Predicting User Stances from Target-Agnostic Information using Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Sep 22, 2024
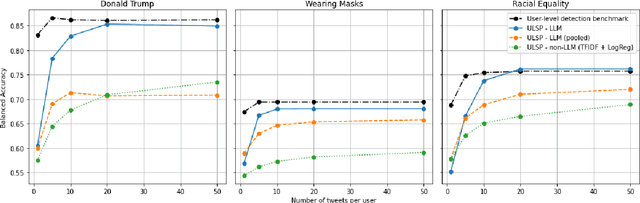
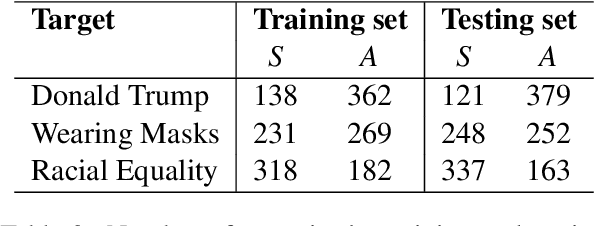
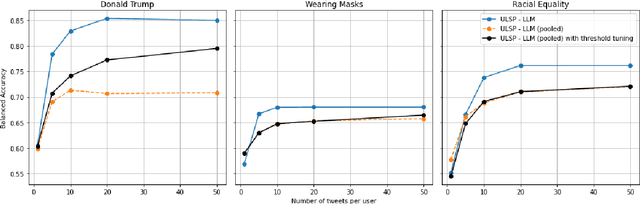
We investigate Large Language Models' (LLMs) ability to predict a user's stance on a target given a collection of his/her target-agnostic social media posts (i.e., user-level stance prediction). While we show early evidence that LLMs are capable of this task, we highlight considerable variability in the performance of the model across (i) the type of stance target, (ii) the prediction strategy and (iii) the number of target-agnostic posts supplied. Post-hoc analyses further hint at the usefulness of target-agnostic posts in providing relevant information to LLMs through the presence of both surface-level (e.g., target-relevant keywords) and user-level features (e.g., encoding users' moral values). Overall, our findings suggest that LLMs might offer a viable method for determining public stances towards new topics based on historical and target-agnostic data. At the same time, we also call for further research to better understand LLMs' strong performance on the stance prediction task and how their effectiveness varies across task contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge