Robert Qiu
Redefinition of Digital Twin and its Situation Awareness Framework Designing Towards Fourth Paradigm for Energy Internet of Things
Jul 12, 2024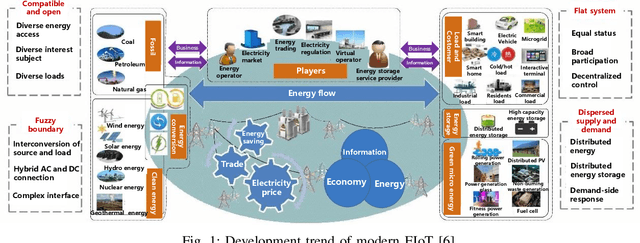

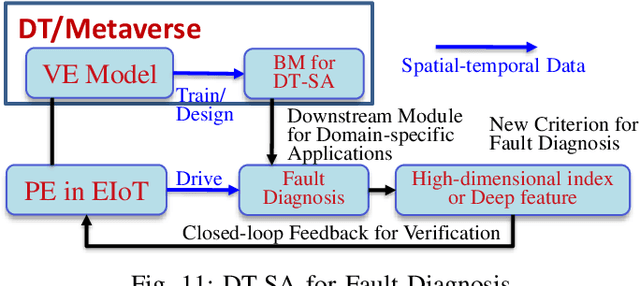
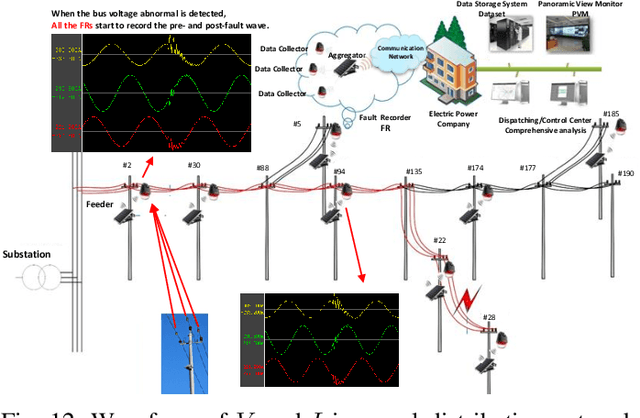
Abstract:Traditional knowledge-based situation awareness (SA) modes struggle to adapt to the escalating complexity of today's Energy Internet of Things (EIoT), necessitating a pivotal paradigm shift. In response, this work introduces a pioneering data-driven SA framework, termed digital twin-based situation awareness (DT-SA), aiming to bridge existing gaps between data and demands, and further to enhance SA capabilities within the complex EIoT landscape. First, we redefine the concept of digital twin (DT) within the EIoT context, aligning it with data-intensive scientific discovery paradigm (the Fourth Paradigm) so as to waken EIoT's sleeping data; this contextual redefinition lays the cornerstone of our DT-SA framework for EIoT. Then, the framework is comprehensively explored through its four fundamental steps: digitalization, simulation, informatization, and intellectualization. These steps initiate a virtual ecosystem conducive to a continuously self-adaptive, self-learning, and self-evolving big model (BM), further contributing to the evolution and effectiveness of DT-SA in engineering. Our framework is characterized by the incorporation of system theory and Fourth Paradigm as guiding ideologies, DT as data engine, and BM as intelligence engine. This unique combination forms the backbone of our approach. This work extends beyond engineering, stepping into the domain of data science -- DT-SA not only enhances management practices for EIoT users/operators, but also propels advancements in pattern analysis and machine intelligence (PAMI) within the intricate fabric of a complex system. Numerous real-world cases validate our DT-SA framework.
Self-supervised Point Cloud Registration with Deep Versatile Descriptors
Jan 25, 2022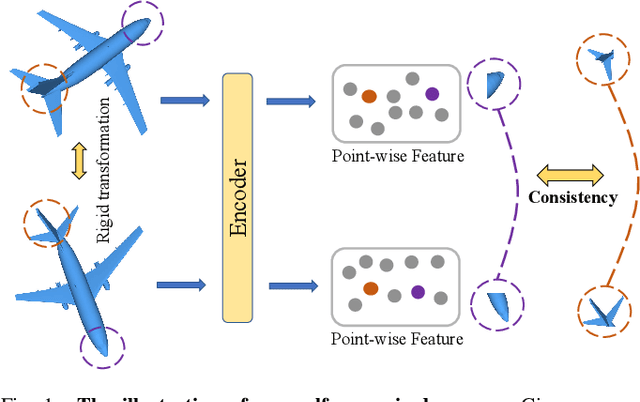
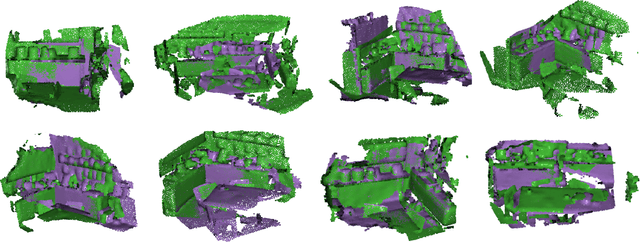
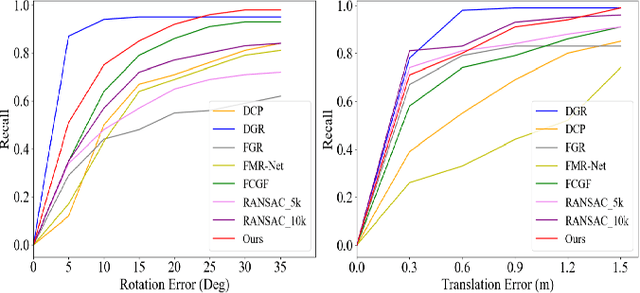
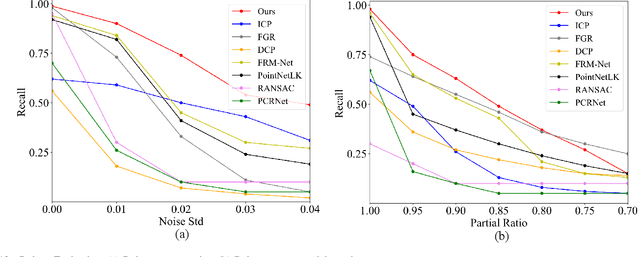
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed an increasing trend toward solving point cloud registration problems with various deep learning-based algorithms. Compared to supervised/semi-supervised registration methods, unsupervised methods require no human annotations. However, unsupervised methods mainly depend on the global descriptors, which ignore the high-level representations of local geometries. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised registration scheme with a novel Deep Versatile Descriptors (DVD), jointly considering global representations and local representations. The DVD is motivated by a key observation that the local distinctive geometric structures of the point cloud by two subset points can be employed to enhance the representation ability of the feature extraction module. Furthermore, we utilize two additional tasks (reconstruction and normal estimation) to enhance the transformation awareness of the proposed DVDs. Lastly, we conduct extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets, demonstrating that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance against competing methods over a wide range of experimental settings.
MARS: Mixed Virtual and Real Wearable Sensors for Human Activity Recognition with Multi-Domain Deep Learning Model
Oct 09, 2020



Abstract:Together with the rapid development of the Internet of Things (IoT), human activity recognition (HAR) using wearable Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) becomes a promising technology for many research areas. Recently, deep learning-based methods pave a new way of understanding and performing analysis of the complex data in the HAR system. However, the performance of these methods is mostly based on the quality and quantity of the collected data. In this paper, we innovatively propose to build a large database based on virtual IMUs and then address technical issues by introducing a multiple-domain deep learning framework consisting of three technical parts. In the first part, we propose to learn the single-frame human activity from the noisy IMU data with hybrid convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in the semi-supervised form. For the second part, the extracted data features are fused according to the principle of uncertainty-aware consistency, which reduces the uncertainty by weighting the importance of the features. The transfer learning is performed in the last part based on the newly released Archive of Motion Capture as Surface Shapes (AMASS) dataset, containing abundant synthetic human poses, which enhances the variety and diversity of the training dataset and is beneficial for the process of training and feature transfer in the proposed method. The efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed method have been demonstrated in the real deep inertial poser (DIP) dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed methods can surprisingly converge within a few iterations and outperform all competing methods.
Adversarial Feature Learning of Online Monitoring Data for Operation Reliability Assessment in Distribution Network
Aug 27, 2018



Abstract:With deployments of online monitoring systems in distribution networks, massive amounts of data collected through them contain rich information on the operating status of distribution networks. By leveraging the data, based on bidirectional generative adversarial networks (BiGANs), we propose an unsupervised approach for online distribution reliability assessment. It is capable of discovering the latent structure and automatically learning the most representative features of the spatio-temporal data in distribution networks in an adversarial way and it does not rely on any assumptions of the input data. Based on the extracted features, a statistical magnitude for them is calculated to indicate the data behavior. Furthermore, distribution reliability states are divided into different levels and we combine them with the calculated confidence level $1-\alpha$, during which clear criteria is defined empirically. Case studies on both synthetic data and real-world online monitoring data show that our proposed approach is feasible for the assessment of distribution operation reliability and outperforms other existed techniques.
Individual Recognition in Schizophrenia using Deep Learning Methods with Random Forest and Voting Classifiers: Insights from Resting State EEG Streams
Jan 17, 2018
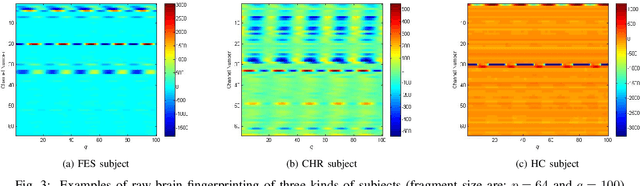
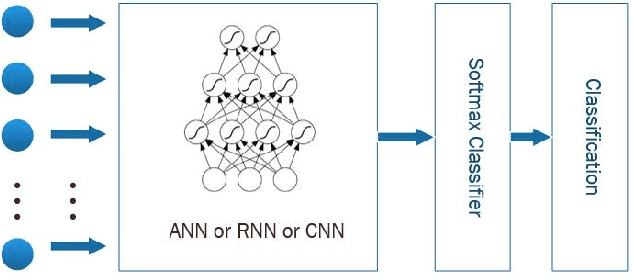
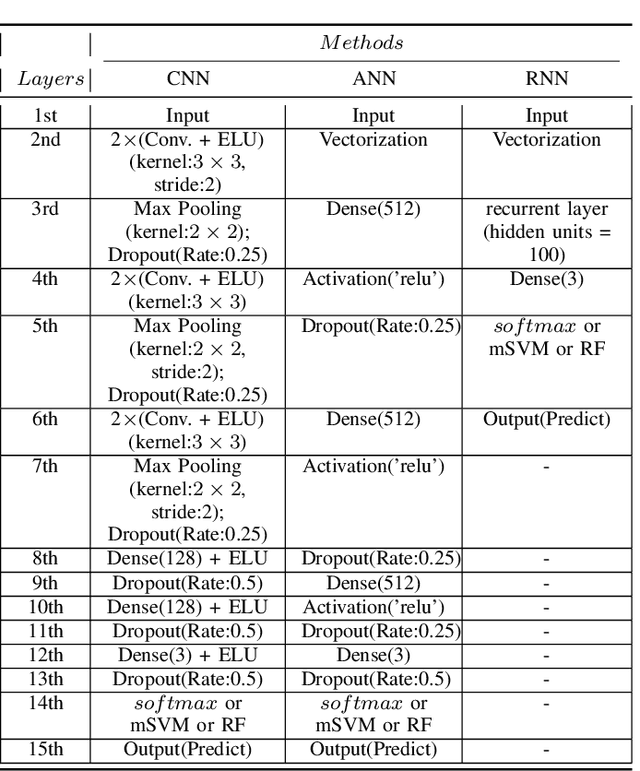
Abstract:Recently, there has been a growing interest in monitoring brain activity for individual recognition system. So far these works are mainly focussing on single channel data or fragment data collected by some advanced brain monitoring modalities. In this study we propose new individual recognition schemes based on spatio-temporal resting state Electroencephalography (EEG) data. Besides, instead of using features derived from artificially-designed procedures, modified deep learning architectures which aim to automatically extract an individual's unique features are developed to conduct classification. Our designed deep learning frameworks are proved of a small but consistent advantage of replacing the $softmax$ layer with Random Forest. Additionally, a voting layer is added at the top of designed neural networks in order to tackle the classification problem arisen from EEG streams. Lastly, various experiments are implemented to evaluate the performance of the designed deep learning architectures; Results indicate that the proposed EEG-based individual recognition scheme yields a high degree of classification accuracy: $81.6\%$ for characteristics in high risk (CHR) individuals, $96.7\%$ for clinically stable first episode patients with schizophrenia (FES) and $99.2\%$ for healthy controls (HC).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge