Atsushi Shimada
Scaffolding Metacognition in Programming Education: Understanding Student-AI Interactions and Design Implications
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT now provide novice programmers with unprecedented access to instant, personalized support. While this holds clear promise, their influence on students' metacognitive processes remains underexplored. Existing work has largely focused on correctness and usability, with limited attention to whether and how students' use of AI assistants supports or bypasses key metacognitive processes. This study addresses that gap by analyzing student-AI interactions through a metacognitive lens in university-level programming courses. We examined more than 10,000 dialogue logs collected over three years, complemented by surveys of students and educators. Our analysis focused on how prompts and responses aligned with metacognitive phases and strategies. Synthesizing these findings across data sources, we distill design considerations for AI-powered coding assistants that aim to support rather than supplant metacognitive engagement. Our findings provide guidance for developing educational AI tools that strengthen students' learning processes in programming education.
Ranking-Based At-Risk Student Prediction Using Federated Learning and Differential Features
May 14, 2025Abstract:Digital textbooks are widely used in various educational contexts, such as university courses and online lectures. Such textbooks yield learning log data that have been used in numerous educational data mining (EDM) studies for student behavior analysis and performance prediction. However, these studies have faced challenges in integrating confidential data, such as academic records and learning logs, across schools due to privacy concerns. Consequently, analyses are often conducted with data limited to a single school, which makes developing high-performing and generalizable models difficult. This study proposes a method that combines federated learning and differential features to address these issues. Federated learning enables model training without centralizing data, thereby preserving student privacy. Differential features, which utilize relative values instead of absolute values, enhance model performance and generalizability. To evaluate the proposed method, a model for predicting at-risk students was trained using data from 1,136 students across 12 courses conducted over 4 years, and validated on hold-out test data from 5 other courses. Experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method addresses privacy concerns while achieving performance comparable to that of models trained via centralized learning in terms of Top-n precision, nDCG, and PR-AUC. Furthermore, using differential features improved prediction performance across all evaluation datasets compared to non-differential approaches. The trained models were also applicable for early prediction, achieving high performance in detecting at-risk students in earlier stages of the semester within the validation datasets.
LECTOR: Summarizing E-book Reading Content for Personalized Student Support
May 12, 2025Abstract:Educational e-book platforms provide valuable information to teachers and researchers through two main sources: reading activity data and reading content data. While reading activity data is commonly used to analyze learning strategies and predict low-performing students, reading content data is often overlooked in these analyses. To address this gap, this study proposes LECTOR (Lecture slides and Topic Relationships), a model that summarizes information from reading content in a format that can be easily integrated with reading activity data. Our first experiment compared LECTOR to representative Natural Language Processing (NLP) models in extracting key information from 2,255 lecture slides, showing an average improvement of 5% in F1-score. These results were further validated through a human evaluation involving 28 students, which showed an average improvement of 21% in F1-score over a model predominantly used in current educational tools. Our second experiment compared reading preferences extracted by LECTOR with traditional reading activity data in predicting low-performing students using 600,712 logs from 218 students. The results showed a tendency to improve the predictive performance by integrating LECTOR. Finally, we proposed examples showing the potential application of the reading preferences extracted by LECTOR in designing personalized interventions for students.
* Published open-access in the International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education (IJAIED), see https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-025-00478-6
Single-Agent vs. Multi-Agent LLM Strategies for Automated Student Reflection Assessment
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:We explore the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated assessment of open-text student reflections and prediction of academic performance. Traditional methods for evaluating reflections are time-consuming and may not scale effectively in educational settings. In this work, we employ LLMs to transform student reflections into quantitative scores using two assessment strategies (single-agent and multi-agent) and two prompting techniques (zero-shot and few-shot). Our experiments, conducted on a dataset of 5,278 reflections from 377 students over three academic terms, demonstrate that the single-agent with few-shot strategy achieves the highest match rate with human evaluations. Furthermore, models utilizing LLM-assessed reflection scores outperform baselines in both at-risk student identification and grade prediction tasks. These findings suggest that LLMs can effectively automate reflection assessment, reduce educators' workload, and enable timely support for students who may need additional assistance. Our work emphasizes the potential of integrating advanced generative AI technologies into educational practices to enhance student engagement and academic success.
Attention Mamba: Time Series Modeling with Adaptive Pooling Acceleration and Receptive Field Enhancements
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:"This work has been submitted to the lEEE for possible publication. Copyright may be transferred without noticeafter which this version may no longer be accessible." Time series modeling serves as the cornerstone of real-world applications, such as weather forecasting and transportation management. Recently, Mamba has become a promising model that combines near-linear computational complexity with high prediction accuracy in time series modeling, while facing challenges such as insufficient modeling of nonlinear dependencies in attention and restricted receptive fields caused by convolutions. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces an innovative framework, Attention Mamba, featuring a novel Adaptive Pooling block that accelerates attention computation and incorporates global information, effectively overcoming the constraints of limited receptive fields. Furthermore, Attention Mamba integrates a bidirectional Mamba block, efficiently capturing long-short features and transforming inputs into the Value representations for attention mechanisms. Extensive experiments conducted on diverse datasets underscore the effectiveness of Attention Mamba in extracting nonlinear dependencies and enhancing receptive fields, establishing superior performance among leading counterparts. Our codes will be available on GitHub.
Knowledge Distillation in RNN-Attention Models for Early Prediction of Student Performance
Dec 19, 2024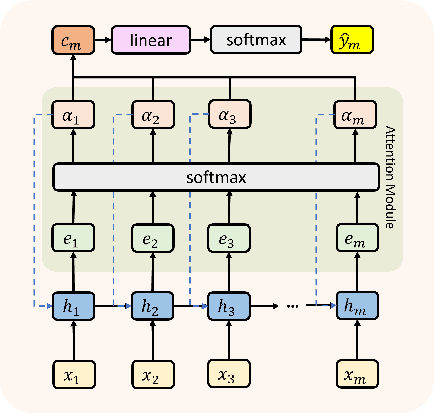


Abstract:Educational data mining (EDM) is a part of applied computing that focuses on automatically analyzing data from learning contexts. Early prediction for identifying at-risk students is a crucial and widely researched topic in EDM research. It enables instructors to support at-risk students to stay on track, preventing student dropout or failure. Previous studies have predicted students' learning performance to identify at-risk students by using machine learning on data collected from e-learning platforms. However, most studies aimed to identify at-risk students utilizing the entire course data after the course finished. This does not correspond to the real-world scenario that at-risk students may drop out before the course ends. To address this problem, we introduce an RNN-Attention-KD (knowledge distillation) framework to predict at-risk students early throughout a course. It leverages the strengths of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) in handling time-sequence data to predict students' performance at each time step and employs an attention mechanism to focus on relevant time steps for improved predictive accuracy. At the same time, KD is applied to compress the time steps to facilitate early prediction. In an empirical evaluation, RNN-Attention-KD outperforms traditional neural network models in terms of recall and F1-measure. For example, it obtained recall and F1-measure of 0.49 and 0.51 for Weeks 1--3 and 0.51 and 0.61 for Weeks 1--6 across all datasets from four years of a university course. Then, an ablation study investigated the contributions of different knowledge transfer methods (distillation objectives). We found that hint loss from the hidden layer of RNN and context vector loss from the attention module on RNN could enhance the model's prediction performance for identifying at-risk students. These results are relevant for EDM researchers employing deep learning models.
Evaluating the Impact of Data Augmentation on Predictive Model Performance
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:In supervised machine learning (SML) research, large training datasets are essential for valid results. However, obtaining primary data in learning analytics (LA) is challenging. Data augmentation can address this by expanding and diversifying data, though its use in LA remains underexplored. This paper systematically compares data augmentation techniques and their impact on prediction performance in a typical LA task: prediction of academic outcomes. Augmentation is demonstrated on four SML models, which we successfully replicated from a previous LAK study based on AUC values. Among 21 augmentation techniques, SMOTE-ENN sampling performed the best, improving the average AUC by 0.01 and approximately halving the training time compared to the baseline models. In addition, we compared 99 combinations of chaining 21 techniques, and found minor, although statistically significant, improvements across models when adding noise to SMOTE-ENN (+0.014). Notably, some augmentation techniques significantly lowered predictive performance or increased performance fluctuation related to random chance. This paper's contribution is twofold. Primarily, our empirical findings show that sampling techniques provide the most statistically reliable performance improvements for LA applications of SML, and are computationally more efficient than deep generation methods with complex hyperparameter settings. Second, the LA community may benefit from validating a recent study through independent replication.
Attention-Seeker: Dynamic Self-Attention Scoring for Unsupervised Keyphrase Extraction
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes Attention-Seeker, an unsupervised keyphrase extraction method that leverages self-attention maps from a Large Language Model to estimate the importance of candidate phrases. Our approach identifies specific components - such as layers, heads, and attention vectors - where the model pays significant attention to the key topics of the text. The attention weights provided by these components are then used to score the candidate phrases. Unlike previous models that require manual tuning of parameters (e.g., selection of heads, prompts, hyperparameters), Attention-Seeker dynamically adapts to the input text without any manual adjustments, enhancing its practical applicability. We evaluate Attention-Seeker on four publicly available datasets: Inspec, SemEval2010, SemEval2017, and Krapivin. Our results demonstrate that, even without parameter tuning, Attention-Seeker outperforms most baseline models, achieving state-of-the-art performance on three out of four datasets, particularly excelling in extracting keyphrases from long documents.
Comparison of Large Language Models for Generating Contextually Relevant Questions
Jul 30, 2024Abstract:This study explores the effectiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Question Generation in educational settings. Three LLMs are compared in their ability to create questions from university slide text without fine-tuning. Questions were obtained in a two-step pipeline: first, answer phrases were extracted from slides using Llama 2-Chat 13B; then, the three models generated questions for each answer. To analyze whether the questions would be suitable in educational applications for students, a survey was conducted with 46 students who evaluated a total of 246 questions across five metrics: clarity, relevance, difficulty, slide relation, and question-answer alignment. Results indicate that GPT-3.5 and Llama 2-Chat 13B outperform Flan T5 XXL by a small margin, particularly in terms of clarity and question-answer alignment. GPT-3.5 especially excels at tailoring questions to match the input answers. The contribution of this research is the analysis of the capacity of LLMs for Automatic Question Generation in education.
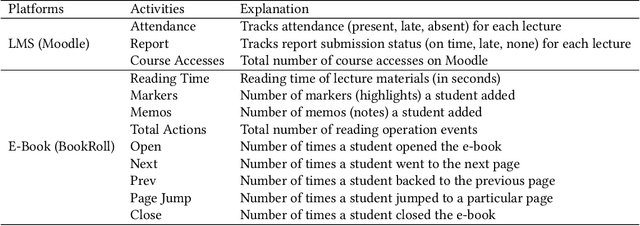
Evaluating Algorithmic Bias in Models for Predicting Academic Performance of Filipino Students
May 16, 2024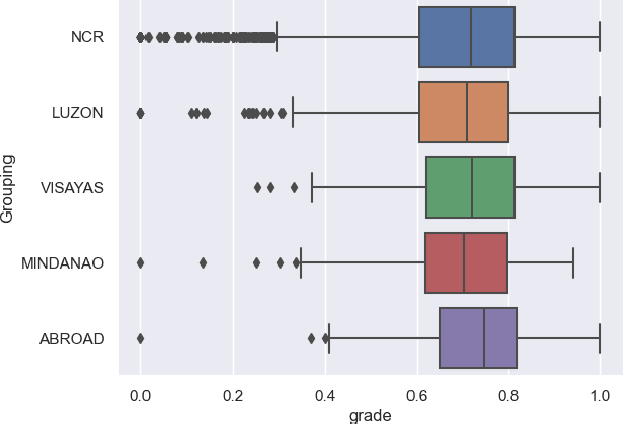
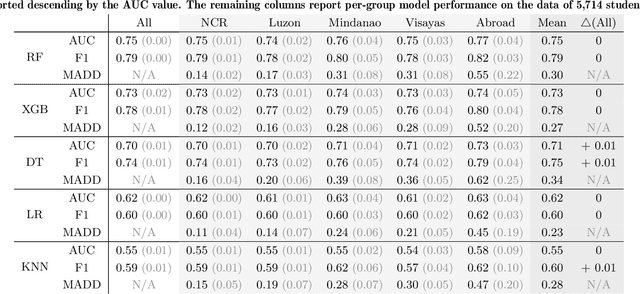
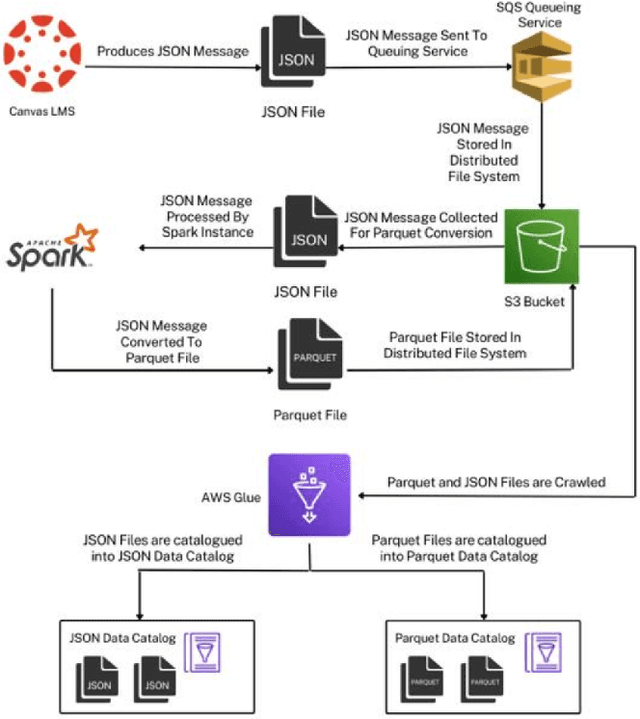
Abstract:Algorithmic bias is a major issue in machine learning models in educational contexts. However, it has not yet been studied thoroughly in Asian learning contexts, and only limited work has considered algorithmic bias based on regional (sub-national) background. As a step towards addressing this gap, this paper examines the population of 5,986 students at a large university in the Philippines, investigating algorithmic bias based on students' regional background. The university used the Canvas learning management system (LMS) in its online courses across a broad range of domains. Over the period of three semesters, we collected 48.7 million log records of the students' activity in Canvas. We used these logs to train binary classification models that predict student grades from the LMS activity. The best-performing model reached AUC of 0.75 and weighted F1-score of 0.79. Subsequently, we examined the data for bias based on students' region. Evaluation using three metrics: AUC, weighted F1-score, and MADD showed consistent results across all demographic groups. Thus, no unfairness was observed against a particular student group in the grade predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge