Gaoyuan Liang
Cross-domain attribute representation based on convolutional neural network
May 17, 2018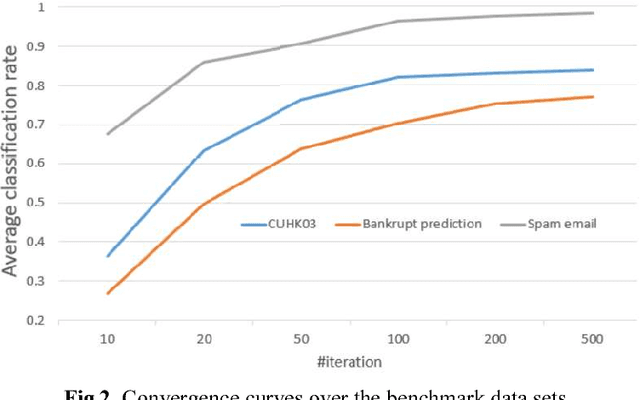
Abstract:In the problem of domain transfer learning, we learn a model for the predic-tion in a target domain from the data of both some source domains and the target domain, where the target domain is in lack of labels while the source domain has sufficient labels. Besides the instances of the data, recently the attributes of data shared across domains are also explored and proven to be very helpful to leverage the information of different domains. In this paper, we propose a novel learning framework for domain-transfer learning based on both instances and attributes. We proposed to embed the attributes of dif-ferent domains by a shared convolutional neural network (CNN), learn a domain-independent CNN model to represent the information shared by dif-ferent domains by matching across domains, and a domain-specific CNN model to represent the information of each domain. The concatenation of the three CNN model outputs is used to predict the class label. An iterative algo-rithm based on gradient descent method is developed to learn the parameters of the model. The experiments over benchmark datasets show the advantage of the proposed model.
A novel image tag completion method based on convolutional neural network
Jun 03, 2017
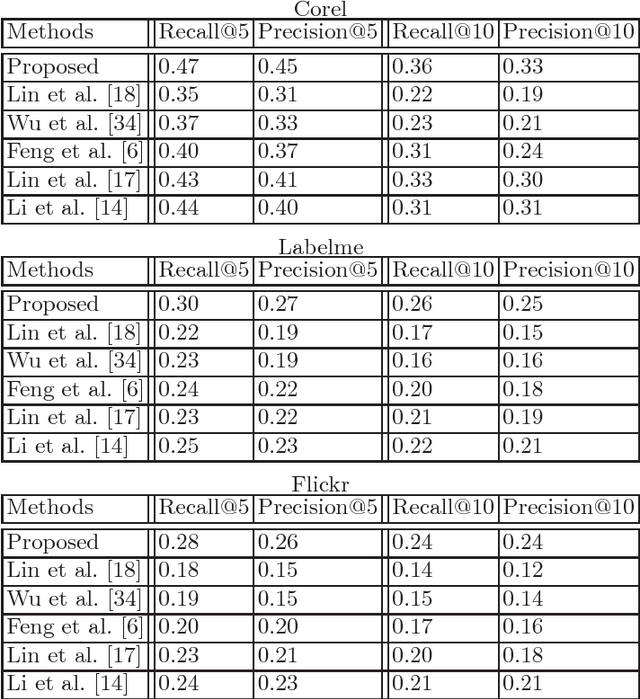

Abstract:In the problems of image retrieval and annotation, complete textual tag lists of images play critical roles. However, in real-world applications, the image tags are usually incomplete, thus it is important to learn the complete tags for images. In this paper, we study the problem of image tag complete and proposed a novel method for this problem based on a popular image representation method, convolutional neural network (CNN). The method estimates the complete tags from the convolutional filtering outputs of images based on a linear predictor. The CNN parameters, linear predictor, and the complete tags are learned jointly by our method. We build a minimization problem to encourage the consistency between the complete tags and the available incomplete tags, reduce the estimation error, and reduce the model complexity. An iterative algorithm is developed to solve the minimization problem. Experiments over benchmark image data sets show its effectiveness.
Learning convolutional neural network to maximize Pos@Top performance measure
Mar 01, 2017
Abstract:In the machine learning problems, the performance measure is used to evaluate the machine learning models. Recently, the number positive data points ranked at the top positions (Pos@Top) has been a popular performance measure in the machine learning community. In this paper, we propose to learn a convolutional neural network (CNN) model to maximize the Pos@Top performance measure. The CNN model is used to represent the multi-instance data point, and a classifier function is used to predict the label from the its CNN representation. We propose to minimize the loss function of Pos@Top over a training set to learn the filters of CNN and the classifier parameter. The classifier parameter vector is solved by the Lagrange multiplier method, and the filters are updated by the gradient descent method alternately in an iterative algorithm. Experiments over benchmark data sets show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art Pos@Top maximization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge