Rohith Agaram
GHNeRF: Learning Generalizable Human Features with Efficient Neural Radiance Fields
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have demonstrated promising results in 3D scene representations, including 3D human representations. However, these representations often lack crucial information on the underlying human pose and structure, which is crucial for AR/VR applications and games. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach, termed GHNeRF, designed to address these limitations by learning 2D/3D joint locations of human subjects with NeRF representation. GHNeRF uses a pre-trained 2D encoder streamlined to extract essential human features from 2D images, which are then incorporated into the NeRF framework in order to encode human biomechanic features. This allows our network to simultaneously learn biomechanic features, such as joint locations, along with human geometry and texture. To assess the effectiveness of our method, we conduct a comprehensive comparison with state-of-the-art human NeRF techniques and joint estimation algorithms. Our results show that GHNeRF can achieve state-of-the-art results in near real-time.
HyP-NeRF: Learning Improved NeRF Priors using a HyperNetwork
Jun 09, 2023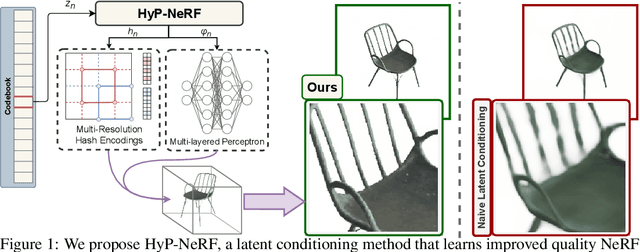
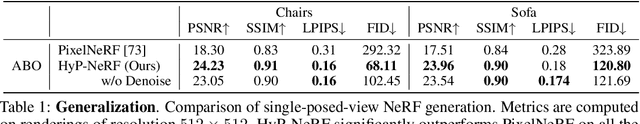
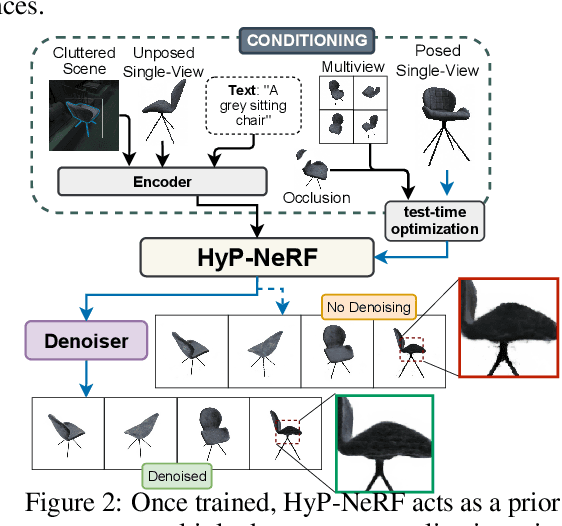
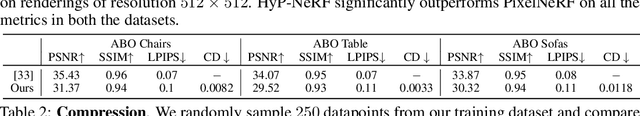
Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have become an increasingly popular representation to capture high-quality appearance and shape of scenes and objects. However, learning generalizable NeRF priors over categories of scenes or objects has been challenging due to the high dimensionality of network weight space. To address the limitations of existing work on generalization, multi-view consistency and to improve quality, we propose HyP-NeRF, a latent conditioning method for learning generalizable category-level NeRF priors using hypernetworks. Rather than using hypernetworks to estimate only the weights of a NeRF, we estimate both the weights and the multi-resolution hash encodings resulting in significant quality gains. To improve quality even further, we incorporate a denoise and finetune strategy that denoises images rendered from NeRFs estimated by the hypernetwork and finetunes it while retaining multiview consistency. These improvements enable us to use HyP-NeRF as a generalizable prior for multiple downstream tasks including NeRF reconstruction from single-view or cluttered scenes and text-to-NeRF. We provide qualitative comparisons and evaluate HyP-NeRF on three tasks: generalization, compression, and retrieval, demonstrating our state-of-the-art results.
Canonical Fields: Self-Supervised Learning of Pose-Canonicalized Neural Fields
Dec 05, 2022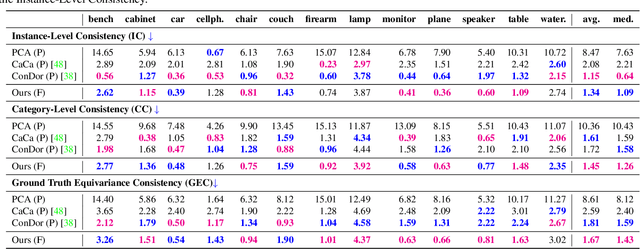
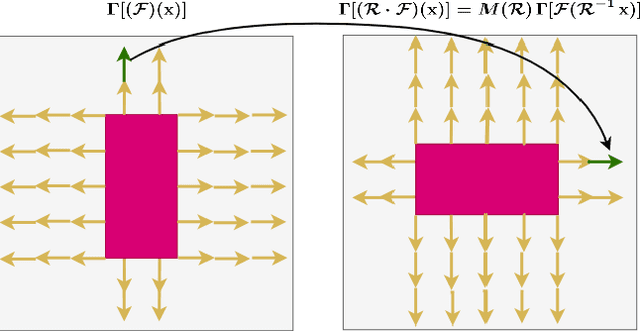
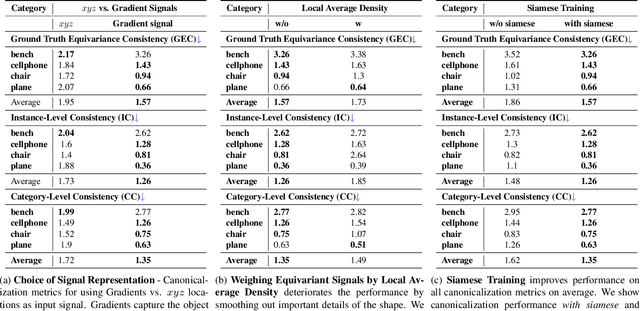
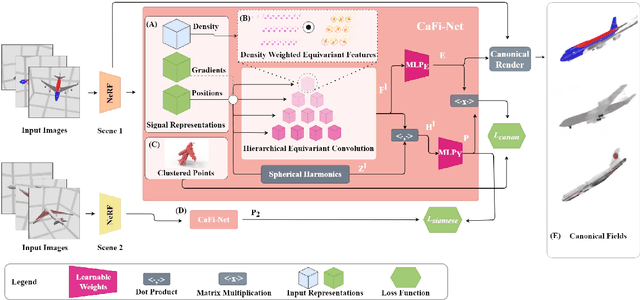
Abstract:Coordinate-based implicit neural networks, or neural fields, have emerged as useful representations of shape and appearance in 3D computer vision. Despite advances however, it remains challenging to build neural fields for categories of objects without datasets like ShapeNet that provide canonicalized object instances that are consistently aligned for their 3D position and orientation (pose). We present Canonical Field Network (CaFi-Net), a self-supervised method to canonicalize the 3D pose of instances from an object category represented as neural fields, specifically neural radiance fields (NeRFs). CaFi-Net directly learns from continuous and noisy radiance fields using a Siamese network architecture that is designed to extract equivariant field features for category-level canonicalization. During inference, our method takes pre-trained neural radiance fields of novel object instances at arbitrary 3D pose, and estimates a canonical field with consistent 3D pose across the entire category. Extensive experiments on a new dataset of 1300 NeRF models across 13 object categories show that our method matches or exceeds the performance of 3D point cloud-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge