Ru-Ze Liang
A novel image tag completion method based on convolutional neural network
Jun 03, 2017
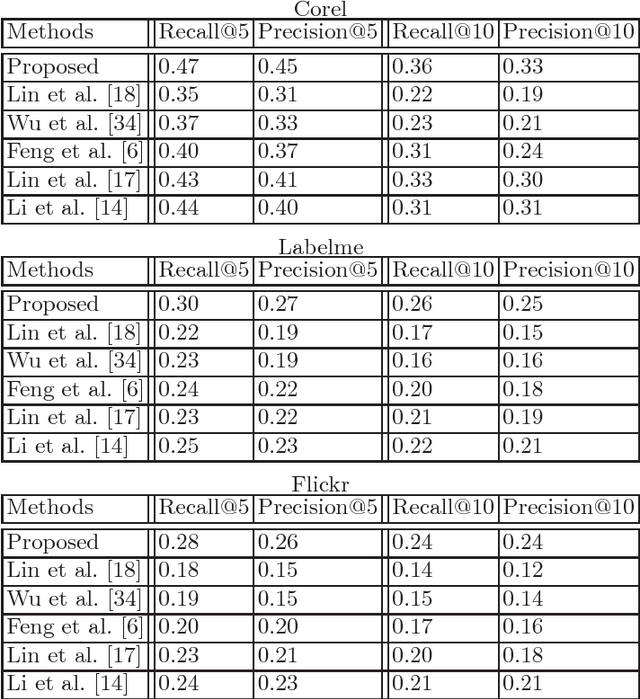

Abstract:In the problems of image retrieval and annotation, complete textual tag lists of images play critical roles. However, in real-world applications, the image tags are usually incomplete, thus it is important to learn the complete tags for images. In this paper, we study the problem of image tag complete and proposed a novel method for this problem based on a popular image representation method, convolutional neural network (CNN). The method estimates the complete tags from the convolutional filtering outputs of images based on a linear predictor. The CNN parameters, linear predictor, and the complete tags are learned jointly by our method. We build a minimization problem to encourage the consistency between the complete tags and the available incomplete tags, reduce the estimation error, and reduce the model complexity. An iterative algorithm is developed to solve the minimization problem. Experiments over benchmark image data sets show its effectiveness.
Learning convolutional neural network to maximize Pos@Top performance measure
Mar 01, 2017
Abstract:In the machine learning problems, the performance measure is used to evaluate the machine learning models. Recently, the number positive data points ranked at the top positions (Pos@Top) has been a popular performance measure in the machine learning community. In this paper, we propose to learn a convolutional neural network (CNN) model to maximize the Pos@Top performance measure. The CNN model is used to represent the multi-instance data point, and a classifier function is used to predict the label from the its CNN representation. We propose to minimize the loss function of Pos@Top over a training set to learn the filters of CNN and the classifier parameter. The classifier parameter vector is solved by the Lagrange multiplier method, and the filters are updated by the gradient descent method alternately in an iterative algorithm. Experiments over benchmark data sets show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art Pos@Top maximization methods.
Stochastic Learning of Multi-Instance Dictionary for Earth Mover's Distance based Histogram Comparison
Sep 03, 2016

Abstract:Dictionary plays an important role in multi-instance data representation. It maps bags of instances to histograms. Earth mover's distance (EMD) is the most effective histogram distance metric for the application of multi-instance retrieval. However, up to now, there is no existing multi-instance dictionary learning methods designed for EMD based histogram comparison. To fill this gap, we develop the first EMD-optimal dictionary learning method using stochastic optimization method. In the stochastic learning framework, we have one triplet of bags, including one basic bag, one positive bag, and one negative bag. These bags are mapped to histograms using a multi-instance dictionary. We argue that the EMD between the basic histogram and the positive histogram should be smaller than that between the basic histogram and the negative histogram. Base on this condition, we design a hinge loss. By minimizing this hinge loss and some regularization terms of the dictionary, we update the dictionary instances. The experiments over multi-instance retrieval applications shows its effectiveness when compared to other dictionary learning methods over the problems of medical image retrieval and natural language relation classification.
Optimizing Top Precision Performance Measure of Content-Based Image Retrieval by Learning Similarity Function
Aug 20, 2016

Abstract:In this paper we study the problem of content-based image retrieval. In this problem, the most popular performance measure is the top precision measure, and the most important component of a retrieval system is the similarity function used to compare a query image against a database image. However, up to now, there is no existing similarity learning method proposed to optimize the top precision measure. To fill this gap, in this paper, we propose a novel similarity learning method to maximize the top precision measure. We model this problem as a minimization problem with an objective function as the combination of the losses of the relevant images ranked behind the top-ranked irrelevant image, and the squared Frobenius norm of the similarity function parameter. This minimization problem is solved as a quadratic programming problem. The experiments over two benchmark data sets show the advantages of the proposed method over other similarity learning methods when the top precision is used as the performance measure.
A novel transfer learning method based on common space mapping and weighted domain matching
Aug 16, 2016
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel learning framework for the problem of domain transfer learning. We map the data of two domains to one single common space, and learn a classifier in this common space. Then we adapt the common classifier to the two domains by adding two adaptive functions to it respectively. In the common space, the target domain data points are weighted and matched to the target domain in term of distributions. The weighting terms of source domain data points and the target domain classification responses are also regularized by the local reconstruction coefficients. The novel transfer learning framework is evaluated over some benchmark cross-domain data sets, and it outperforms the existing state-of-the-art transfer learning methods.
Semi-supervised structured output prediction by local linear regression and sub-gradient descent
Aug 16, 2016

Abstract:We propose a novel semi-supervised structured output prediction method based on local linear regression in this paper. The existing semi-supervise structured output prediction methods learn a global predictor for all the data points in a data set, which ignores the differences of local distributions of the data set, and the effects to the structured output prediction. To solve this problem, we propose to learn the missing structured outputs and local predictors for neighborhoods of different data points jointly. Using the local linear regression strategy, in the neighborhood of each data point, we propose to learn a local linear predictor by minimizing both the complexity of the predictor and the upper bound of the structured prediction loss. The minimization problem is solved by sub-gradient descent algorithms. We conduct experiments over two benchmark data sets, and the results show the advantages of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge