Roberto L. Castro
Quartet: Native FP4 Training Can Be Optimal for Large Language Models
May 20, 2025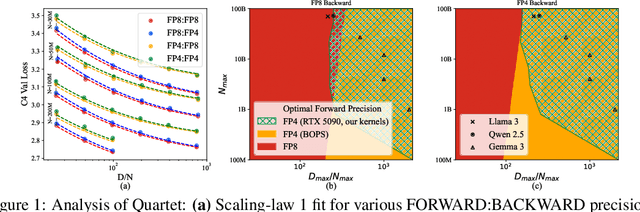
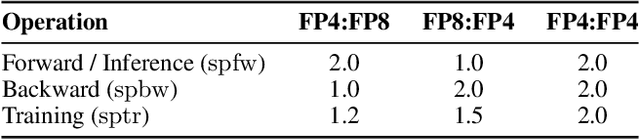
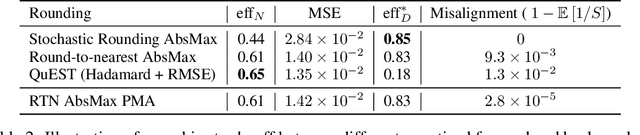
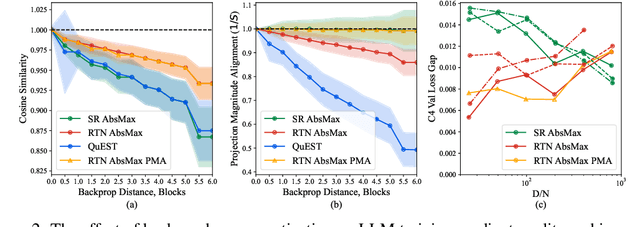
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has been paralleled by unprecedented increases in computational demands, with training costs for state-of-the-art models doubling every few months. Training models directly in low-precision arithmetic offers a solution, by improving both computational throughput and energy efficiency. Specifically, NVIDIA's recent Blackwell architecture facilitates extremely low-precision operations, specifically FP4 variants, promising substantial efficiency gains. Yet, current algorithms for training LLMs in FP4 precision face significant accuracy degradation and often rely on mixed-precision fallbacks. In this paper, we systematically investigate hardware-supported FP4 training and introduce Quartet, a new approach enabling accurate, end-to-end FP4 training with all the major computations (in e.g. linear layers) being performed in low precision. Through extensive evaluations on Llama-type models, we reveal a new low-precision scaling law that quantifies performance trade-offs across varying bit-widths and allows us to identify a "near-optimal" low-precision training technique in terms of accuracy-vs-computation, called Quartet. We implement Quartet using optimized CUDA kernels tailored for NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, and show that it can achieve state-of-the-art accuracy for FP4 precision, successfully training billion-scale models. Our method demonstrates that fully FP4-based training is a competitive alternative to standard-precision and FP8 training. Our code is available at https://github.com/IST-DASLab/Quartet.
QuEST: Stable Training of LLMs with 1-Bit Weights and Activations
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:One approach to reducing the massive costs of large language models (LLMs) is the use of quantized or sparse representations for training or deployment. While post-training compression methods are very popular, the question of obtaining even more accurate compressed models by directly training over such representations, i.e., Quantization-Aware Training (QAT), is still open: for example, a recent study (arXiv:2411.04330v2) put the "optimal" bit-width at which models can be trained using QAT, while staying accuracy-competitive with standard FP16/BF16 precision, at 8-bits weights and activations. We advance this state-of-the-art via a new method called QuEST, which is Pareto-competitive with FP16, i.e., it provides better accuracy at lower model size, while training models with weights and activations in 4-bits or less. Moreover, QuEST allows stable training with 1-bit weights and activations. QuEST achieves this by improving two key aspects of QAT methods: (1) accurate and fast quantization of the (continuous) distributions of weights and activations via Hadamard normalization and MSE-optimal fitting; (2) a new trust gradient estimator based on the idea of explicitly minimizing the error between the noisy gradient computed over quantized states and the "true" (but unknown) full-precision gradient. Experiments on Llama-type architectures show that QuEST induces stable scaling laws across the entire range of hardware-supported precisions, and can be extended to sparse representations. We provide GPU kernel support showing that models produced by QuEST can be executed efficiently. Our code is available at https://github.com/IST-DASLab/QuEST.
HALO: Hadamard-Assisted Lossless Optimization for Efficient Low-Precision LLM Training and Fine-Tuning
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Quantized training of Large Language Models (LLMs) remains an open challenge, as maintaining accuracy while performing all matrix multiplications in low precision has proven difficult. This is particularly the case when fine-tuning pre-trained models, which often already have large weight and activation outlier values that render quantized optimization difficult. We present HALO, a novel quantization-aware training approach for Transformers that enables accurate and efficient low-precision training by combining 1) strategic placement of Hadamard rotations in both forward and backward passes, to mitigate outliers during the low-precision computation, 2) FSDP integration for low-precision communication, and 3) high-performance kernel support. Our approach ensures that all large matrix multiplications during the forward and backward passes are executed in lower precision. Applied to LLAMA-family models, HALO achieves near-full-precision-equivalent results during fine-tuning on various tasks, while delivering up to 1.31x end-to-end speedup for full fine-tuning on RTX 4090 GPUs. Our method supports both standard and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, both backed by efficient kernel implementations. Our results demonstrate the first practical approach to fully quantized LLM fine-tuning that maintains accuracy in FP8 precision, while delivering performance benefits.
MARLIN: Mixed-Precision Auto-Regressive Parallel Inference on Large Language Models
Aug 21, 2024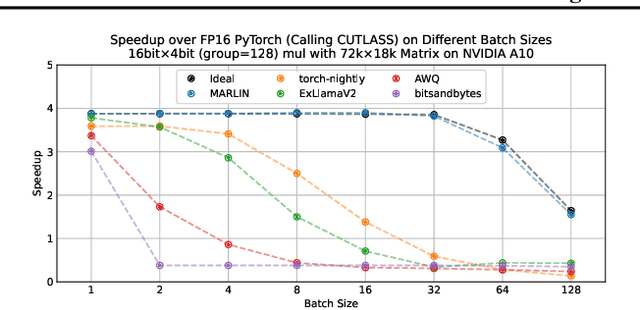
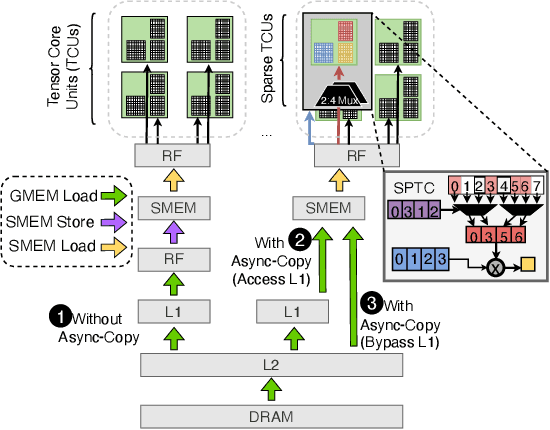
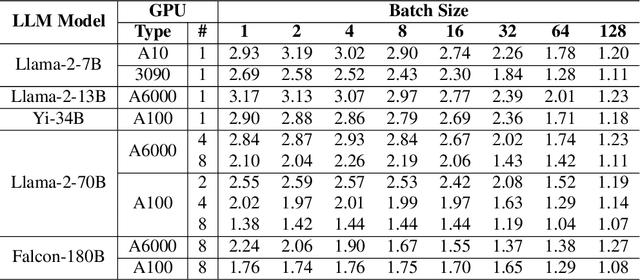
Abstract:As inference on Large Language Models (LLMs) emerges as an important workload in machine learning applications, weight quantization has become a standard technique for efficient GPU deployment. Quantization not only reduces model size, but has also been shown to yield substantial speedups for single-user inference, due to reduced memory movement, with low accuracy impact. Yet, it remains open whether speedups are achievable also in \emph{batched} settings with multiple parallel clients, which are highly relevant for practical serving. It is unclear whether GPU kernels can be designed to remain practically memory-bound, while supporting the substantially increased compute requirements of batched workloads. This paper resolves this question positively by describing the design of Mixed-precision Auto-Regressive LINear kernels, called MARLIN. Concretely, given a model whose weights are compressed via quantization to, e.g., 4 bits per element, MARLIN shows that batchsizes up to 16-32 can be supported with close to maximum ($4\times$) quantization speedup, and larger batchsizes up to 64-128 with gradually decreasing, but still significant, acceleration. MARLIN accomplishes this via a combination of techniques, such as asynchronous memory access, complex task scheduling and pipelining, and bespoke quantization support. Our experiments show that MARLIN's near-optimal performance on individual LLM layers across different scenarios can also lead to end-to-end LLM inference speedups (of up to $2.8\times$) when integrated with the popular vLLM serving engine. Finally, MARLIN is extensible to further compression techniques, like NVIDIA 2:4 sparsity, leading to additional speedups.
VENOM: A Vectorized N:M Format for Unleashing the Power of Sparse Tensor Cores
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:The increasing success and scaling of Deep Learning models demands higher computational efficiency and power. Sparsification can lead to both smaller models as well as higher compute efficiency, and accelerated hardware is becoming available. However, exploiting it efficiently requires kernel implementations, pruning algorithms, and storage formats, to utilize hardware support of specialized sparse vector units. An example of those are the NVIDIA's Sparse Tensor Cores (SPTCs), which promise a 2x speedup. However, SPTCs only support the 2:4 format, limiting achievable sparsity ratios to 50%. We present the V:N:M format, which enables the execution of arbitrary N:M ratios on SPTCs. To efficiently exploit the resulting format, we propose Spatha, a high-performance sparse-library for DL routines. We show that Spatha achieves up to 37x speedup over cuBLAS. We also demonstrate a second-order pruning technique that enables sparsification to high sparsity ratios with V:N:M and little to no loss in accuracy in modern transformers.
Reusing Trained Layers of Convolutional Neural Networks to Shorten Hyperparameters Tuning Time
Jun 16, 2020



Abstract:Hyperparameters tuning is a time-consuming approach, particularly when the architecture of the neural network is decided as part of this process. For instance, in convolutional neural networks (CNNs), the selection of the number and the characteristics of the hidden (convolutional) layers may be decided. This implies that the search process involves the training of all these candidate network architectures. This paper describes a proposal to reuse the weights of hidden (convolutional) layers among different trainings to shorten this process. The rationale is that if a set of convolutional layers have been trained to solve a given problem, the weights calculated in this training may be useful when a new convolutional layer is added to the network architecture. This idea has been tested using the CIFAR-10 dataset, testing different CNNs architectures with up to 3 convolutional layers and up to 3 fully connected layers. The experiments compare the training time and the validation loss when reusing and not reusing convolutional layers. They confirm that this strategy reduces the training time while it even increases the accuracy of the resulting neural network. This finding opens up the future possibility of integrating this strategy in existing AutoML methods with the purpose of reducing the total search time.
A Hybrid Approach for Tracking Individual Players in Broadcast Match Videos
Mar 10, 2020



Abstract:Tracking people in a video sequence is a challenging task that has been approached from many perspectives. This task becomes even more complicated when the person to track is a player in a broadcasted sport event, the reasons being the existence of difficulties such as frequent camera movements or switches, total and partial occlusions between players, and blurry frames due to the codification algorithm of the video. This paper introduces a player tracking solution which is both fast and accurate. This allows to track a player precisely in real-time. The approach combines several models that are executed concurrently in a relatively modest hardware, and whose accuracy has been validated against hand-labeled broadcast video sequences. Regarding the accuracy, the tests show that the area under curve (AUC) of our approach is around 0.6, which is similar to generic state of the art solutions. As for performance, our proposal can process high definition videos (1920x1080 px) at 80 fps.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge