Rene F. Kizilcec
Codebook-Injected Dialogue Segmentation for Multi-Utterance Constructs Annotation: LLM-Assisted and Gold-Label-Free Evaluation
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Dialogue Act (DA) annotation typically treats communicative or pedagogical intent as localized to individual utterances or turns. This leads annotators to agree on the underlying action while disagreeing on segment boundaries, reducing apparent reliability. We propose codebook-injected segmentation, which conditions boundary decisions on downstream annotation criteria, and evaluate LLM-based segmenters against standard and retrieval-augmented baselines. To assess these without gold labels, we introduce evaluation metrics for span consistency, distinctiveness, and human-AI distributional agreement. We found DA-awareness produces segments that are internally more consistent than text-only baselines. While LLMs excel at creating construct-consistent spans, coherence-based baselines remain superior at detecting global shifts in dialogue flow. Across two datasets, no single segmenter dominates. Improvements in within-segment coherence frequently trade off against boundary distinctiveness and human-AI distributional agreement. These results highlight segmentation as a consequential design choice that should be optimized for downstream objectives rather than a single performance score.
How well do Large Language Models Recognize Instructional Moves? Establishing Baselines for Foundation Models in Educational Discourse
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly adopted in educational technologies for a variety of tasks, from generating instructional materials and assisting with assessment design to tutoring. While prior work has investigated how models can be adapted or optimized for specific tasks, far less is known about how well LLMs perform at interpreting authentic educational scenarios without significant customization. As LLM-based systems become widely adopted by learners and educators in everyday academic contexts, understanding their out-of-the-box capabilities is increasingly important for setting expectations and benchmarking. We compared six LLMs to estimate their baseline performance on a simple but important task: classifying instructional moves in authentic classroom transcripts. We evaluated typical prompting methods: zero-shot, one-shot, and few-shot prompting. We found that while zero-shot performance was moderate, providing comprehensive examples (few-shot prompting) significantly improved performance for state-of-the-art models, with the strongest configuration reaching Cohen's Kappa = 0.58 against expert-coded annotations. At the same time, improvements were neither uniform nor complete: performance varied considerably by instructional move, and higher recall frequently came at the cost of increased false positives. Overall, these findings indicate that foundation models demonstrate meaningful yet limited capacity to interpret instructional discourse, with prompt design helping to surface capability but not eliminating fundamental reliability constraints.
AI Annotation Orchestration: Evaluating LLM verifiers to Improve the Quality of LLM Annotations in Learning Analytics
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used to annotate learning interactions, yet concerns about reliability limit their utility. We test whether verification-oriented orchestration-prompting models to check their own labels (self-verification) or audit one another (cross-verification)-improves qualitative coding of tutoring discourse. Using transcripts from 30 one-to-one math sessions, we compare three production LLMs (GPT, Claude, Gemini) under three conditions: unverified annotation, self-verification, and cross-verification across all orchestration configurations. Outputs are benchmarked against a blinded, disagreement-focused human adjudication using Cohen's kappa. Overall, orchestration yields a 58 percent improvement in kappa. Self-verification nearly doubles agreement relative to unverified baselines, with the largest gains for challenging tutor moves. Cross-verification achieves a 37 percent improvement on average, with pair- and construct-dependent effects: some verifier-annotator pairs exceed self-verification, while others reduce alignment, reflecting differences in verifier strictness. We contribute: (1) a flexible orchestration framework instantiating control, self-, and cross-verification; (2) an empirical comparison across frontier LLMs on authentic tutoring data with blinded human "gold" labels; and (3) a concise notation, verifier(annotator) (e.g., Gemini(GPT) or Claude(Claude)), to standardize reporting and make directional effects explicit for replication. Results position verification as a principled design lever for reliable, scalable LLM-assisted annotation in Learning Analytics.
Investigating Student Interaction Patterns with Large Language Model-Powered Course Assistants in Computer Science Courses
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Providing students with flexible and timely academic support is a challenge at most colleges and universities, leaving many students without help outside scheduled hours. Large language models (LLMs) are promising for bridging this gap, but interactions between students and LLMs are rarely overseen by educators. We developed and studied an LLM-powered course assistant deployed across multiple computer science courses to characterize real-world use and understand pedagogical implications. By Spring 2024, our system had been deployed to approximately 2,000 students across six courses at three institutions. Analysis of the interaction data shows that usage remains strong in the evenings and nights and is higher in introductory courses, indicating that our system helps address temporal support gaps and novice learner needs. We sampled 200 conversations per course for manual annotation: most sampled responses were judged correct and helpful, with a small share unhelpful or erroneous; few responses included dedicated examples. We also examined an inquiry-based learning strategy: only around 11% of sampled conversations contained LLM-generated follow-up questions, which were often ignored by students in advanced courses. A Bloom's taxonomy analysis reveals that current LLM capabilities are limited in generating higher-order cognitive questions. These patterns suggest opportunities for pedagogically oriented LLM-based educational systems and greater educator involvement in configuring prompts, content, and policies.
Auditing and Mitigating Cultural Bias in LLMs
Nov 23, 2023



Abstract:Culture fundamentally shapes people's reasoning, behavior, and communication. Generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies may cause a shift towards a dominant culture. As people increasingly use AI to expedite and even automate various professional and personal tasks, cultural values embedded in AI models may bias authentic expression. We audit large language models for cultural bias, comparing their responses to nationally representative survey data, and evaluate country-specific prompting as a mitigation strategy. We find that GPT-4, 3.5 and 3 exhibit cultural values resembling English-speaking and Protestant European countries. Our mitigation strategy reduces cultural bias in recent models but not for all countries/territories. To avoid cultural bias in generative AI, especially in high-stakes contexts, we suggest using culture matching and ongoing cultural audits.
Augmenting Holistic Review in University Admission using Natural Language Processing for Essays and Recommendation Letters
Jun 30, 2023


Abstract:University admission at many highly selective institutions uses a holistic review process, where all aspects of the application, including protected attributes (e.g., race, gender), grades, essays, and recommendation letters are considered, to compose an excellent and diverse class. In this study, we empirically evaluate how influential protected attributes are for predicting admission decisions using a machine learning (ML) model, and in how far textual information (e.g., personal essay, teacher recommendation) may substitute for the loss of protected attributes in the model. Using data from 14,915 applicants to an undergraduate admission office at a selective U.S. institution in the 2022-2023 cycle, we find that the exclusion of protected attributes from the ML model leads to substantially reduced admission-prediction performance. The inclusion of textual information via both a TF-IDF representation and a Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) model partially restores model performance, but does not appear to provide a full substitute for admitting a similarly diverse class. In particular, while the text helps with gender diversity, the proportion of URM applicants is severely impacted by the exclusion of protected attributes, and the inclusion of new attributes generated from the textual information does not recover this performance loss.
On the limits of algorithmic prediction across the globe
Mar 28, 2021
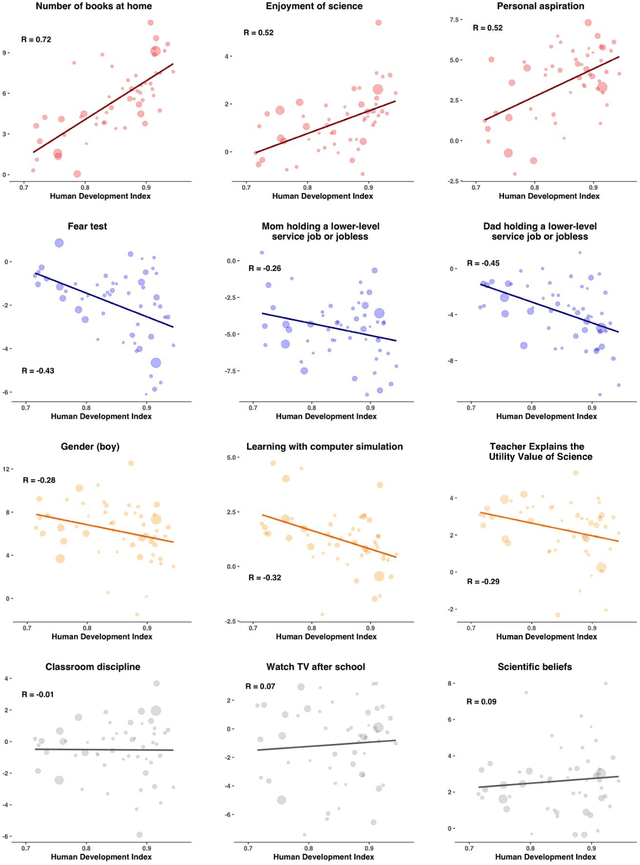
Abstract:The impact of predictive algorithms on people's lives and livelihoods has been noted in medicine, criminal justice, finance, hiring and admissions. Most of these algorithms are developed using data and human capital from highly developed nations. We tested how well predictive models of human behavior trained in a developed country generalize to people in less developed countries by modeling global variation in 200 predictors of academic achievement on nationally representative student data for 65 countries. Here we show that state-of-the-art machine learning models trained on data from the United States can predict achievement with high accuracy and generalize to other developed countries with comparable accuracy. However, accuracy drops linearly with national development due to global variation in the importance of different achievement predictors, providing a useful heuristic for policymakers. Training the same model on national data yields high accuracy in every country, which highlights the value of local data collection.
Artificial intelligence in communication impacts language and social relationships
Feb 10, 2021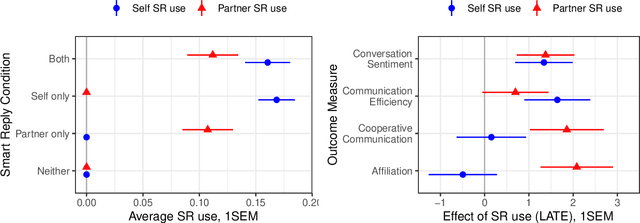
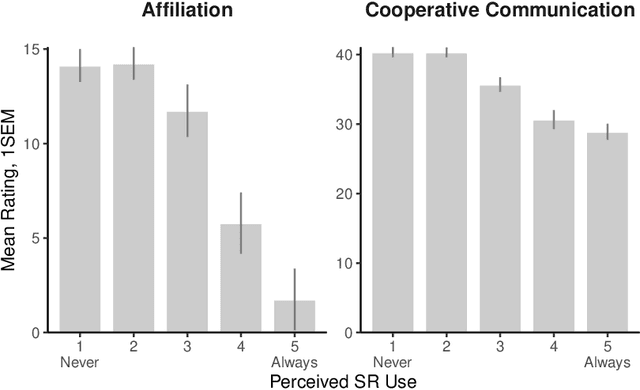
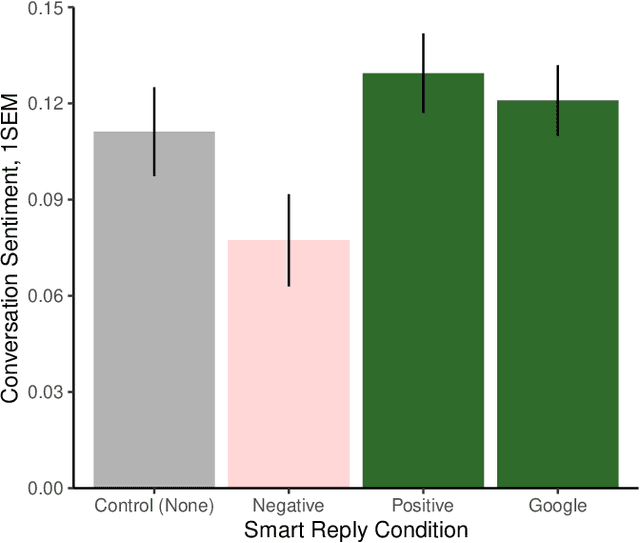
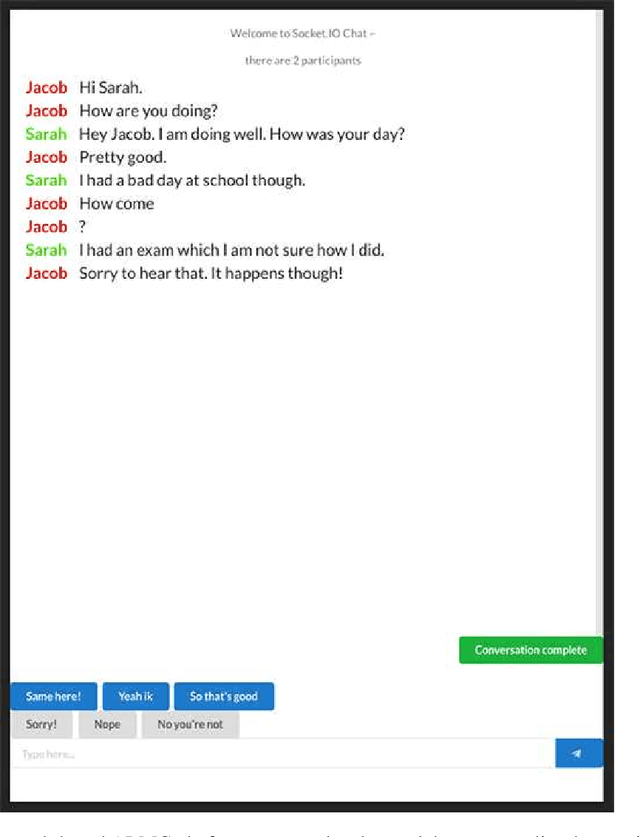
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is now widely used to facilitate social interaction, but its impact on social relationships and communication is not well understood. We study the social consequences of one of the most pervasive AI applications: algorithmic response suggestions ("smart replies"). Two randomized experiments (n = 1036) provide evidence that a commercially-deployed AI changes how people interact with and perceive one another in pro-social and anti-social ways. We find that using algorithmic responses increases communication efficiency, use of positive emotional language, and positive evaluations by communication partners. However, consistent with common assumptions about the negative implications of AI, people are evaluated more negatively if they are suspected to be using algorithmic responses. Thus, even though AI can increase communication efficiency and improve interpersonal perceptions, it risks changing users' language production and continues to be viewed negatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge