets the best Data Driven Classroom Interviews: A manual for an interview app and its associated methodology
Nov 17, 2025

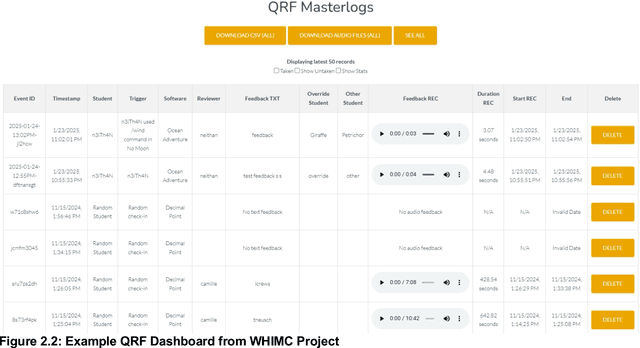
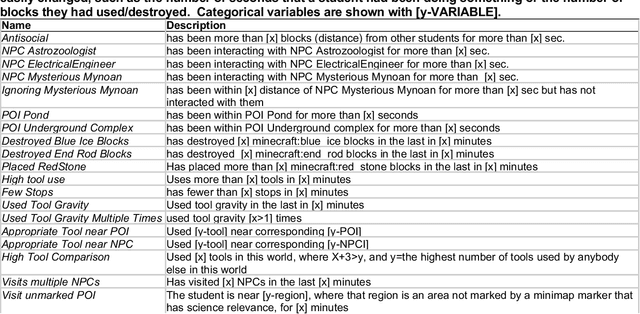
Abstract:Data Driven Classroom Interviews (DDCIs) are an interviewing technique that is facilitated by recent technological developments in the learning analytics community. DDCIs are short, targeted interviews that allow researchers to contextualize students' interactions with a digital learning environment (e.g., intelligent tutoring systems or educational games) while minimizing the amount of time that the researcher interrupts that learning experience, and focusing researcher time on the events they most want to focus on DDCIs are facilitated by a research tool called the Quick Red Fox (QRF)--an open-source server-client Android app that optimizes researcher time by directing interviewers to users that have just displayed an interesting behavior (previously defined by the research team). QRF integrates with existing student modeling technologies (e.g., behavior-sensing, affect-sensing, detection of self-regulated learning) to alert researchers to key moments in a learner's experience. This manual documents the tech while providing training on the processes involved in developing triggers and interview techniques; it also suggests methods of analyses.
ABROCA Distributions For Algorithmic Bias Assessment: Considerations Around Interpretation
Nov 28, 2024Abstract:Algorithmic bias continues to be a key concern of learning analytics. We study the statistical properties of the Absolute Between-ROC Area (ABROCA) metric. This fairness measure quantifies group-level differences in classifier performance through the absolute difference in ROC curves. ABROCA is particularly useful for detecting nuanced performance differences even when overall Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) values are similar. We sample ABROCA under various conditions, including varying AUC differences and class distributions. We find that ABROCA distributions exhibit high skewness dependent on sample sizes, AUC differences, and class imbalance. When assessing whether a classifier is biased, this skewness inflates ABROCA values by chance, even when data is drawn (by simulation) from populations with equivalent ROC curves. These findings suggest that ABROCA requires careful interpretation given its distributional properties, especially when used to assess the degree of bias and when classes are imbalanced.
Detecting Unsuccessful Students in Cybersecurity Exercises in Two Different Learning Environments
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:This full paper in the research track evaluates the usage of data logged from cybersecurity exercises in order to predict students who are potentially at risk of performing poorly. Hands-on exercises are essential for learning since they enable students to practice their skills. In cybersecurity, hands-on exercises are often complex and require knowledge of many topics. Therefore, students may miss solutions due to gaps in their knowledge and become frustrated, which impedes their learning. Targeted aid by the instructor helps, but since the instructor's time is limited, efficient ways to detect struggling students are needed. This paper develops automated tools to predict when a student is having difficulty. We formed a dataset with the actions of 313 students from two countries and two learning environments: KYPO CRP and EDURange. These data are used in machine learning algorithms to predict the success of students in exercises deployed in these environments. After extracting features from the data, we trained and cross-validated eight classifiers for predicting the exercise outcome and evaluated their predictive power. The contribution of this paper is comparing two approaches to feature engineering, modeling, and classification performance on data from two learning environments. Using the features from either learning environment, we were able to detect and distinguish between successful and struggling students. A decision tree classifier achieved the highest balanced accuracy and sensitivity with data from both learning environments. The results show that activity data from cybersecurity exercises are suitable for predicting student success. In a potential application, such models can aid instructors in detecting struggling students and providing targeted help. We publish data and code for building these models so that others can adopt or adapt them.
Evaluating Algorithmic Bias in Models for Predicting Academic Performance of Filipino Students
May 16, 2024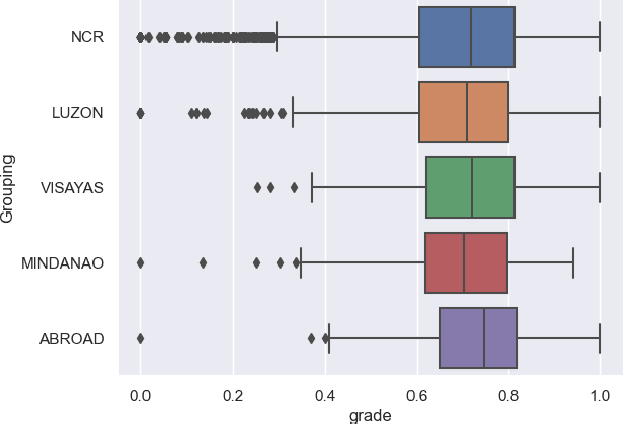
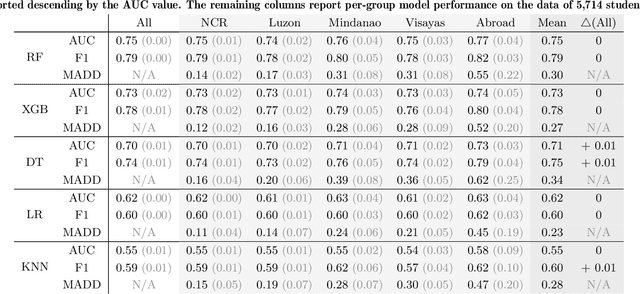
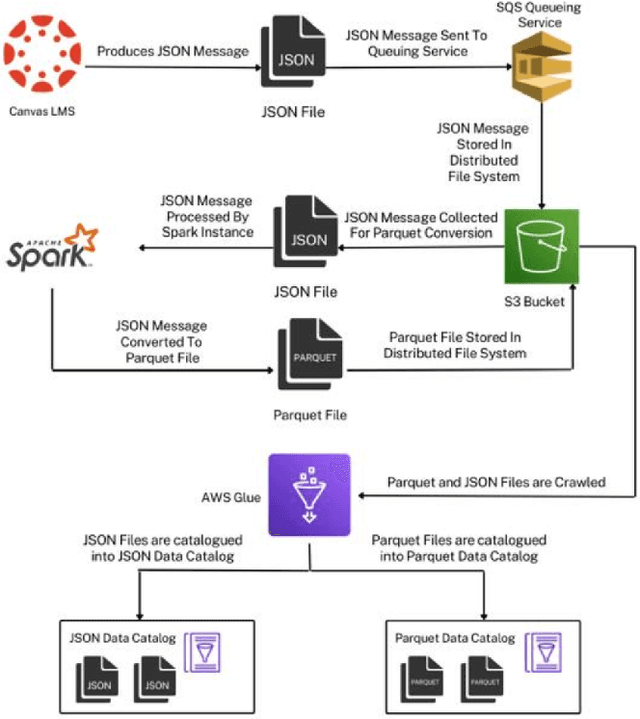
Abstract:Algorithmic bias is a major issue in machine learning models in educational contexts. However, it has not yet been studied thoroughly in Asian learning contexts, and only limited work has considered algorithmic bias based on regional (sub-national) background. As a step towards addressing this gap, this paper examines the population of 5,986 students at a large university in the Philippines, investigating algorithmic bias based on students' regional background. The university used the Canvas learning management system (LMS) in its online courses across a broad range of domains. Over the period of three semesters, we collected 48.7 million log records of the students' activity in Canvas. We used these logs to train binary classification models that predict student grades from the LMS activity. The best-performing model reached AUC of 0.75 and weighted F1-score of 0.79. Subsequently, we examined the data for bias based on students' region. Evaluation using three metrics: AUC, weighted F1-score, and MADD showed consistent results across all demographic groups. Thus, no unfairness was observed against a particular student group in the grade predictions.
On Fixing the Right Problems in Predictive Analytics: AUC Is Not the Problem
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Recently, ACM FAccT published an article by Kwegyir-Aggrey and colleagues (2023), critiquing the use of AUC ROC in predictive analytics in several domains. In this article, we offer a critique of that article. Specifically, we highlight technical inaccuracies in that paper's comparison of metrics, mis-specification of the interpretation and goals of AUC ROC, the article's use of the accuracy metric as a gold standard for comparison to AUC ROC, and the article's application of critiques solely to AUC ROC for concerns that would apply to the use of any metric. We conclude with a re-framing of the very valid concerns raised in that article, and discuss how the use of AUC ROC can remain a valid and appropriate practice in a well-informed predictive analytics approach taking those concerns into account. We conclude by discussing the combined use of multiple metrics, including machine learning bias metrics, and AUC ROC's place in such an approach. Like broccoli, AUC ROC is healthy, but also like broccoli, researchers and practitioners in our field shouldn't eat a diet of only AUC ROC.
Using Think-Aloud Data to Understand Relations between Self-Regulation Cycle Characteristics and Student Performance in Intelligent Tutoring Systems
Dec 09, 2023



Abstract:Numerous studies demonstrate the importance of self-regulation during learning by problem-solving. Recent work in learning analytics has largely examined students' use of SRL concerning overall learning gains. Limited research has related SRL to in-the-moment performance differences among learners. The present study investigates SRL behaviors in relationship to learners' moment-by-moment performance while working with intelligent tutoring systems for stoichiometry chemistry. We demonstrate the feasibility of labeling SRL behaviors based on AI-generated think-aloud transcripts, identifying the presence or absence of four SRL categories (processing information, planning, enacting, and realizing errors) in each utterance. Using the SRL codes, we conducted regression analyses to examine how the use of SRL in terms of presence, frequency, cyclical characteristics, and recency relate to student performance on subsequent steps in multi-step problems. A model considering students' SRL cycle characteristics outperformed a model only using in-the-moment SRL assessment. In line with theoretical predictions, students' actions during earlier, process-heavy stages of SRL cycles exhibited lower moment-by-moment correctness during problem-solving than later SRL cycle stages. We discuss system re-design opportunities to add SRL support during stages of processing and paths forward for using machine learning to speed research depending on the assessment of SRL based on transcription of think-aloud data.
Auditing and Mitigating Cultural Bias in LLMs
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:Culture fundamentally shapes people's reasoning, behavior, and communication. Generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies may cause a shift towards a dominant culture. As people increasingly use AI to expedite and even automate various professional and personal tasks, cultural values embedded in AI models may bias authentic expression. We audit large language models for cultural bias, comparing their responses to nationally representative survey data, and evaluate country-specific prompting as a mitigation strategy. We find that GPT-4, 3.5 and 3 exhibit cultural values resembling English-speaking and Protestant European countries. Our mitigation strategy reduces cultural bias in recent models but not for all countries/territories. To avoid cultural bias in generative AI, especially in high-stakes contexts, we suggest using culture matching and ongoing cultural audits.
Towards Generalizable Detection of Urgency of Discussion Forum Posts
Jul 14, 2023Abstract:Students who take an online course, such as a MOOC, use the course's discussion forum to ask questions or reach out to instructors when encountering an issue. However, reading and responding to students' questions is difficult to scale because of the time needed to consider each message. As a result, critical issues may be left unresolved, and students may lose the motivation to continue in the course. To help address this problem, we build predictive models that automatically determine the urgency of each forum post, so that these posts can be brought to instructors' attention. This paper goes beyond previous work by predicting not just a binary decision cut-off but a post's level of urgency on a 7-point scale. First, we train and cross-validate several models on an original data set of 3,503 posts from MOOCs at University of Pennsylvania. Second, to determine the generalizability of our models, we test their performance on a separate, previously published data set of 29,604 posts from MOOCs at Stanford University. While the previous work on post urgency used only one data set, we evaluated the prediction across different data sets and courses. The best-performing model was a support vector regressor trained on the Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings of the posts, achieving an RMSE of 1.1 on the training set and 1.4 on the test set. Understanding the urgency of forum posts enables instructors to focus their time more effectively and, as a result, better support student learning.
Large Language Models (GPT) for automating feedback on programming assignments
Jun 30, 2023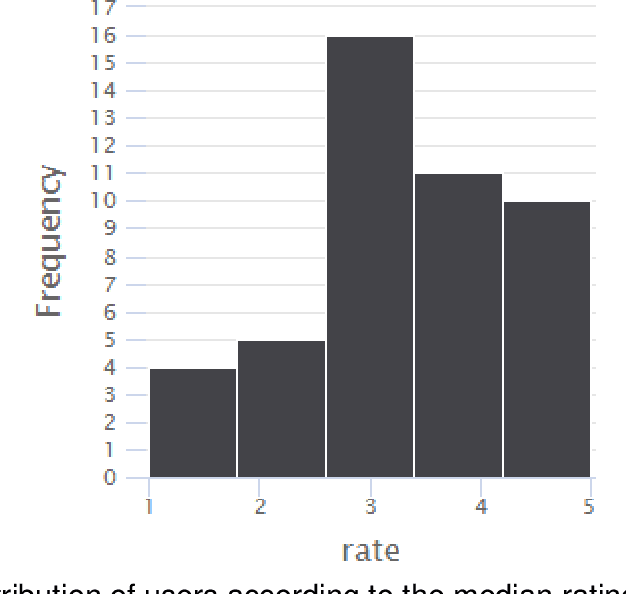



Abstract:Addressing the challenge of generating personalized feedback for programming assignments is demanding due to several factors, like the complexity of code syntax or different ways to correctly solve a task. In this experimental study, we automated the process of feedback generation by employing OpenAI's GPT-3.5 model to generate personalized hints for students solving programming assignments on an automated assessment platform. Students rated the usefulness of GPT-generated hints positively. The experimental group (with GPT hints enabled) relied less on the platform's regular feedback but performed better in terms of percentage of successful submissions across consecutive attempts for tasks, where GPT hints were enabled. For tasks where the GPT feedback was made unavailable, the experimental group needed significantly less time to solve assignments. Furthermore, when GPT hints were unavailable, students in the experimental condition were initially less likely to solve the assignment correctly. This suggests potential over-reliance on GPT-generated feedback. However, students in the experimental condition were able to correct reasonably rapidly, reaching the same percentage correct after seven submission attempts. The availability of GPT hints did not significantly impact students' affective state.
Extending Deep Knowledge Tracing: Inferring Interpretable Knowledge and Predicting Post-System Performance
Oct 14, 2019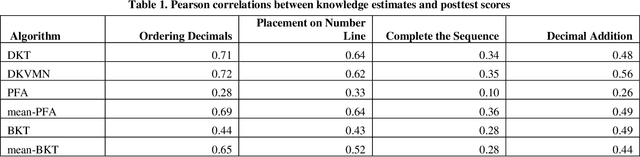
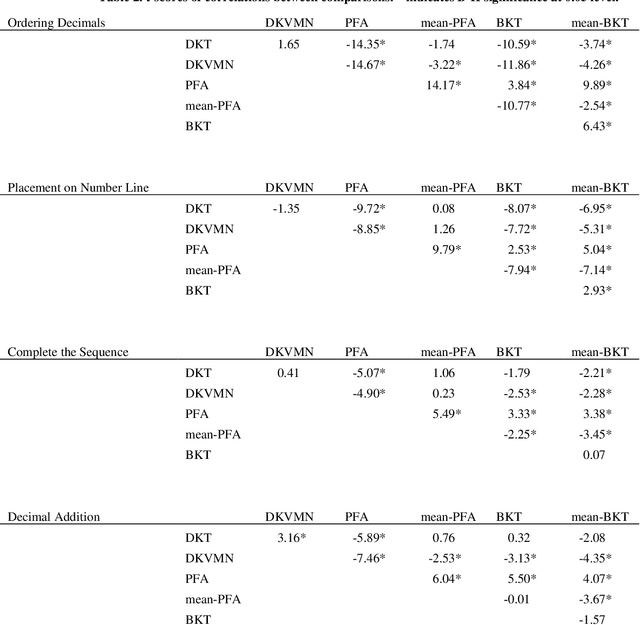
Abstract:Recent student knowledge modeling algorithms such as DKT and DKVMN have been shown to produce accurate predictions of problem correctness within the same learning system. However, these algorithms do not generate estimates of student knowledge. In this paper we present an extension that infers knowledge estimates from correctness predictions. We apply this extension to DKT and DKVMN, resulting in knowledge estimates that correlate better with a posttest than knowledge estimates produced by PFA or BKT. We also apply our extension to correctness predictions from PFA and BKT, finding that knowledge predictions produced with it correlate better with the posttest than BKT and PFA's own knowledge predictions. These findings are significant since the primary aim of education is to prepare students for later experiences outside of the immediate learning activity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge