Prasanta Bhattacharya
Investigating the effectiveness of multimodal data in forecasting SARS-COV-2 case surges
May 28, 2025Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic response relied heavily on statistical and machine learning models to predict key outcomes such as case prevalence and fatality rates. These predictions were instrumental in enabling timely public health interventions that helped break transmission cycles. While most existing models are grounded in traditional epidemiological data, the potential of alternative datasets, such as those derived from genomic information and human behavior, remains underexplored. In the current study, we investigated the usefulness of diverse modalities of feature sets in predicting case surges. Our results highlight the relative effectiveness of biological (e.g., mutations), public health (e.g., case counts, policy interventions) and human behavioral features (e.g., mobility and social media conversations) in predicting country-level case surges. Importantly, we uncover considerable heterogeneity in predictive performance across countries and feature modalities, suggesting that surge prediction models may need to be tailored to specific national contexts and pandemic phases. Overall, our work highlights the value of integrating alternative data sources into existing disease surveillance frameworks to enhance the prediction of pandemic dynamics.
Economics of Sourcing Human Data
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Progress in AI has relied on human-generated data, from annotator marketplaces to the wider Internet. However, the widespread use of large language models now threatens the quality and integrity of human-generated data on these very platforms. We argue that this issue goes beyond the immediate challenge of filtering AI-generated content--it reveals deeper flaws in how data collection systems are designed. Existing systems often prioritize speed, scale, and efficiency at the cost of intrinsic human motivation, leading to declining engagement and data quality. We propose that rethinking data collection systems to align with contributors' intrinsic motivations--rather than relying solely on external incentives--can help sustain high-quality data sourcing at scale while maintaining contributor trust and long-term participation.
Rethinking stance detection: A theoretically-informed research agenda for user-level inference using language models
Feb 04, 2025
Abstract:Stance detection has emerged as a popular task in natural language processing research, enabled largely by the abundance of target-specific social media data. While there has been considerable research on the development of stance detection models, datasets, and application, we highlight important gaps pertaining to (i) a lack of theoretical conceptualization of stance, and (ii) the treatment of stance at an individual- or user-level, as opposed to message-level. In this paper, we first review the interdisciplinary origins of stance as an individual-level construct to highlight relevant attributes (e.g., psychological features) that might be useful to incorporate in stance detection models. Further, we argue that recent pre-trained and large language models (LLMs) might offer a way to flexibly infer such user-level attributes and/or incorporate them in modelling stance. To better illustrate this, we briefly review and synthesize the emerging corpus of studies on using LLMs for inferring stance, and specifically on incorporating user attributes in such tasks. We conclude by proposing a four-point agenda for pursuing stance detection research that is theoretically informed, inclusive, and practically impactful.
Predicting User Stances from Target-Agnostic Information using Large Language Models
Sep 22, 2024
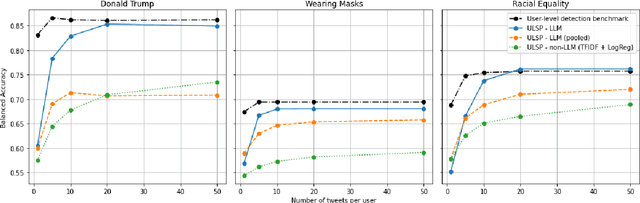
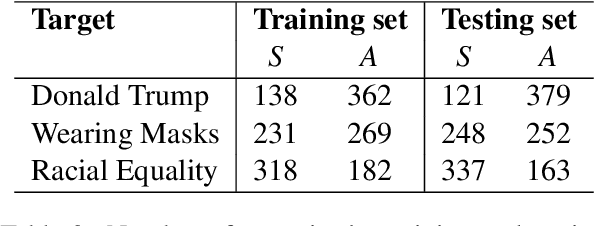
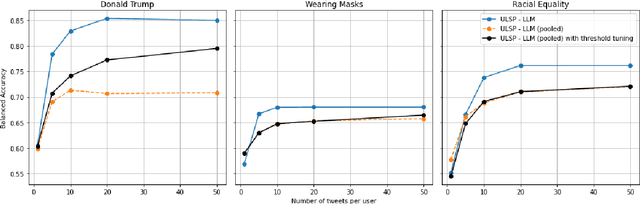
Abstract:We investigate Large Language Models' (LLMs) ability to predict a user's stance on a target given a collection of his/her target-agnostic social media posts (i.e., user-level stance prediction). While we show early evidence that LLMs are capable of this task, we highlight considerable variability in the performance of the model across (i) the type of stance target, (ii) the prediction strategy and (iii) the number of target-agnostic posts supplied. Post-hoc analyses further hint at the usefulness of target-agnostic posts in providing relevant information to LLMs through the presence of both surface-level (e.g., target-relevant keywords) and user-level features (e.g., encoding users' moral values). Overall, our findings suggest that LLMs might offer a viable method for determining public stances towards new topics based on historical and target-agnostic data. At the same time, we also call for further research to better understand LLMs' strong performance on the stance prediction task and how their effectiveness varies across task contexts.
Enhancing Stance Classification with Quantified Moral Foundations
Oct 15, 2023



Abstract:This study enhances stance detection on social media by incorporating deeper psychological attributes, specifically individuals' moral foundations. These theoretically-derived dimensions aim to provide a comprehensive profile of an individual's moral concerns which, in recent work, has been linked to behaviour in a range of domains, including society, politics, health, and the environment. In this paper, we investigate how moral foundation dimensions can contribute to predicting an individual's stance on a given target. Specifically we incorporate moral foundation features extracted from text, along with message semantic features, to classify stances at both message- and user-levels across a range of targets and models. Our preliminary results suggest that encoding moral foundations can enhance the performance of stance detection tasks and help illuminate the associations between specific moral foundations and online stances on target topics. The results highlight the importance of considering deeper psychological attributes in stance analysis and underscores the role of moral foundations in guiding online social behavior.
Task Preferences across Languages on Community Question Answering Platforms
Dec 18, 2022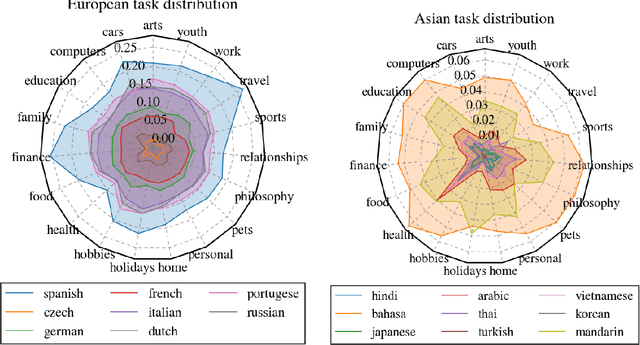
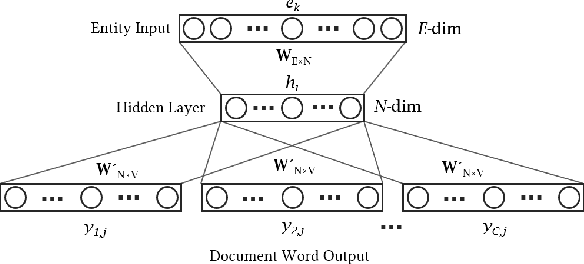
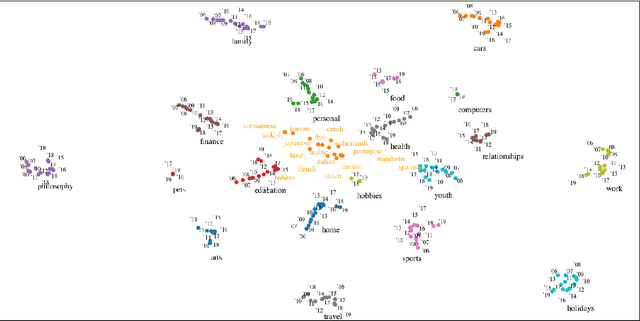
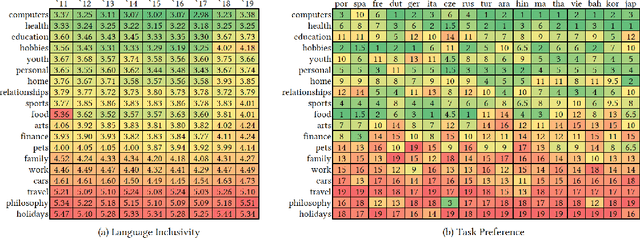
Abstract:With the steady emergence of community question answering (CQA) platforms like Quora, StackExchange, and WikiHow, users now have an unprecedented access to information on various kind of queries and tasks. Moreover, the rapid proliferation and localization of these platforms spanning geographic and linguistic boundaries offer a unique opportunity to study the task requirements and preferences of users in different socio-linguistic groups. In this study, we implement an entity-embedding model trained on a large longitudinal dataset of multi-lingual and task-oriented question-answer pairs to uncover and quantify the (i) prevalence and distribution of various online tasks across linguistic communities, and (ii) emerging and receding trends in task popularity over time in these communities. Our results show that there exists substantial variance in task preference as well as popularity trends across linguistic communities on the platform. Findings from this study will help Q&A platforms better curate and personalize content for non-English users, while also offering valuable insights to businesses looking to target non-English speaking communities online.
A Discussion on Building Practical NLP Leaderboards: The Case of Machine Translation
Jun 11, 2021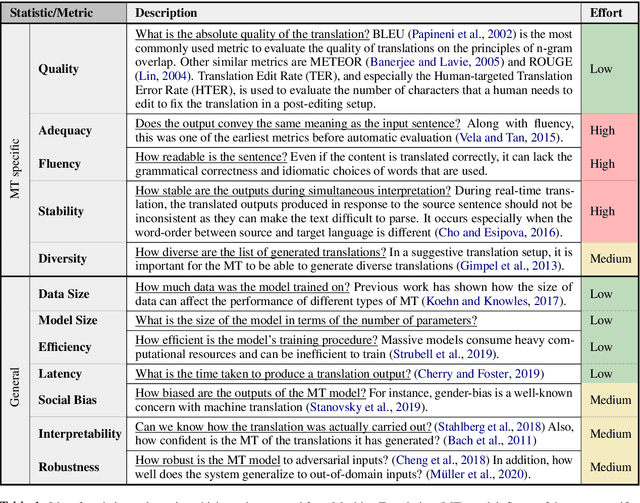
Abstract:Recent advances in AI and ML applications have benefited from rapid progress in NLP research. Leaderboards have emerged as a popular mechanism to track and accelerate progress in NLP through competitive model development. While this has increased interest and participation, the over-reliance on single, and accuracy-based metrics have shifted focus from other important metrics that might be equally pertinent to consider in real-world contexts. In this paper, we offer a preliminary discussion of the risks associated with focusing exclusively on accuracy metrics and draw on recent discussions to highlight prescriptive suggestions on how to develop more practical and effective leaderboards that can better reflect the real-world utility of models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge