Ruikang Liu
A Simple Linear Patch Revives Layer-Pruned Large Language Models
May 30, 2025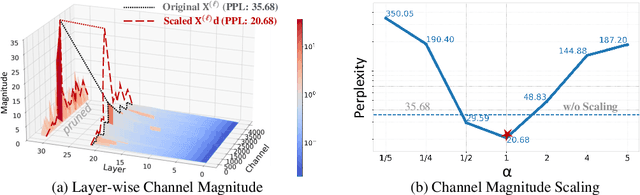
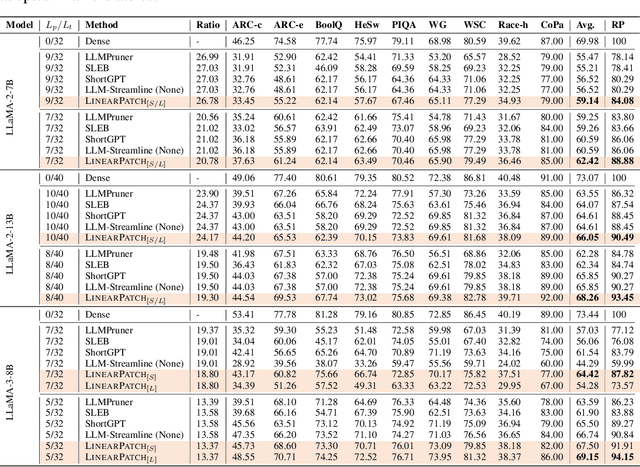
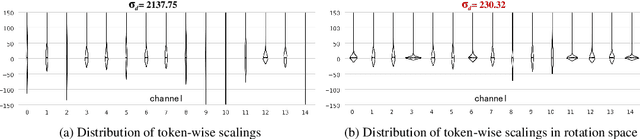
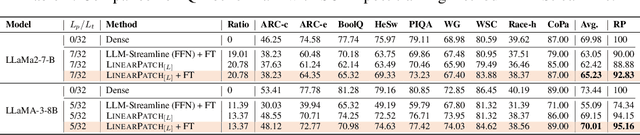
Abstract:Layer pruning has become a popular technique for compressing large language models (LLMs) due to its simplicity. However, existing layer pruning methods often suffer from significant performance drops. We identify that this degradation stems from the mismatch of activation magnitudes across layers and tokens at the pruning interface. To address this, we propose LinearPatch, a simple plug-and-play technique to revive the layer-pruned LLMs. The proposed method adopts Hadamard transformation to suppress massive outliers in particular tokens, and channel-wise scaling to align the activation magnitudes. These operations can be fused into a single matrix, which functions as a patch to bridge the pruning interface with negligible inference overhead. LinearPatch retains up to 94.15% performance of the original model when pruning 5 layers of LLaMA-3-8B on the question answering benchmark, surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods by 4%. In addition, the patch matrix can be further optimized with memory efficient offline knowledge distillation. With only 5K samples, the retained performance of LinearPatch can be further boosted to 95.16% within 30 minutes on a single computing card.
Quantization Hurts Reasoning? An Empirical Study on Quantized Reasoning Models
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning language models have demonstrated remarkable performance in complex tasks, but their extended chain-of-thought reasoning process increases inference overhead. While quantization has been widely adopted to reduce the inference cost of large language models, its impact on reasoning models remains understudied. In this study, we conduct the first systematic study on quantized reasoning models, evaluating the open-sourced DeepSeek-R1-Distilled Qwen and LLaMA families ranging from 1.5B to 70B parameters, and QwQ-32B. Our investigation covers weight, KV cache, and activation quantization using state-of-the-art algorithms at varying bit-widths, with extensive evaluation across mathematical (AIME, MATH-500), scientific (GPQA), and programming (LiveCodeBench) reasoning benchmarks. Our findings reveal that while lossless quantization can be achieved with W8A8 or W4A16 quantization, lower bit-widths introduce significant accuracy risks. We further identify model size, model origin, and task difficulty as critical determinants of performance. Contrary to expectations, quantized models do not exhibit increased output lengths. In addition, strategically scaling the model sizes or reasoning steps can effectively enhance the performance. All quantized models and codes will be open-sourced in https://github.com/ruikangliu/Quantized-Reasoning-Models.
FlatQuant: Flatness Matters for LLM Quantization
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:Recently, quantization has been widely used for the compression and acceleration of large language models~(LLMs). Due to the outliers in LLMs, it is crucial to flatten weights and activations to minimize quantization error with the equally spaced quantization points. Prior research explores various pre-quantization transformations to suppress outliers, such as per-channel scaling and Hadamard transformation. However, we observe that these transformed weights and activations can still remain steep and outspread. In this paper, we propose FlatQuant (Fast and Learnable Affine Transformation), a new post-training quantization approach to enhance flatness of weights and activations. Our approach identifies optimal affine transformations tailored to each linear layer, calibrated in hours via a lightweight objective. To reduce runtime overhead, we apply Kronecker decomposition to the transformation matrices, and fuse all operations in FlatQuant into a single kernel. Extensive experiments show that FlatQuant sets up a new state-of-the-art quantization benchmark. For instance, it achieves less than $\textbf{1}\%$ accuracy drop for W4A4 quantization on the LLaMA-3-70B model, surpassing SpinQuant by $\textbf{7.5}\%$. For inference latency, FlatQuant reduces the slowdown induced by pre-quantization transformation from 0.26x of QuaRot to merely $\textbf{0.07x}$, bringing up to $\textbf{2.3x}$ speedup for prefill and $\textbf{1.7x}$ speedup for decoding, respectively. Code is available at: \url{https://github.com/ruikangliu/FlatQuant}.
IntactKV: Improving Large Language Model Quantization by Keeping Pivot Tokens Intact
Mar 02, 2024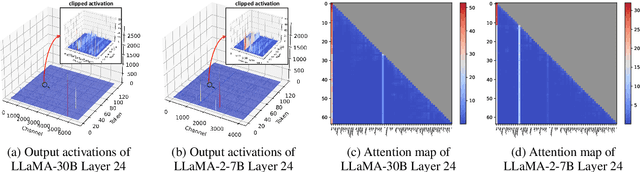
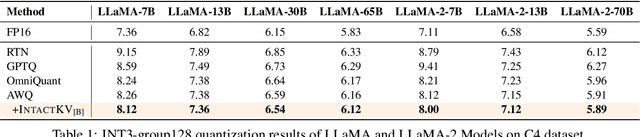
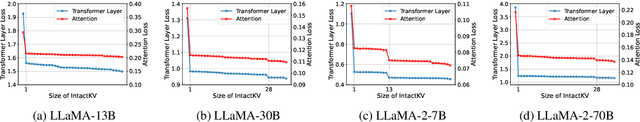
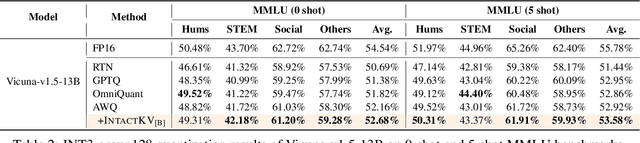
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in natural language processing but demand intensive computation. To mitigate this, various quantization methods have been explored, yet they compromise LLM performance. This paper unveils a previously overlooked type of outlier in LLMs. Such outliers are found to allocate most of the attention scores on initial tokens of input, termed as pivot tokens, which is crucial to the performance of quantized LLMs. Given that, we propose IntactKV to generate the KV cache of pivot tokens losslessly from the full-precision model. The approach is simple and easy to combine with existing quantization solutions. Besides, IntactKV can be calibrated as additional LLM parameters to boost the quantized LLMs further. Mathematical analysis also proves that IntactKV effectively reduces the upper bound of quantization error. Empirical results show that IntactKV brings consistent improvement and achieves lossless weight-only INT4 quantization on various downstream tasks, leading to the new state-of-the-art for LLM quantization.
Learning Imbalanced Data with Vision Transformers
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:The real-world data tends to be heavily imbalanced and severely skew the data-driven deep neural networks, which makes Long-Tailed Recognition (LTR) a massive challenging task. Existing LTR methods seldom train Vision Transformers (ViTs) with Long-Tailed (LT) data, while the off-the-shelf pretrain weight of ViTs always leads to unfair comparisons. In this paper, we systematically investigate the ViTs' performance in LTR and propose LiVT to train ViTs from scratch only with LT data. With the observation that ViTs suffer more severe LTR problems, we conduct Masked Generative Pretraining (MGP) to learn generalized features. With ample and solid evidence, we show that MGP is more robust than supervised manners. In addition, Binary Cross Entropy (BCE) loss, which shows conspicuous performance with ViTs, encounters predicaments in LTR. We further propose the balanced BCE to ameliorate it with strong theoretical groundings. Specially, we derive the unbiased extension of Sigmoid and compensate extra logit margins to deploy it. Our Bal-BCE contributes to the quick convergence of ViTs in just a few epochs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that with MGP and Bal-BCE, LiVT successfully trains ViTs well without any additional data and outperforms comparable state-of-the-art methods significantly, e.g., our ViT-B achieves 81.0% Top-1 accuracy in iNaturalist 2018 without bells and whistles. Code is available at https://github.com/XuZhengzhuo/LiVT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge